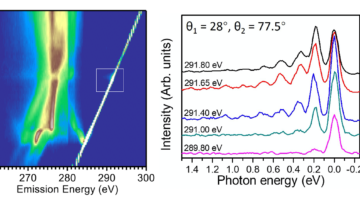
Resonant inelastic x-ray scattering (RIXS) has recently been shown to be a promising technique for studying electron–phonon coupling in correlated materials. When a photoexcited electron interacts with phonons during decay, it shows up in the RIXS spectra as clear phonon overtones: higher-order excitations that appear as ripples in intensity. Read more »
Design and synthesis of high performance flexible and green supercapacitors made of manganese‐dioxide‐decorated alkali lignin
Researchers synthesized a plant‐based composite electrode for use in flexible supercapacitors and used synchrotron x‐ray microtomography to better understand the impact of microstructure and morphology on electrode porosity and electrical conductance. Read more »
Stress-Induced Structural Transformations in Gold Nanocrystals
Metallic nanocrystals are widely used in catalysis, electronics, photonics, and sensing applications, but our understanding of their stability under operational stresses is limited. These studies of gold nanocrystals at high pressures found that large-scale structural transformation is possible and must be considered at the nanoscale. Read more »
Jennifer Doudna and the Nobel Prize: The Advanced Light Source Perspective
The 2020 Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded to Jennifer Doudna and Emmanuelle Charpentier for the development of a world-changing gene-editing technology. At the ALS, Doudna’s work on CRISPR-Cas9 was enabled by many visionary people with innovative ideas, implemented in support of a world-class structural biology program. Read more »![]()
Magneto-structural studies of an unusual [MnIIIMnIIGdIII(OR)4]4− partial cubane from 2,2′-bis-p–tBu-calix[4]arene
TBC[4] is a molecular framework that has proven to be a highly versatile ligand for the synthesis of a breadth of polymetallic transition metal, lanthanide metal, and 3d–4f complexes. We outline the synthesis, structure and magnetic behaviour of a new bis-TBC[4]-supported complex, together with theoretical magneto-structural studies examining the exchange interactions. Read more »
Coming Down the Pike: Long-Haul Trucks Powered by Hydrogen Fuel Cells
DOE has announced several major investments to take hydrogen fuel cells to the next level, and Berkeley Lab is set to play a leading role. Ten DOE national labs have been selected to participate in two new consortia and a third continuing one to improve the durability, lifetime, and efficiency of fuel cells. Read more »
Controlling Magnetization Vector Depth Profiles of La0.7Sr0.3CoO3/La0.7Sr0.3MnO3 Exchange Spring Bilayers via Interface Reconstruction
Polarized neutron reflectometry was combined with soft x-ray magnetic spectroscopy to quantify the changes in the magnetic and chemical depth profiles in La0.7Sr0.3CoO3/La0.7Sr0.3MnO3 bilayers, confirming the formation of interfacial layers with distinct magnetization and chemical density. Read more »
Study Finds ‘Missing Link’ in the Evolutionary History of Carbon-Fixing Protein Rubisco
Scientists discovered an ancient form of rubisco, the most abundant enzyme on Earth and critical to life as we know it. Found in previously unknown environmental microbes, the newly identified rubisco provides insight into the evolution of the photosynthetic organisms that underlie the planet’s food chains. Read more »
Targeting the trypanosome kinetochore with CLK1 protein kinase inhibitors
Saldivia et al. identify CLK1 as the target for the amidobenzimidazoles series of compounds. Inhibition of this protein kinase impairs inner kinetochore recruitment, causing cell-cycle arrest and cell death in trypanosomal pathogens such as Trypanosoma brucei. Read more »
Providing New Technologies for Vaccine Development
Antigens can sometimes be attached to a protein scaffold to mimic the shape of a virus and elicit a stronger immune response. Scientists developed a method to design such proteins, and ALS data helped to visualize the atomic structure and determine the dynamics of the designed scaffolds. Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- …
- 83
- Next Page »