Scientists have designed a new material system to overcome one of the biggest challenges in recycling consumer products: mixed-plastic recycling. Their achievement will help enable a much broader range of fully recyclable plastic products and brings into reach an efficient circular economy for durable goods like automobiles. Read more »
Improving the Efficiency of Atmospheric Water Harvesting
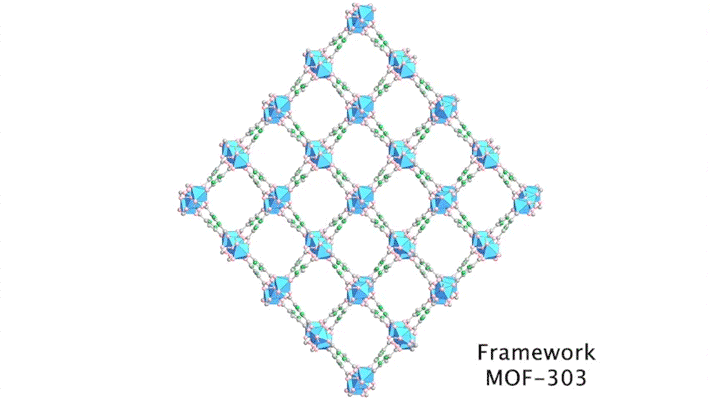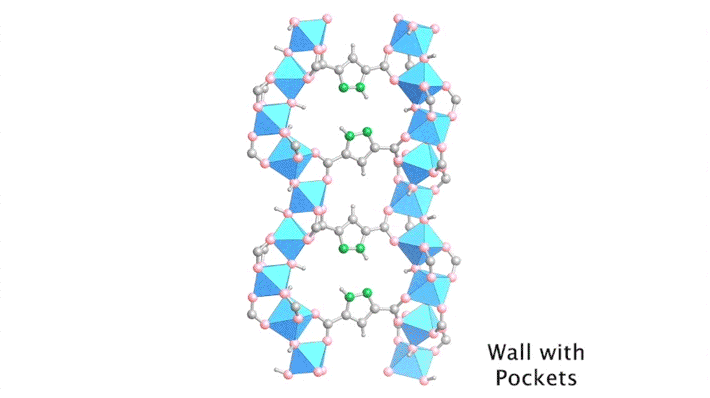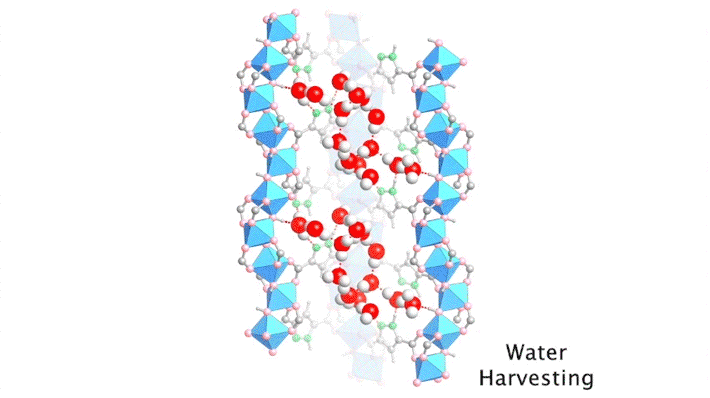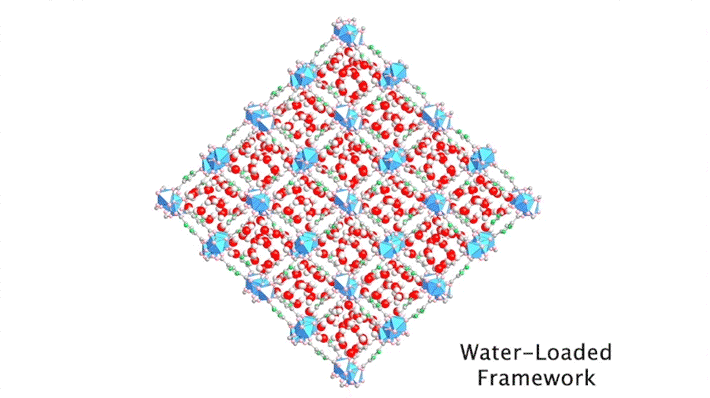
Researchers traced the step-by-step path of water-molecule uptake in a porous compound, then made pinpoint modifications to shape the material’s water-sorption behavior. The results led to improvements in the compound’s efficiency at harvesting water from the air, an important step toward alleviating water shortages in the future. Read more »![]()
![]()
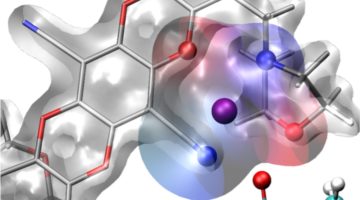
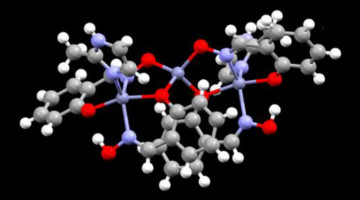
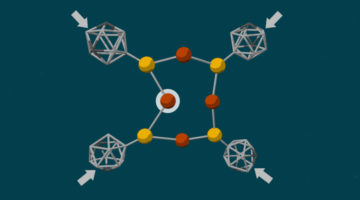
A {Ni12}-Wheel-Based Metal–Organic Framework for Coordinative Binding of Sulphur Dioxide and Nitrogen Dioxide
SO2 and NO2 are important air pollutants, and understanding the mechanism of capture materials drives the development of new clean-up technologies. In situ synchrotron x-ray crystallographic and spectroscopic experiments were used to establish a detailed molecular mechanism consisting of reversible coordination of SO2 and NO2 at the six open NiII sites on the unprecedented {Ni12}-wheel of a robust metal–organic framework material at crystallographic resolution. Read more »
Designing Selective Membranes for Batteries Using a Drug Discovery Toolbox
Researchers designed a polymer membrane with molecular cages built into its pores that hold positively charged ions from a lithium salt. These “solvation cages” increased lithium-ion flow by an order of magnitude and could allow high-voltage battery cells to operate at higher power and more efficiently, important for both electric vehicles and aircraft. Read more »
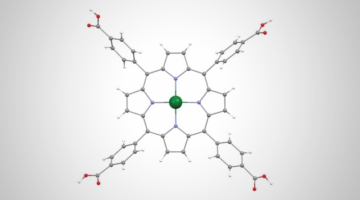
Molecular Complex Removes Copper Ions from Water
X-ray analyses provided key insights into the copper uptake mechanisms in a new organic-inorganic hybrid material that quickly and selectively removes copper ions from water. The material provides an efficient tool for copper remediation as well as a blueprint for creating other hybrid materials for removing toxic metals from water. Read more »![]()
![]()
Scientists Design New Framework for Clean Water
A promising solution to water pollution from abandoned copper mines relies on materials that adsorb copper ions from wastewater, but commercially available products lack the required chemical specificity and load capacity. A team of scientists has designed a new crystalline material that targets and traps copper ions from wastewater with unprecedented precision and speed. Read more »
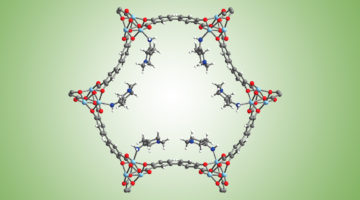
Rational Design of a Uranyl Metal–Organic Framework for the Capture and Colorimetric Detection of Organic Dyes
Diffraction data for a new uranyl-containing metal–organic framework reveals a structure of interpenetrating 3D nets with large pores. The material is stable in aqueous media and due to the large void space (constituting 76% of the unit cell by volume) can sequester organic dyes, the uptake of which induces a visible change to the color of the material. Read more »
Water Improves Material’s Ability to Capture CO2
With the help of the ALS, researchers from UC Berkeley and ExxonMobil fine-tuned a material to capture CO2 in the presence of water. The parties have applied for a patent on the material, which was developed for use on the relatively humid flue gases emitted by certain natural gas power plants, a cleaner-burning alternative to coal. Read more »![]()
![]()
A 2D Lattice of Molecular Qubits for Quantum Computing
Researchers developed a way to build a 2D lattice of molecular-spin qubits (quantum bits of information), with control over qubit orientation and localization. The work enables the integration of molecular quantum-information hardware into the scalable, robust, solid-state architectures needed for performing quantum computation. Read more »![]()
![]()
Molecular Anvils Trigger Chemical Reactions
“Molecular anvils” (diamondoids) were used to trigger chemical reactions using pressure, yielding products that differ from those produced in conventionally driven reactions with the same reactants. The discovery opens up new possibilities for the high-specificity synthesis of valuable but challenging molecules in an environmentally friendly process. Read more »![]()
![]()