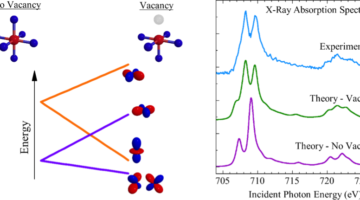
Researchers studied In2O3:Fe, a promising spintronic material, to determine what leads to its surprisingly robust magnetic properties, how to optimize it, and what to look for in other candidate spintronics materials. Read more »
Science Briefs
Superlattices Patterned by Polymers
Scientists have shown that self-assembled superlattices, made up of nanoparticles with polymer chains grafted onto their surfaces (“hairy nanoparticles,” or polymer “brushes”), can be tailored to exhibit desired characteristics for applications ranging from nano- to biotechnology. Read more »
On the Way to Unlimited Energy
With the help of four different ALS beamlines, scientists were able to understand and improve the morphology of the main device structure in organic photovoltaic cells. Read more »![]()
Improving Anti-Influenza Medications
Protein crystallography at ALS Beamline 8.3.1 helped scientists understand the M2 proton-channel structure from the influenza A virus, an understanding that is needed to design better anti-influenza medications. Read more »
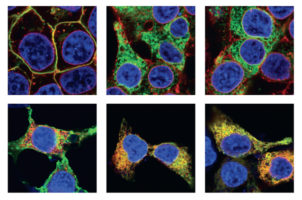
Improving Meningococcal Vaccines
Scientists have found a way to improve the stability of an essential antigenic protein to develop vaccines with higher efficacy for prevention of bacterial meningitis. Read more »
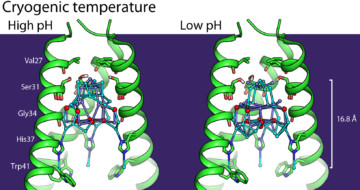
New Hope for Retinitis Pigmentosa Patients
Using FTIR microspectroscopy at the NSLS in Brookhaven and at ALS Beamline 1.4.3, scientists got a first glimpse into the structural changes that result from point mutations in opsin, one of the causes of retinitis pigmentosa. Read more »![]()
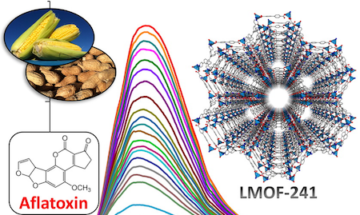
Luminescent MOFs for Mycotoxin Detection
Crystal diffractometry at ALS Beamline 11.3.1 helped scientists develop and understand a new, highly sensitive luminescent metal–organic framework for mycotoxin detection. Read more »
Conduction Along Magnetic Interfaces could Improve Memory Devices
Scientists have provided the first direct evidence of a controversial phenomenon: the boundaries between magnetic regions in an electrical insulator can become electrically conductive. This discovery can potentially lead to improvements in future memory storage devices. Read more »
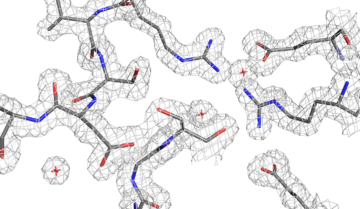
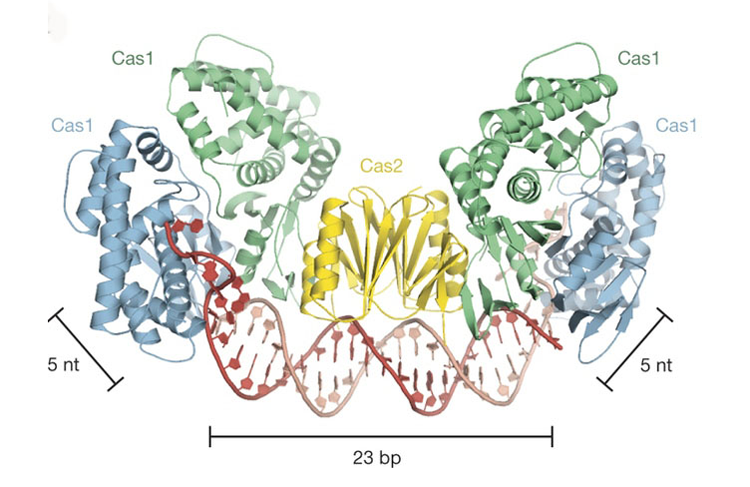
Foreign DNA Capture during CRISPR–Cas Adaptive Immunity
Using macromolecular crystallography at Beamline 8.3.1 at the ALS, Berkeley researchers discovered how CRISPR/Cas captures foreign DNA for the bacterial immune system. Read more »
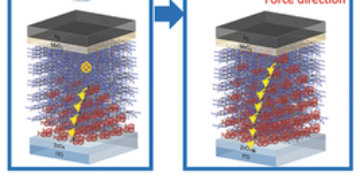
On the Road to ANG Vehicles with Increased Driving Ranges
An international team of researchers, using gas adsorption studies, in situ powder x-ray diffraction, and single-crystal x-ray diffraction, showed that there is a way to develop a new flexible metal–organic framework (MOF) material for enhanced natural gas storage on vehicles. Read more »