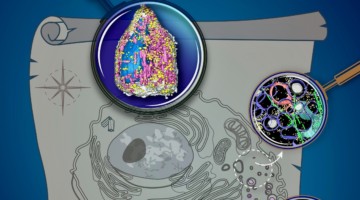
Researchers used soft x-ray tomography to reveal never-before-seen details about insulin secretion in pancreatic cells taken from rats. By quantifying subcellular rearrangements in response to drugs, the results are an important first step for bridging the longstanding gap between structural biology and physiology. Read more »
Coordinated decline of leaf hydraulic and stomatal conductances under drought is not linked to leaf xylem embolism for different grapevine cultivars
Drought decreases water transport capacity of leaves and limits gas exchange, which involves reduced leaf hydraulic conductance (Kleaf) in both the xylem and outside-xylem pathways. We combined Kleaf and gas exchange measurements, micro-computed tomography of intact leaves, and spatially explicit modeling of the outside-xylem pathways to evaluate the role of vein embolism and Kleaf in the responses of two different grapevine cultivars to drought. Read more »
Speeding Toward Improved Hydrogen Fuel Production
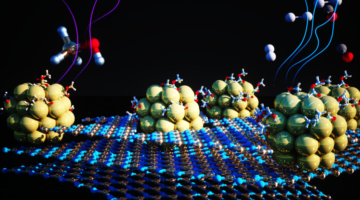
Researchers synthesized a material that speeds up one of the limiting steps in extracting hydrogen from alcohols. The catalyst cleanly and efficiently accelerates the removal of hydrogen atoms from a liquid chemical carrier. The material is robust, made from earth-abundant metals, and will help make hydrogen a viable energy source for a wide range of applications. Read more »
Demolition Day: Building 7, Last Bastion of “Old Town,” Makes Way for the Future
On Saturday morning, November 28, 2020, a demolition crew made quick work of de-constructing Building 7, a 75-year-old two-story wooden structure adjacent to the Advanced Light Source (ALS) and the last holdout from a cluster of buildings in the area known as “Old Town.” Read more »
ALS in the News (December 2020)
-
-
- ASU physics professor receives $300,000 grant
- Twisting light and COVID treatment: News from [Imperial] College
- 9 Berkeley Lab scientists named 2020 AAAS Fellows
- New method sees fibers in 3D, uses it to estimate conductivity
- For plants, endophytes promote phosphorus uptake
- Scientists design new framework for clean water
- A better understanding of coral skeleton growth suggests ways to restore reefs
-
Newly Discovered Photosynthesis Enzyme Yields Evolutionary Clues
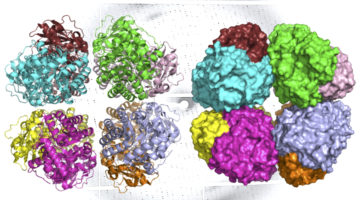
Scientists have discovered a primitive form of rubisco, a photosynthesis enzyme that has helped shape life on Earth. Detailed information about its structure, determined using complementary techniques at the ALS, will help scientists understand how carbon-fixing organisms oxygenated the atmosphere and how modern plants evolved. Read more »
New Insights into Lithium-Metal Surface Reactions for Next-Generation Batteries
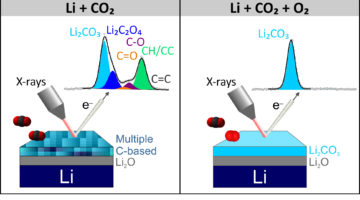
In this work, researchers studied how CO2 gas modifies the chemical composition of lithium-metal surfaces. A better understanding of the interactions between lithium and surrounding gases will help design stabilization strategies and move from lithium-ion technology to high-energy-density technologies based on lithium metal. Read more »
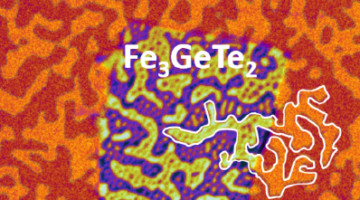
From Stripes to Skyrmions in a Surprising Material
Researchers showed that tiny bubbles of ordered spins (skyrmions) can be induced to form in a material previously considered incompatible with skyrmion formation. The discovery opens up a new class of material systems that exhibit technologically desirable nanoscale features attractive for spintronic applications. Read more »![]()
![]()
Super-Resolution Measurement of X-Ray Mirrors
ALS researchers, in collaboration with software and nanofabrication small businesses, developed a way to improve the accuracy of instruments that measure the surfaces of x-ray mirrors. The work significantly improves the quality of the data needed for the fabrication and optimal performance of advanced x-ray beamlines and space telescopes. Read more »![]()
![]()
Extreme Low-Temperature Combustion Chemistry: Ozone-Initiated Oxidation of Methyl Hexanoate
The accelerating effect of ozone on the oxidation of methyl hexanoate was probed with time-of-flight mass spectrometry. A new oxidation regime was observed at temperatures below the well-known low-temperature chemistry regime. The results indicate that the chemistry in this regime is initiated by thermal ozone dissociation and subsequent H abstraction from methyl hexanoate by O atoms. Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- …
- 83
- Next Page »