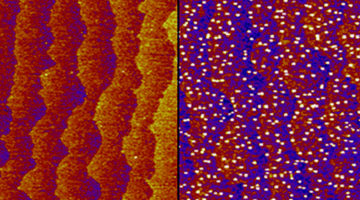
Using a multimodal approach, researchers learned how chemical properties correlate with structural changes during nanoparticle growth. The work will enable a greater understanding of the mechanisms affecting the durability of nanoparticles used to catalyze a broad range of chemical reactions, including clean-energy reactions. Read more »![]()
![]()
ALS Work Using Spectroscopy
These techniques are used to study the energies of particles that are emitted or absorbed by samples that are exposed to the light-source beam and are commonly used to determine the characteristics of chemical bonding and electron motion.
Liquid Heterostructures: Generation of Liquid–Liquid Interfaces in Free-Flowing Liquid Sheets
Microscope image of a microfluidic nozzle producing a liquid heterostructure: a layered flat liquid sheet with outer toluene layers and an inner water layer. The colored bands arise from thin film interference, indicating the presence of buried liquid‒liquid interfaces and submicron layer thicknesses. Read more »
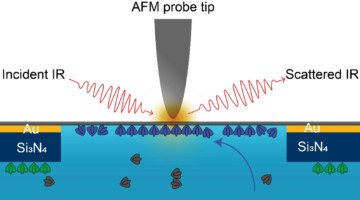
A Nano-IR Probe for Proteins in Liquid Environments
A new technique using infrared (IR) light revealed how the self-assembly of proteins is affected by environmental conditions in a surrounding liquid. This nanoscale probe of soft matter in a liquid matrix will facilitate advances in biology, plastics processing, and energy-relevant applications such as electrocatalysts and batteries. Read more »![]()
![]()
Highly Selective Methane to Methanol Conversion on Inverse SnO2/Cu2O/Cu(111) Catalysts: Unique Properties of SnO2 Nanostructures and the Inhibition of the Direct Oxidative Combustion of Methane
Inverse catalysts generally consist of oxide nanoparticles supported on metal substrates, which can exhibit exceptional catalytic properties. The small SnO2 nanoparticles uniformly dispersed on a Cu2O/Cu(111) substrate enabled a unique SnO2–Cu2O interface that can completely convert methane to methanol directly under the environments of oxygen and water. Read more »
Multilayer Stack Opens Door to Low-Power Electronics
Researchers found that a multilayer stack of ultrathin materials exhibits a phenomenon called negative capacitance, which reduces the voltage required for transistor operation. The material is fully compatible with today’s silicon-based technology and is capable of reducing power consumption without sacrificing transistor size or performance. Read more »![]()
![]()
Jinghua Guo to Receive the 2022 Shirley Award
ALS senior scientist Jinghua Guo is the recipient of this year’s Shirley Award for Outstanding Scientific Achievement at the ALS. Guo is being recognized for pioneering the development of operando soft x-ray spectroscopy, work that’s enabled studies under realistic conditions, which is of great importance in environmental and energy research. Read more »
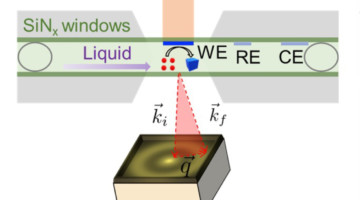
Operando Study of CO2 Reduction by Copper Nanoparticles
Since copper is necessary to catalyze the reduction of CO2, a greenhouse gas, to valuable products, scientists are working hard to improve its selectivity and activity. Now, researchers have developed an operando capability that can help in this effort by simultaneously probing chemical valence and interparticle dynamics. Read more »
Visualizing the Nanoscale Oxygen and Cation Transport Mechanisms during the Early Stages of Oxidation of Fe–Cr–Ni Alloy Using In Situ Atom Probe Tomography
Understanding the early stages of interactions between oxygen and material surfaces is beneficial for fields ranging from materials degradation to forensics and catalysis. In situ atom probe tomography (APT) is demonstrated to track the diffusion of oxygen and metal ions at nanoscale spatial resolution during the early stages of oxidation of a model Fe–Cr–Ni alloy. Read more »
New Insight into Titan’s Hazy Atmospheric Chemistry
Researchers simulated the complex chemistry that may be occurring in the hazy atmosphere of Saturn’s largest moon, Titan, and analyzed the reaction products at the ALS. The work provided new insights into what future Titan probes may encounter upon arrival and what the atmosphere of Earth may have been like eons ago. Read more »
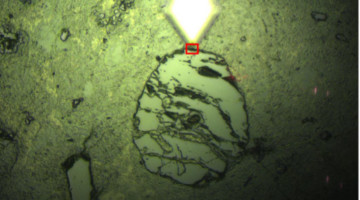
Nanoscale Infrared Study of Meteorite Mineralogy
Using a nanoscale infrared probe, researchers found that the minerals in a meteorite—an artifact representing the solar system’s past—were altered by water on very fine spatial scales. The work sheds light on conditions in the early solar system and lays groundwork for analyzing asteroid samples to be returned to Earth by NASA in 2023. Read more »![]()
![]()
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- …
- 31
- Next Page »