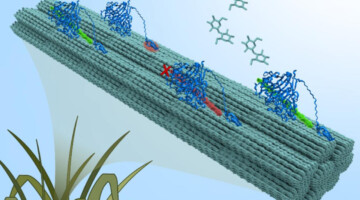
A time-resolved study using infrared spectromicroscopy in a carefully controlled environment revealed why enzymes get bogged down when trying to break up cellulose from plants. The work sheds new light on the challenge of extracting the sugars locked up in plants for use in making petroleum-free fuels, chemicals, and medicines. Read more »![]()
![]()
ALS in the News (February 2024)
-
-
-
-
- Researchers leverage SAXS to understand aspect of microbial metabolism
- Type 2 diabetes alters the behavior of discs in the vertebral column
- Watching the enzymes that convert plant fiber into simple sugars
- Some of the brightest x-rays on Earth are made just above the UC Berkeley campus (video)
- ‘Flawed’ material resolves superconductor conundrum
-
-
-
Watching the Enzymes that Convert Plant Fiber into Simple Sugars
Research from Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, and UC Davis sheds new light on how to access the sugars locked up in plants to produce petroleum-free fuels, chemicals, and medicines. The technique used combines a novel microfluidic device and infrared spectroscopy to study how a cellulose-degrading enzyme works in real time. Read more »
Magnetically Selective Versatile Transport of Microrobotic Carriers
Field-driven transport systems offer the possibility of biofunctionalized carriers for microrobotics, biomedicine, and cell delivery. Here, researchers show how magnetic fields may selectively manipulate and drive microrobotics along a patterned micromagnet. Different-sized magnetic carriers move in multiple directions, including selective rotation and bidirectional movement. Such steering systems can direct the delivery of drugs or cells into artificial microvascular channels. Read more »
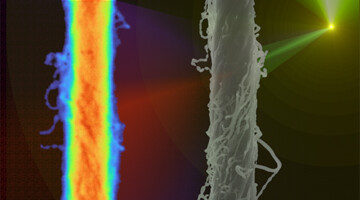
How Processing Affects Structure in Composite Nanotube Yarns
Using the ALS, researchers found quantitative correlations between processing parameters and the structure of ultrafine, polymer-reinforced carbon-nanotube fibers. The work will facilitate the production of high-strength materials, including those needed for positioning target capsules for fusion research at the National Ignition Facility. Read more »![]()
![]()
ALS in the News (January 2024)
-
-
-
-
- Mike Witherell: Seeking big impact from big science
- New tomographic reconstruction algorithm developed at Berkeley Lab sets world record
- Pacific kelp forests are far older than we thought
- Berkeley Lab researchers publish pioneering book on autonomous experimentation
- A new era is emerging at scientific user facilities
- Berkeley Lab’s big science stories of 2023
- Hura, Tsutakawa named Science Deputy, Structural Biology Department Head
- Revolutionizing how we do science: The superfacility story
- Q&A with Adam Weber about clean energy future: Hydrogen research at the Lab
-
-
-
Cobalt or Nickel: Which is Better for High-Energy Battery Cathodes?
High-energy Li-ion batteries can provide both high capacity and high voltage, both of which are important in electric vehicles for greater range and faster acceleration. Here, researchers untangled the contributions of nickel and cobalt in high-energy Li-rich battery cathodes, pointing the way to optimizing them via a compositional approach. Read more »
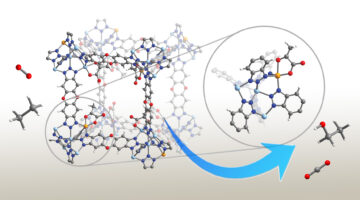
A Bio-Inspired Metal-Organic Framework for Capturing Wellhead Gases
Burning of natural gas at oil and gas wells, called flaring, is a major waste of fossil fuels and a contributor to climate change. In this work, researchers synthesized and characterized a metal-organic framework that uses biomimetic chemistry to convert wellhead gases into economically valuable feedstocks for petrochemical products. Read more »
Flat Bands Signal Electrons Trapped in 3D
Researchers found flat electronic band structures—known hallmarks of electrons trapped in two dimensions—but in a material that extends this phenomenon to three dimensions. The work opens up a material framework for exploring superconductivity and other exotic states in three dimensions for advanced electronic applications. Read more »![]()
![]()
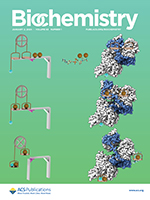
Correlating Conformational Equilibria with Catalysis in the Electron Bifurcating EtfABCX of Thermotoga maritima
Anaerobic SEC-MALS-SAXS at the SIBYLS beamline probes the conformational states behind electron bifurcation in the Thermotoga maritima EtfABCX, revealing insights on mechanisms at the thermodynamic limits of life. Shown are the bifurcation- and electron-conducting-like states experimentally observed for the first time in solution. Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- …
- 83
- Next Page »