The ALS Users’ Executive Committee awarded the 2023 Klaus Halbach Award for Innovative Instrumentation to Slavo Nemsak for “the development of the state-of-the-art combined scattering and spectroscopy setup at ALS Beamline 11.0.2.” Read more »
All News & Updates
Lori Tamura Receives 2023 Tim Renner User Services Award
After 25 years of science writing at the ALS, Lori Tamura has a tried and true method for clearly communicating complex scientific concepts. With her care and skill, she has increased the impact and reach of results from ALS work, and the UEC has recognized that impact with the 2023 Tim Renner User Services Award. Read more »
ALS Postdoctoral Fellowship Program Invites New Applicants
Applications are due October 31 for ALS Collaborative Postdoctoral Fellowships that begin May 1, 2024. Fellows spend a year in residence at the ALS conducting research and instrumentation development in collaboration with their home institution. Read more »
UEC Nominations Due October 27, 2023
The Advanced Light Source Users’ Executive Committee (UEC) invites nominations for its upcoming election for three new UEC members (2024–2026 term). Nominations will be accepted through Friday, October 27, 2023. Take a look at what is involved, and remember that self-nominations are welcome! Read more »
September 2023 Message from the UEC
UEC Chair Inna Vishik celebrates a successful user meeting and invites attendees to re-live the happy memories as well as share their thoughts in the survey. She also shares ways to get involved. Read more »
Accelerating Sustainable Semiconductors With ‘Multielement Ink’
Scientists have developed “multielement ink”—the first “high-entropy” semiconductor that can be processed at low temperature or room temperature. The new semiconducting material could accelerate the sustainable production of next-gen microelectronics, photovoltaics, solid state lighting, and display devices. Read more »
Insight into How Thermoresponsive Nanomaterials Work
By combining soft x-ray scattering with electron microscopy, researchers learned how nanoscale polymer assemblies in solution restructure in response to heating. The approach can be generalized to many complex, solution-phase, nanoscale processes, and holds promise for driving advances in applications from drug delivery to catalysis. Read more »![]()
![]()
September Call for 2022 and 2023 Publications
All publications resulting from work done in whole, or in part, at the ALS must be recorded by the User Office for the Department of Energy (DOE). Please help ensure our records are complete by reporting your ALS publications, especially those published in 2022 and 2023. Read more »
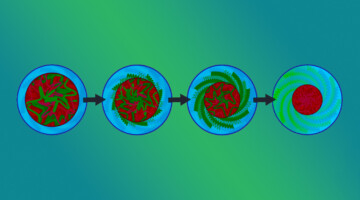
Precisely patterned nanofibres made from extendable protein multiplexes
Superhelical symmetry can be found in helical repeat proteins, and de novo helical repeat proteins are rigid and amenable to stacking in a head-to-tail fashion, which is an important factor in building up coincident symmetries. Now, using cyclic helical repeat proteins, Baker and colleagues generate protein nanostructures—as depicted on the cover—with coincident cyclic and superhelical symmetry axes. Read more »
Haris Mahic, Accelerator and Floor Operator
As an accelerator and floor operator, Haris’s work takes him all over the ALS. But, it is his photography hobby that has left an indelible mark on the ALS homepage. Let’s take a closer look at how he helps keep the ALS running and what brought him here in the first place. Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- …
- 139
- Next Page »