Researchers have successfully demonstrated how machine-learning tools can improve beam-size stability via adjustments that largely cancel out these fluctuations—reducing them from a level of a few percent down to 0.4 percent, with submicron precision. The demonstration shows that the technique could be viable for scientific light sources around the globe. Read more »
Go With the Flow: Scientists Design Better Batteries for a Renewable Energy Grid
Researchers developed a versatile yet affordable battery membrane—from a class of polymers known as AquaPIMs. This class of polymers makes long-lasting and low-cost grid batteries possible based solely on readily available materials such as zinc, iron, and water. Read more »
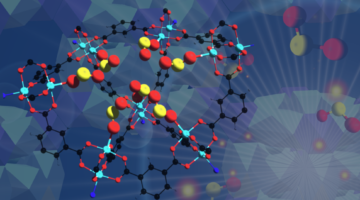
New MOF Can Take On Toxic Sulfur Dioxide Gas
An international team has developed a robust material that can selectively take in toxic sulfur dioxide gas at record concentrations and preserve it for use in chemical production. The researchers verified its performance using a combination of techniques that included x-ray experiments at the ALS. Read more »
ALS in the News (October 2019)
- How electrons move in a catastrophe
- Transforming sulphur dioxide from harmful to useful
- NERSC shuts down supercomputers amid PG&E blackout
- Peering into batteries: X-rays reveal lithium-ion’s mysteries
- Following the data trail to accelerated discovery
- 2019 Director’s Awards
- Newly found structures in tooth enamel might finally explain its bizarre strength
- Potent antibody curbs Nipah and Hendra virus attack
- Multimodal x-ray and electron microscopy of the Allende meteorite
2019 ALS User Meeting Highlights
ALS users and staff gathered to hear the latest news from Washington, the ALS, and each other. The program featured a diverse set of scientific talks and a full slate of workshops and tutorials offering deep dives into topics of interest and, for those new to light sources, introductory presentations designed to demystify the light-source experience. Read more »
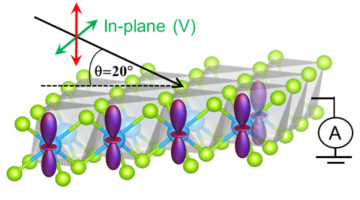
Anomalous Orbital Structure in Two-Dimensional Materials
Researchers explored how structural distortions of the atomic lattice influence exotic electronic states in two-dimensional transition-metal dichalcogenides (TMDs). Polarization-dependent spectroscopy revealed an unexpectedly large crystal-field splitting of the valence electron states, a result of strong hybridization in metal–chalcogen orbitals. Read more »
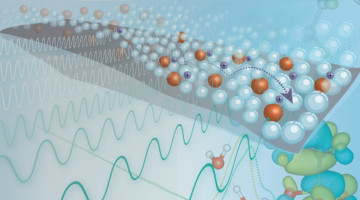
Multimodal Study of Ion-Conducting Membranes
Using multiple x-ray characterization tools, researchers showed how chemical and structural changes improve the performance of a novel ion-conducting polymer (ionomer) membrane from 3M Company. The work provides insight into factors impacting the proton conductivity of ionomers used for fuel cells and the production of hydrogen fuel. Read more »![]()
![]()
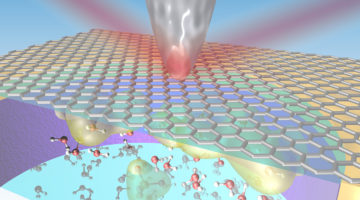
Infrared Nanospectroscopy at Graphene–Liquid Interfaces
Researchers developed a new infrared approach to probing the first few molecular layers of a liquid in contact with a graphene electrode under operating conditions. The work offers a new way to study the interfaces that are key to understanding batteries, corrosion, and other bio- and electrochemical phenomena. Read more »![]()
![]()
Padraic Shafer to Receive the 2019 Shirley Award
Congratulations to Padraic Shafer, this year’s recipient of the Shirley Award for Outstanding Scientific Achievement! Shafer, ALS staff scientist and leader of the ALS’s dichroism program, is being recognized “for unveiling the nature of chiral quantum materials through the innovative use of x-ray scattering at the Advanced Light Source.” Read more »
ALS in the News (September 2019)
- New $100M Innovation Hub to accelerate R&D for a secure water future
- New route to carbon-neutral fuels from carbon dioxide discovered by Stanford-DTU team
- X-ray experiments contribute to studies of a drug now approved to combat tuberculosis
- Seven new Bakar Fellows already are making an impact
- A CRISPR doyen discusses gene-editing challenges (video)
- Study reveals ‘radical’ wrinkle in forming complex carbon molecules in space
- The chemistry of art: Scientists explore aged paint in microscopic detail to inform preservation efforts
- SMART algorithm makes beamline data collection smarter
- Enhancing materials for hi-res patterning to advance microelectronics
- In Memoriam: Charles Fadley, Distinguished Professor Emeritus of Physics
- Doudna awarded prize for helping build a better, more harmonious world
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- …
- 83
- Next Page »