A time-resolved diffraction study conducted at the ALS revealed mechanistic insight into a multi-step chemical reaction for the economical production of aluminum–cerium alloy, a high-performance material with superior temperature stability. The results provide crucial information for the application of the method on an industrial scale. Read more »![]()
Science Briefs
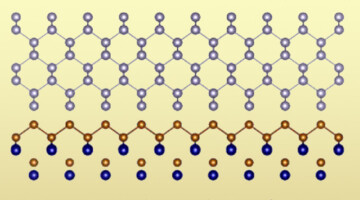
Stabilizing Pristine α-Sn Thin Films for Topological Investigation
Researchers developed a recipe for the room-temperature stabilization of thin films of α-Sn, a form of elemental tin that exhibits a variety of topologically nontrivial phases, but only at low temperatures. By dramatically reducing contamination from the film’s substrate, the recipe greatly simplifies electronic structure studies. Read more »![]()
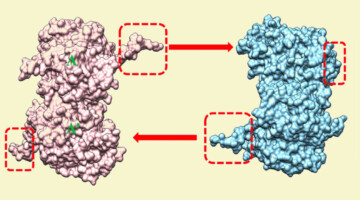
Mechanistic Insight into a Viral-Factory Component
Recent protein-structure studies conducted at the ALS provided mechanistic insights into the function of a protein (σNS) involved in viral replication. Understanding these mechanisms will foster the development of therapeutic strategies against viruses that use σNS-like proteins to replicate. Read more »
Surprise Mineral Precursor Found in Coral Skeletons and Mollusk Shells
Researchers studied samples from corals, mollusks, and sea urchins, at edges where mineral precursors start to form the new shell or skeleton. There, they found a surprise: corals and mollusks produced a mineral precursor that had never been observed before in living organisms or rocks, and had only recently been created synthetically. Read more »
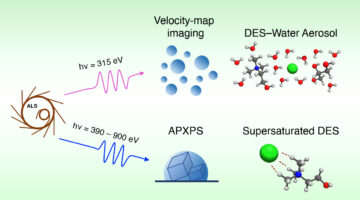
Probing the Liquid/Vapor Interface of a Tunable Solvent
Despite the ready tunability and industrial promise of deep eutectic solvents (DESs), there have been few x-ray spectroscopy studies at their liquid/vapor interfaces—which is relevant for their use in applications such as greenhouse-gas capture. Here, researchers probed the liquid/vapor interface of a benchmark DES using complementary spectroscopies. Read more »
Pacific Kelp Forests Are Far Older than We Thought
Researchers scanned newly discovered kelp fossils using x-ray tomography at the ALS. The images provided morphological information about the ancient kelp and, along with isotopic analyses, provided insights into the evolutionary history of northeastern Pacific Ocean kelp forests, which flourished more than 32 million years ago. Read more »
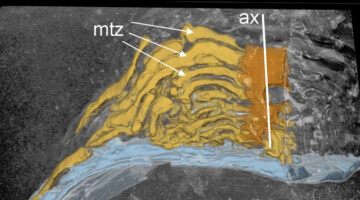
Surtsey Volcano: A Rare Window into Earth’s Oceanic Crust
Surtsey, a very young oceanic island in Iceland, emerged through explosive volcanic activity in 1963. Utilizing various techniques, including x-ray microdiffraction at the ALS, researchers gained unique insights into the transformation of volcanic glass to form mineral cements in the basaltic rock of underwater volcanoes. Read more »
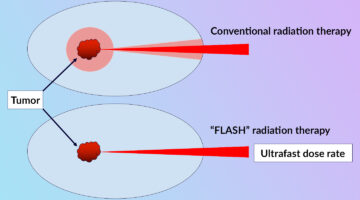
Clarifying the FLASH Effect for Cancer Radiation Therapy
To clarify the underlying mechanisms of the FLASH effect, in which the delivery of ultrafast, high-intensity doses of radiation to tumors counterintuitively reduces damage to surrounding healthy cells, researchers directly compared the oxidative effects of conventional and FLASH techniques using x-ray footprinting at the ALS. Read more »
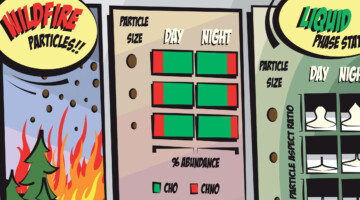
Case Study of Aerosol Particles Influenced by Wildfire
Researchers studied atmospheric aerosols influenced by wildfires in the Pacific Northwest. They examined the connection between particle size, chemical composition, and phase state, in particles collected during the day and at night. The information is important for modeling the effects of wildfire smoke on atmospheric properties. Read more »
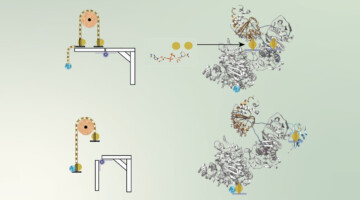
Bifurcation of High- and Low-Energy Electrons in Microbial Metabolism
A class of chemical reaction found only in biology, electron bifurcation channels two electrons from one donor to two separate acceptors, with one electron elevated in energy at the expense of lowering the energy of the second. Researchers used the ALS to study this process in a microbial protein involved in this bioenergetic pathway. Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- …
- 23
- Next Page »