Berger et al. utilize extreme ultraviolet, second-harmonic generation (XUV-SHG) spectroscopy to investigate the polar metal phase of lithium osmate (LiOsO3), where the coexistence of polarity and metallicity is unexpected. As the first demonstration of XUV-SHG spectroscopy around a phase transition, these results pave the way for using nonlinear XUV methods to investigate broken symmetry from an element-specific perspective. Read more »
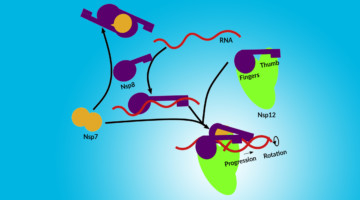
Assembly of the SARS-CoV-2 Replication Mechanism
Using a multimodal approach that included x-ray scattering at the ALS, researchers determined how components of the SARS-CoV-2 replication mechanism fit together. A better understanding of how this protein complex works provides insight into potential structural or functional weak spots to exploit for drug development. Read more »![]()
![]()
David Prendergast Wins 2021 Shirley Award
David Prendergast, an internationally recognized computational scientist whose first-principles calculations of x-ray spectra have helped with the interpretation of countless experiments done at the ALS, has been awarded the 2021 Shirley Award for Outstanding Scientific Achievement by the ALS Users’ Executive Committee. Read more »
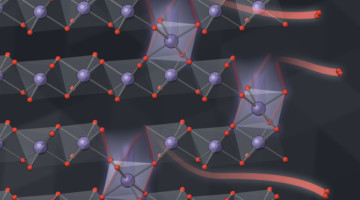
A Multiscale Picture of Oxygen Loss in Battery Electrodes
In lithium-ion batteries, oxygen atoms leak out of electrode particles as the lithium moves back and forth between electrodes. Now, researchers have measured this process at multiple length scales, showing how the oxygen loss changes the electrode’s structure and chemistry, gradually reducing the amount of energy it can store. Read more »
In a Hawaiian Lava Fountain, Fluid Magma Turns Brittle
Compared to the violent explosions of Mount Vesuvius or Mount St. Helens, Hawaiian volcanic eruptions are relatively calm, characterized by flowing rivers and fountains of lava. Here, researchers have discovered that even low-viscosity magma sometimes behaves more like brittle glass that shatters into fine particles. Read more »
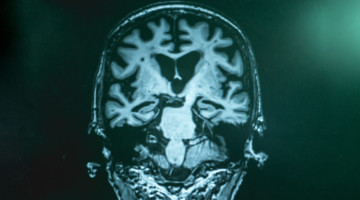
Nanoscale Metallic Particles Detected in Brain Tissue
Researchers detected nanoscale deposits of elemental copper and iron in brain tissues isolated from Alzheimer’s disease subjects. The discovery suggests new directions of study to determine the role that elemental metals might play in neurochemistry, neurobiology, and the development of neurodegenerative disease. Read more »![]()
![]()
Chemical (and Strategic) Transformations at Beamline 9.0
The Chemical Dynamics beamline, used for gas-phase vacuum ultraviolet (VUV) experiments, was one of the first beamlines built at the ALS. Since then, the program has undergone several strategic transformations, enabling the study of complexity in clusters, aerosols, and nanoparticles using both VUV and soft x-ray radiation. Read more »
Main Attraction: Scientists Create World’s Thinnest Magnet
A one-atom-thin 2D magnet that operates at room temperature could lead to new applications in computing and electronics—such as high-density, compact spintronic memory devices—and new tools for the study of quantum physics. X-ray experiments at the ALS characterized the material’s magnetic parameters under high temperature. Read more »
Deconstructing the Infectious Machinery of the SARS-CoV-2 Virus
Scientists collaborated to model the complex protein responsible for SARS-CoV-2 replication, revealing its potential weak spots for drug development. The investigation hinged on data collected from many advanced imaging techniques, including small-angle x-ray scattering (SAXS), crystallography, and small-angle neutron scattering (SANS). Read more »
Mineral Microstructures Shed Light on Planet-Scale Dynamics
To explore what happens to minerals under the extreme conditions in Earth’s mantle, researchers developed an x-ray technique that bridges the gap between methods that reveal bulk properties and those that focus on individual crystals. Use of the technique has shed light on the dynamics of tectonic-plate subduction in Earth’s lower mantle. Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- …
- 83
- Next Page »