Sickle cell disease (SCD), which affects millions of people worldwide, has traditionally been treated with a cytotoxic drug that has a range of negative side effects and variable patient response. Bay Area biopharmaceutical company Global Blood Therapeutics (GBT) is on a mission to develop a better treatment and is using the ALS to help. Read more »![]()
All News & Updates
September 2017 Call for General User Proposals
The User Office is accepting new General User Proposals (GUPs) from scientists who wish to conduct research at the ALS in the January–July 2018 cycle. The deadline for submissions is September 6, 2017. Read more »
Early Registration for 2017 User Meeting Ends Sept. 18
Discounted early registration ends Monday, September 18, for the 2017 ALS User Meeting, which will take place October 2–4 at Berkeley Lab. The ALS Users’ Executive Committee (UEC) and meeting organizers have assembled a full program featuring news from DOE, keynote talks, and science highlights, as well as 13 focused workshops, a student poster “slam,” and the presentation of awards at the annual banquet. To register and view the draft agenda and logistical information, visit the User Meeting webpage. Read more »
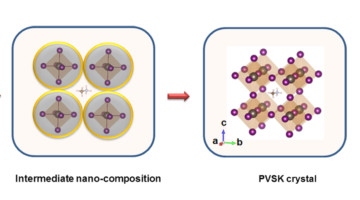
Formation of a Photovoltaic Material from Precursor to Crystal
Lead halide perovskites have emerged as high-performance photovoltaic materials, demonstrating remarkably rapid improvements in efficiency. In situ printing and time-resolved x-ray characterization have provided new insights into the relationship between device efficiency, perovskite crystallinity, and film morphology. Read more »
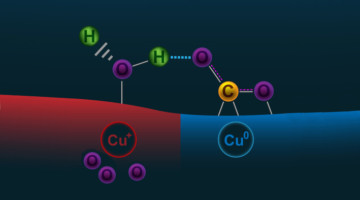
Subsurface Oxygen Boosts Activity of Copper Catalysts
Scientists are seeking ways to reduce levels of CO2 in the atmosphere by improving the processes that convert CO2 gas into ethanol (a liquid fuel). But copper, the best catalyst for this, is not very efficient. Now, ambient-pressure x-ray experiments have revealed how subsurface oxygen boosts copper’s catalytic activity. Read more »![]()
![]()
In Situ Electrical Resistance and X-Ray Tomography Study of Copper–Tin Polymer Composites during Thermal Annealing
In situ electrical conductivity and x-ray tomography experiments were conducted on a conductive polymer composite containing polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) copolymer, copper (Cu), and tin (Sn) during thermal annealing. This study provides detailed insight into the morphological origins of the beneficial effect of thermal annealing on the electrical properties of conductive composites containing low melting metal fillers. Read more »
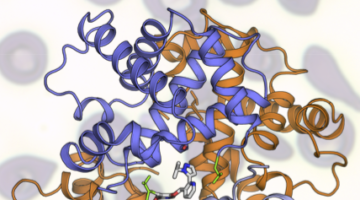
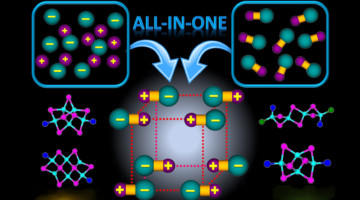
A Bacterial Jigsaw Puzzle Is Solved
Bacterial microcompartments (BMCs) are hollow protein shells that encapsulate enzymes involved in bacterial metabolism. Crystallography studies have provided atomic-resolution views of a fully assembled BMC, revealing basic principles of shell construction for fighting pathogens or bioengineering applications. Read more »![]()
![]()
Hybrid LED Phosphors Combine Performance and Durability
Light-emitting diodes (LEDs) last a long time and are very energy efficient. However, white LEDs currently rely on phosphor materials doped with rare-earth elements (REEs) that are increasingly costly and in short supply. A new class of hybrid phosphor materials shows promise as REE-free alternatives. Read more »
ALS User Marie Jackson Featured on Science Friday
Marie Jackson (pictured center, with ALS scientists Nobumichi Tamura and Camelia Stan), an ALS User from the University of Utah, was recently featured on Science Friday. She discussed her work on understanding crystal growth in Roman concrete (featured in this month’s science brief) with host Ira Flatow. Listen to the segment. Read more »
Deadline Extended: Nominations for the 2017 ALS User Meeting Awards
The deadline for nominations for the 2017 ALS User Meeting awards has been extended to July 31. Consider putting forward an individual (or team) who has made a significant contribution to the scientific and/or user support programs at the ALS. The online nomination forms are on the UEC website together with a description of each award. Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- …
- 139
- Next Page »