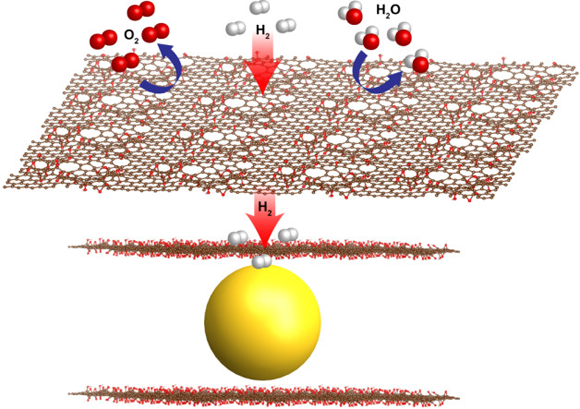
Hydrogen is the lightest and most plentiful element on Earth and could serve as a carbon-free, virtually limitless energy source. Recently, researchers working at the ALS and the Molecular Foundry developed a promising new materials recipe based on magnesium nanocrystals and graphene for a hydrogen fuel cell with improved performance in key areas. Read more »![]()
![]()
Science Highlights
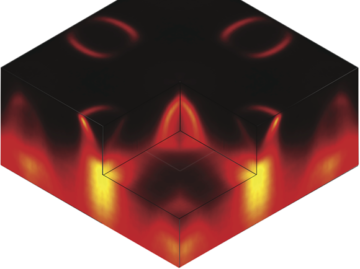
3D Charge Order Found in Superconductor
Resonant soft x-ray diffraction studies of a cuprate high-temperature superconductor revealed a 3D, long-range charge order—the first of its kind ever reported in a cuprate—that competes with superconductivity. A better understanding of such phenomena could help in the design of more robust superconductors with higher transition temperatures. Read more »![]()
![]()
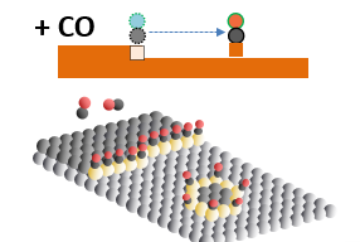
An Atomic-Level Understanding of Copper-Based Catalysts
Copper-based catalysts are widely used in chemical industries to convert water and carbon monoxide to hydrogen, carbon dioxide, and methanol. There are theoretical models used to explain this reaction, but a complete understanding of the process has been lacking. However, recent research at the ALS has shed light on the process, giving scientists key data about how copper-based catalysts function at the atomic level. Read more »![]()
![]()
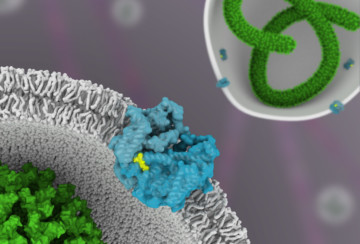
Shutting Out Ebola and Other Viruses
Researchers have used protein crystallography at the ALS to understand how a drug molecule that has shown some efficacy against Ebola in mice inactivates a membrane protein, called TPC1, used by viruses to infect host cells. Read more »![]()
![]()
A New Universal Parameter for Superconductivity
Scientists have been researching high-temperature (high-Tc) superconductors for decades with the goal of finding materials that express superconducting capabilities at room temperature, which would be a requirement for practical and cost-effective applications. The newest materials to gain scientific interest are iron-based superconductors, and the latest research from the ALS on these materials indicates a new factor that determines their superconductivity. Read more »![]()
![]()
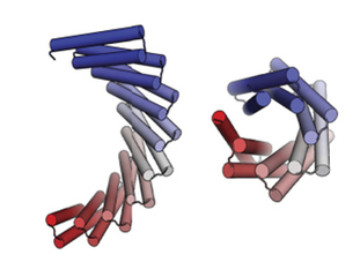
Exploring the Repeat-Protein Universe
Researchers have published a landmark study that used both crystallography and SAXS to validate computationally designed structures of novel proteins with repeated motifs. The results show that the protein-folding universe is far larger than realized, opening up a wide array of new possibilities for biomolecular engineering. Read more »![]()
![]()
Manganese Reduction-Oxidation Drives Plant Debris Decomposition
ALS research has shown that manganese reduction-oxidation (redox) reactions are an important factor in controlling the rate of plant debris decomposition. Understanding the role of manganese will help build better models to predict how litter decomposition rates—and thus nutrient cycling and the ecosystem carbon balance—may behave in future climate scenarios. Read more »![]()
![]()
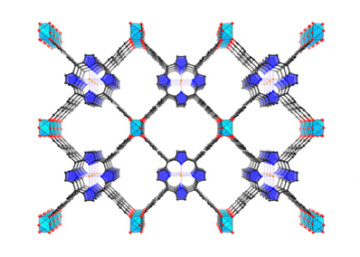
Porous-Framework Electrocatalysts Are Key to Carbon Dioxide Conversion
Researchers have made significant headway in the quest to convert CO2 into valuable chemical products such as fuels, pharmaceuticals, and plastics. Recent work at the ALS has shown MOFs and COFs as a valuable new class of CO2 reduction catalysts. Read more »![]()
![]()
Aerosol Oxidation Speeds Up in Smoggy Air
To better understand the effects of organic aerosols on climate, pollution, and health, researchers measured aerosol reaction rates at ALS Beamline 9.0.2. They discovered an unexpectedly large acceleration in aerosol oxidation in the presence of anthropogenic pollutants commonly found in smoggy air, a result that could help bring models closer in line with observations. Read more »![]()
![]()
A New Pathway for Radionuclide Uptake
Scientists have reported a major advance in understanding the biological chemistry of radioactive metals, opening up new avenues of research into strategies for remedial action in the event of possible human exposure to nuclear contaminants. Read more »![]()
![]()
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- …
- 27
- Next Page »