The performance and stability of metal halide perovskite solar cells strongly depend on precursor materials and deposition methods adopted during the perovskite layer preparation. This review presents an update of studies conducted in situ using a wide range of structural, imaging, and spectroscopic techniques, involving the formation/degradation of halide perovskites. Read more »
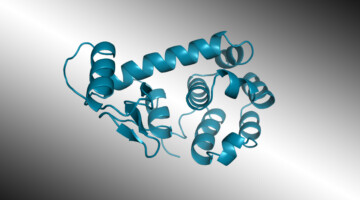
Chatbot-Style AI Designs Novel Functional Protein
Researchers used an artificial intelligence (AI) algorithm, similar to those used in natural-language (“chatbot”) models, to design a functional protein that was then structurally validated at the ALS. The work could speed the development of novel proteins for almost anything from therapeutics to degrading plastic. Read more »![]()
![]()
Intrinsically Chiral Twist-Bend Nematogens: Interplay of Molecular and Structural Chirality in the NTB Phase
Cartoon depiction of the formation of the heliconical chiral twist-bend nematic phase (N*TB) from its constituent bent molecules. The presence of a single enantiomer of the chiral, lactate-based liquid crystal dimers biases the formation of helices with only one handedness, unlike in the conventional NTB phase, observed for achiral molecules, for which the left- and right-handed helices are doubly degenerate. Read more »
Electric Vehicle Batteries Could Get Big Boost With New Polymer Coating
Scientists have developed a conductive polymer coating—called HOS-PFM—that conducts both electrons and ions at the same time. This ensures battery stability and high charge/discharge rates while enhancing battery life. The coating also shows promise as a battery adhesive that could extend the lifetime of a lithium-ion battery from an average of 10 years to about 15 years. Read more »
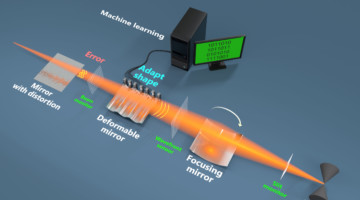
Shaping X-Ray Mirrors Using Machine Learning
Researchers used machine learning to predict and control the shape of an x-ray mirror’s surface with exquisite accuracy and precision. The work represents a key step toward mirrors that can fully exploit the x-rays from upgraded, state-of-the-art light sources and could also enable the engineering of x-ray beams with novel characteristics. Read more »![]()
![]()
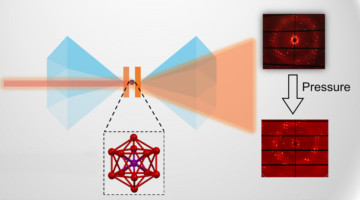
Under Pressure, Gold Nanoclusters Reveal Structure-Property Relationship
Metal nanoclusters have unusual optical properties that are of interest for fundamental reasons as well as for applications like diagnostic imaging and 3D printing. To better understand how nanocluster structure relates to optical properties, researchers performed high-pressure diffraction studies on single crystals of gold nanoclusters. Read more »
ALS in the News (February 2023)
-
-
-
- Berkeley Lab researchers shine a light on vaping chemistry
- How a record-breaking copper catalyst converts CO2 into liquid fuels
- AI technology designs novel functional enzyme
- DOE’s Office of Science is now accepting applications for the Office of Science Graduate Student Research Awards 2023
- USM graduate student earns Berkeley Lab doctoral fellowship
- Paul Adams named Berkeley Lab’s Associate Director for Biosciences
- Building particle accelerators takes more than a village
- Whip it: Novel liquid jet makes droplets march to the beat
-
-
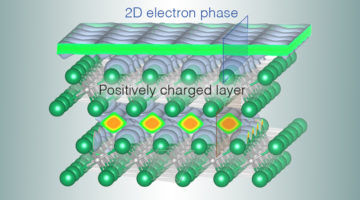
A 2D Electron Liquid Floats on a Crystal Surface
Researchers discovered a liquid-like layer of electrons that floats on the surface of an unusual crystal and appears to undergo a phase transition upon doping. The system is an ideal platform for studying exotic phenomena involving electrons (e.g. superconductivity) without complications arising from other types of interactions. Read more »![]()
![]()
Macromolecular organic matter in samples of the asteroid (162173) Ryugu
We investigated the macromolecular organic matter in samples of the asteroid Ryugu—brought to Earth by the Hayabusa2 spacecraft—measuring its elemental, isotopic, and functional group compositions along with its small-scale structures and morphologies. Analytical methods used included spectro-microscopies, electron microscopy, and isotopic microscopy. Read more »
A Study on the Reaction Mechanism of a Model Organic Cathode in Magnesium-Ion Batteries
Battery and analytical studies of a model benzoquinone-type cathode reveal reversible structural transformations driven by a new precedence of a unique dissolution/precipitation mechanism and raise the question regarding its prevalence in other organic cathode batteries. Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- …
- 83
- Next Page »