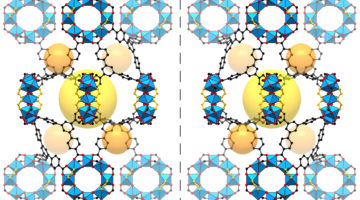
Researchers have created a sort of nanoscale display case that enables new atomic-scale views of hard-to-study chemical and biological samples. The work could help to reveal new structural details for a range of challenging molecules by stabilizing them inside sturdy structures known as metal-organic frameworks (MOFs). Read more »![]()
![]()
All News & Updates
3D Visualization of the Behavior of Grease Additives
Lubricants help keep civilization running smoothly, but is there room for improvement? With the goal of increasing the life span and lowering the costs of all kinds of mechanical and biological systems, researchers used x-ray microtomography to visualize the behavior of grease additives under working conditions. Read more »
Meet the New UEC Members
The results of the ALS Users’ Executive Committee (UEC) election are in, and six new members have been chosen, including a new student representative. They will each serve on the committee for three years (two years for the student representative), starting on January 1, 2017. Read more »
Glowing Crystals Can Detect, Cleanse Contaminated Drinking Water
Tiny, glowing crystals designed to detect and capture heavy-metal toxins such as lead and mercury could prove to be a powerful new tool in locating and cleaning up contaminated water sources. The crystals function like miniature, reusable sensors and traps, and are known as luminescent metal-organic frameworks, or LMOFs. Read more »
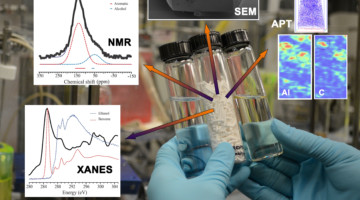
Scientists Trace ‘Poisoning’ in Chemical Reactions to the Atomic Scale
A team of researchers has employed a combination of measurements, including x-ray experiments at the ALS, to gather the most detailed information yet on problematic carbon-based deposits called “coke,” and to find ways to prevent its formation or reduce its effects. Read more »
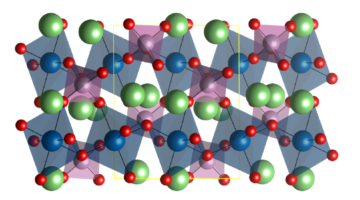
Understanding Barriers to Higher-Capacity Rechargeable Batteries
Vanadyl phosphate can theoretically accept twice the number of lithium ions as battery materials currently in use. In practice, however, it doesn’t live up to expectations. New research at Beamline 6.3.1 using a variety of hard and soft x-ray spectroscopies helps zero in on why. Read more »
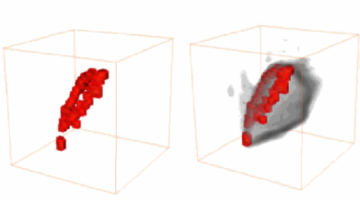
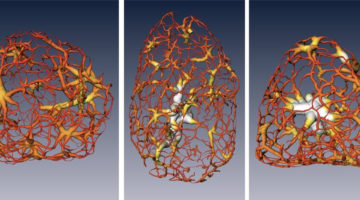
3-D Imaging Technique Maps Migration of DNA-carrying Material at the Center of Cells
Scientists have mapped the reorganization of genetic material that takes place when a stem cell matures into a nerve cell. Detailed 3-D visualizations show an unexpected connectivity in the genetic material in a cell’s nucleus, and provide a new understanding of a cell’s evolving architecture. Read more »
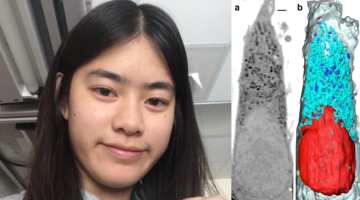
What I Did Last Summer: Co-Authored a Scientific Paper!
Young ALS user Jessica Guo may still be in high school, but she already has a peer-reviewed journal publication to her credit, based on work done at the ALS. She is a co-author of a paper published in Biology of the Cell on mesoscale imaging with cryo-light and x-rays. Read more »
Industrial-Academic Collaboration Gives Nanoscale Insight into Batteries
An industrial collaboration between Hummingbird Scientific and a team of researchers from the ALS, SLAC, Berkeley Lab, Stanford University, and other institutions has resulted in a new x-ray microscopy platform that gives scientists the ability to image nanoscale changes inside lithium-ion battery particles in real time as they charge and discharge. Insights obtained from the imaging platform have already provided surprising new insights and could help researchers improve batteries for electric vehicles as well as smart phones, laptops, and other devices. Read more »![]()
Solar Cells Get Boost with Integration of Water-Splitting Catalyst onto Semiconductor
Scientists have found a way to engineer the atomic-scale chemical properties of a water-splitting catalyst for integration with a solar cell, and the result is a big boost to the stability and efficiency of artificial photosynthesis. Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- …
- 139
- Next Page »