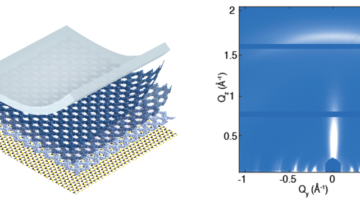
Researchers identified how ion and electron transfer naturally balance at the LaAlO3/SrTiO3 oxide heterointerface, affecting the band alignment and magnetic signature of the interface. The results show that Sr ions are more mobile at the interface than in the bulk, implicating a high importance of ionic charge transfer in oxide heterostructures. Read more »
2D MXene Shows Evidence of a Magnetic Transition
A variety of experiments, including ALS x-ray studies, provided direct evidence of a magnetic transition in a 2D compound called a MXene (pronounced “maxene”). The finding adds new functionality to a family of materials with numerous ways to fine-tune properties for applications ranging from spintronic devices to electromagnetic shielding. Read more »![]()
![]()
ALS in the News (January 2021)
-
-
-
- Squeezing a rock-star material could make it stable enough for solar cells
- Next generation of quantum computing materials take cues from nature
- Modulating helical nanostructures in liquid crystal phase by molecular design
- The odd structure of ORF8: Scientists map the coronavirus protein linked to immune evasion and disease severity
- UCF researchers use advanced light to reveal how different biofuels behave
- Study shows tweaking one layer of atoms on a catalyst’s surface can make it work better
- Unique x-ray microscope reveals dazzling 3D cell images
- Uncovering how plants see blue light
- Berkeley Lab’s top 10 science stories of 2020
- Speeding toward improved hydrogen fuel production
- Research breakthrough could transform clean energy technology
- New method sees fibers in 3D, uses it to estimate conductivity
-
-
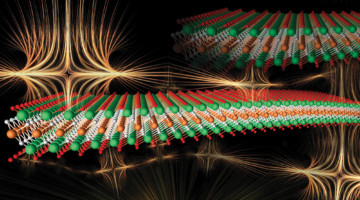
Stacking the Deck for Custom-Built Hybrid Materials
Researchers fabricated an electronically coupled heterostructure from a novel semiconducting 2D polymer and a 2D transition metal dichalcogenide. Dramatic optical and electronic changes emerged as polymer thickness decreased, underscoring the potential for the discovery of emergent phenomena in studies of hybrid heterostructures. Read more »
Inhalable COVID-19 Protection via Synthetic Nanobodies
Protein structures obtained in part at the ALS helped researchers to increase the potency of simplified antibodies (nanobodies) designed to neutralize SARS-CoV-2. Stable enough to be used in inhalers or nasal sprays, the nanobodies offer a new option, aside from injected vaccines, for COVID-19 prevention and treatment. Read more »![]()
![]()
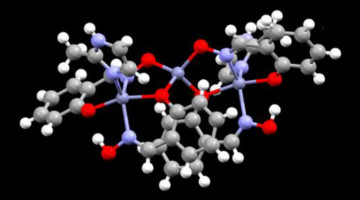
Molecular Complex Removes Copper Ions from Water
X-ray analyses provided key insights into the copper uptake mechanisms in a new organic-inorganic hybrid material that quickly and selectively removes copper ions from water. The material provides an efficient tool for copper remediation as well as a blueprint for creating other hybrid materials for removing toxic metals from water. Read more »![]()
![]()
Xylella fastidiosa causes transcriptional shifts that precede tylose formation and starch depletion in xylem
During Pierce’s disease, Xylella fastidiosa triggers transcriptional changes in grapevines and induces major physiological responses, including tylose formation and starch depletion. X-ray computed microtomography and a machine-learning algorithm were used to track the depletion of starch reserves in the xylem of a grapevine stem infected with Pierce’s disease. Read more »
A 1-Atom-Deep Look at a Water-Splitting Catalyst
X-ray experiments revealed an unexpected transformation in a single atomic layer of a material that contributed to a doubling in the speed of a chemical reaction—the splitting of water into hydrogen and oxygen gases. This process is a first step in producing hydrogen fuel for applications such as electric vehicles powered by hydrogen fuel cells. Read more »
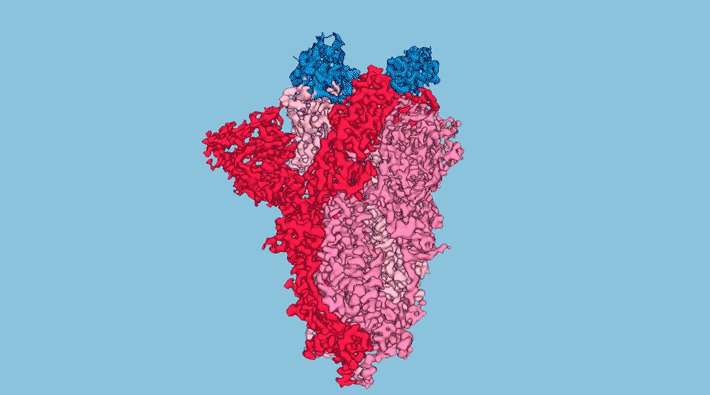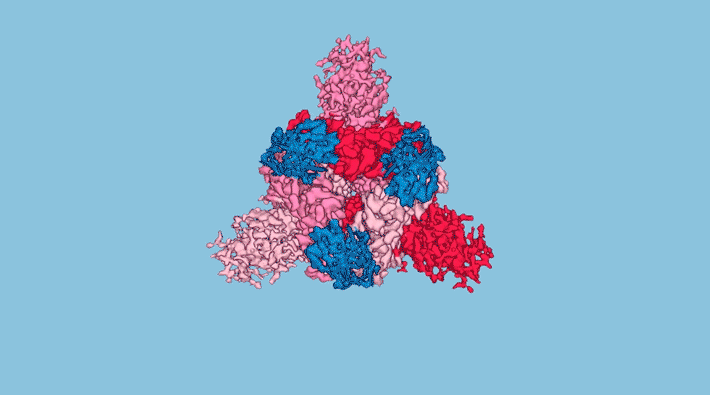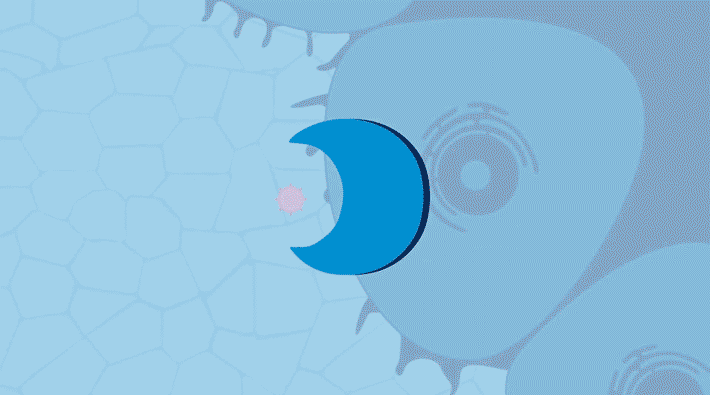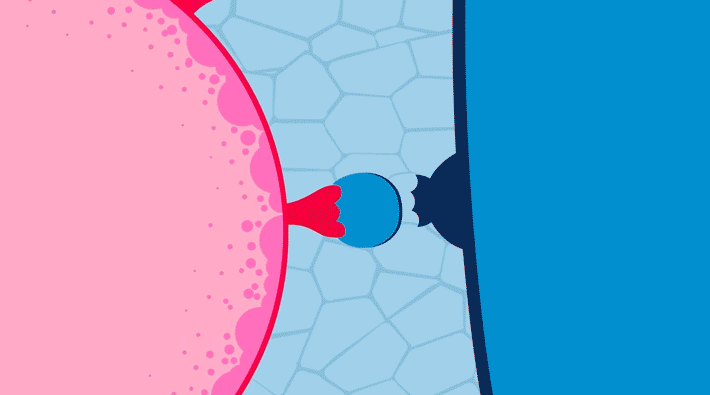
The Odd Structure of ORF8: Scientists Map the Coronavirus Protein Linked to Immune Evasion and Disease Severity
Researchers determined the atomic structure of a coronavirus protein thought to help the pathogen evade and dampen response from human immune cells. Researchers determined the atomic structure of a coronavirus protein thought to help the pathogen evade and dampen response from human immune cells. Read more »
Functionalization of Benzotriazole-Based Conjugated Polymers for Solar Cells: Heteroatom vs Substituents
Understanding the structure-property relationship is important when designing new conjugated polymers for high-efficiency polymer solar cells. Rech et al. systematically explore the impact of a variety of functional groups, including nitrogen heteroatoms, fluorine substituents, and cyano groups. Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- …
- 83
- Next Page »