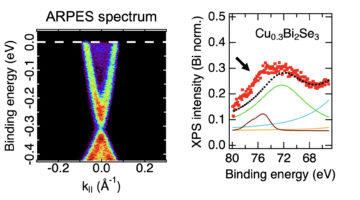
An ambient-pressure study of a topological insulator doped with copper revealed that the copper atoms, inserted between the material’s layers, migrate to the surface when exposed to air. The work represents a novel way of modifying the material’s surface composition, which can confer it with new properties such as superconductivity. Read more »
Science Briefs
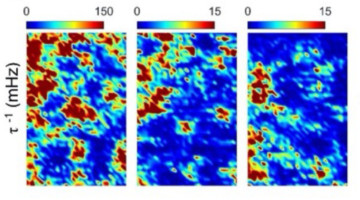
Percolating Puddles in Rich Quantum Landscapes
Combining x-ray photon correlation spectroscopy (XPCS) with scanning micro x-ray diffraction (SµXRD), researchers found that charge density wave domains (known as “puddles”) in a nickelate material exhibit two types of dynamics: small puddles actively “percolate” (fluctuate in size and shape), while large puddles are more static. Read more »
Crossing from One to Two Dimensions in a Single Material
Low-dimensional materials exhibit excellent properties for use in next-generation electronic devices. Now, researchers have discovered an ideal platform for tuning between 1D and 2D physics, expanding the possibilities for device engineering and offering a versatile platform for the exploration of intriguing low-dimensional physics. Read more »
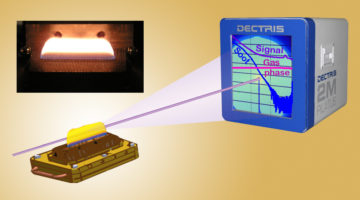
Distinguishing Nanoparticles from Gas-Phase Species in Reacting Flows
Researchers developed a strategy for distinguishing between gas-phase species and newly formed nanoparticles in mixed gas- and particle-phase reacting flows. The approach uses small-angle x-ray scattering to study particle formation as it occurs by explicitly accounting for temperature-dependent scattering from gases. Read more »![]()
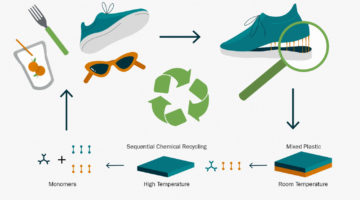
A New Material System for Mixed-Plastic Recycling
Scientists have designed a new material system to overcome one of the biggest challenges in recycling consumer products: mixed-plastic recycling. Their achievement will help enable a much broader range of fully recyclable plastic products and brings into reach an efficient circular economy for durable goods like automobiles. Read more »
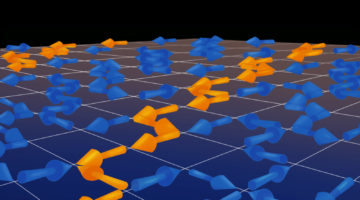
Disorder Drives Long-Range Order in “Tetris Ice” Nanomagnet Arrays
Long-range ordering is typically associated with a decrease in disorder, or entropy. Yet, it can also be driven by increasing entropy in certain special cases. In a recent DOE-funded study, researchers demonstrated that certain artificial spin-ice arrays—nanomagnets lithographically patterned to form Tetris-like shapes—can produce such entropy-driven order. Read more »
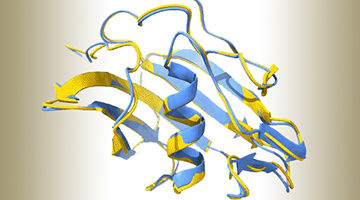
Deep-Learning AI Program Accurately Predicts Key Rotavirus Protein Fold
Rotaviruses are the major causative agents of gastroenteritis worldwide. Attempts to design vaccines are complicated by the rotaviruses’ enormous genetic and immunological diversity. At the ALS, researchers validated the novel structure of a key rotavirus protein, predicted using AlphaFold2, a deep-learning artificial-intelligence program. Read more »
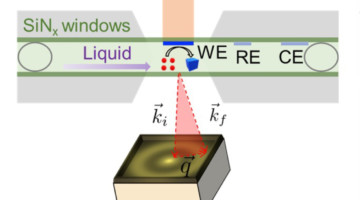
Operando Study of CO2 Reduction by Copper Nanoparticles
Since copper is necessary to catalyze the reduction of CO2, a greenhouse gas, to valuable products, scientists are working hard to improve its selectivity and activity. Now, researchers have developed an operando capability that can help in this effort by simultaneously probing chemical valence and interparticle dynamics. Read more »
New Insight into Titan’s Hazy Atmospheric Chemistry
Researchers simulated the complex chemistry that may be occurring in the hazy atmosphere of Saturn’s largest moon, Titan, and analyzed the reaction products at the ALS. The work provided new insights into what future Titan probes may encounter upon arrival and what the atmosphere of Earth may have been like eons ago. Read more »
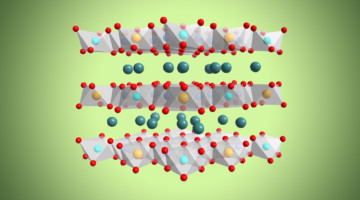
Copper Doping Improves Sodium-Ion Battery Performance
A big plus for batteries based on sodium over lithium is that sodium is more earth-abundant, which lowers costs and eases environmental and supply-chain concerns. Research to improve the performance of sodium-ion batteries includes this effort to use copper doping of the cathode to enhance oxygen redox reversibility. Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- …
- 23
- Next Page »