Scientists have designed a biocompatible polymer that has the potential to advance photothermal therapy, a technique that deploys near-infrared light to combat antibacterial-resistant infections and cancer. The team synthesized the polymer by stringing together small molecules called ionic azaquinodimethanes, which they characterized at the ALS. Read more »
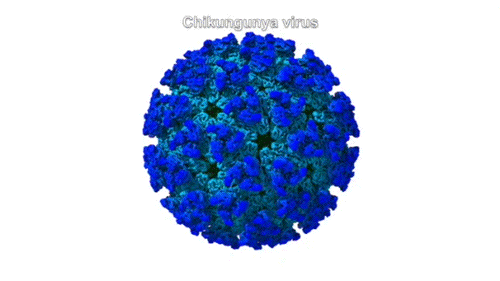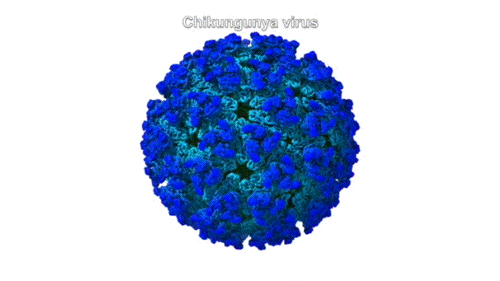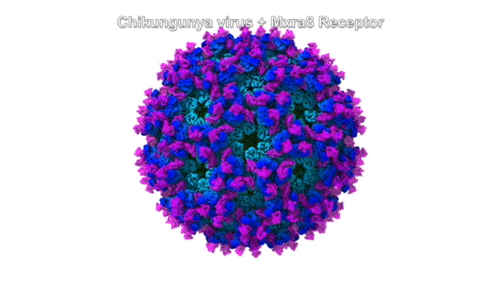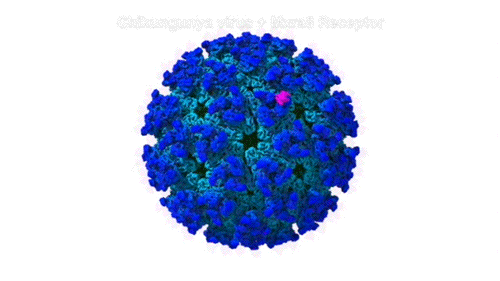
Molecular Handle Enables Viral Attack on Joint Cells
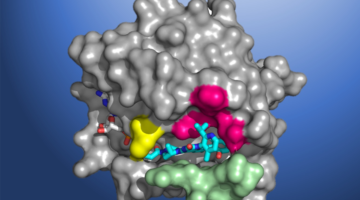
A collaboration of university and industry researchers used x-ray crystallography to investigate how the chikungunya virus, which can cause debilitating joint pain, engages a receptor protein found on the surfaces of joint cells. The work provides a path forward in the fight against a family of viruses that can result in acute and chronic arthritis. Read more »![]()
![]()
Unique Cancer Drug Discovered With Help From Advanced Light Source Begins Historic Clinical Trial
Errors in the KRAS gene, which encodes a crucial cell-signaling protein, are one of the most common causes of cancer. Seeking to develop a long-sought direct inhibitor, researchers at Amgen conducted x-ray crystallography of KRAS(G12C) proteins at the ALS. The high-resolution structural maps helped Amgen make the breakthrough discovery of a small pocket on the molecule. Read more »
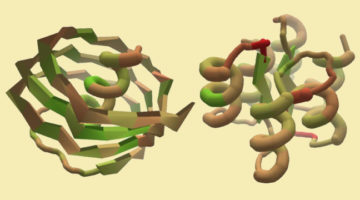
Structural Basis for Finding OG Lesions and Avoiding Undamaged G by the DNA Glycosylase MutY
Finding OG and avoiding G: DNA repair enzyme MutY distinguishes between undamaged guanine (green) and oxidized guanine when targeting OG:A mispairs. A structural motif within the C-terminal domain (violet) responds to OG to G substitution and appears mechanistically coupled to the adenine removal site (gray) in the N-terminal domain (cyan). Read more »
Discovery of a Covalent Inhibitor of KRASG12C (AMG 510) for the Treatment of Solid Tumors
KRASG12C has emerged as a promising target in the treatment of solid tumors; however, clinically viable inhibitors have yet to be identified. Here, researchers report on structure-based design and optimization efforts, culminating in the identification of AMG 510, a highly potent, selective, and well-tolerated KRASG12C inhibitor currently in phase I clinical trials (NCT03600883). Read more »
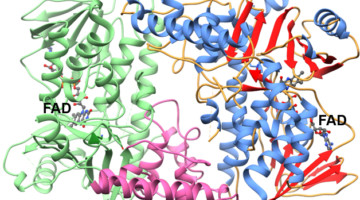
Genetic Blueprint for the Bioproduction of an Antidepressant Drug Candidate
A set of genes from a marine bacterium has been found to encode the biosynthesis of a promising antidepressant drug candidate. This work, which used the ALS to solve the structure of a key enzyme, could enable industrial-scale bioproduction of the drug in ways that are more efficient and sustainable than chemical synthesis. Read more »
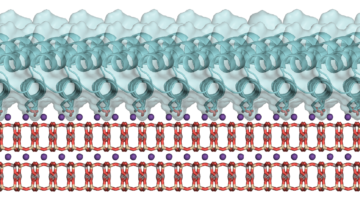
Crystal Misorientation Toughens Human Tooth Enamel
Researchers discovered that, in the nanoscale structure of human enamel (the hard outer layer of teeth), slight crystal misorientations serve as a natural toughening mechanism. The results help explain how human enamel can last a lifetime and provides insight into strategies for designing similarly tough bio-inspired synthetic materials. Read more »![]()
![]()
Scientists Explore Egyptian Mummy Bones With X-Rays and Infrared Light to Gain New Insight on Ancient Life
Researchers from Cairo University worked with teams at the ALS to study soil and bone samples dating back 4,000 years. The experiments are casting a new light on Egyptian soil and ancient mummified bone samples that could provide a richer understanding of daily life and environmental conditions thousands of years ago. Read more »
Custom-Designed Models Reveal How Proteins Assemble on Minerals
Seashells, bone, and other hard tissues form through a little-understood process combining proteins and minerals. Researchers gained insight using a model system of proteins they designed and synthesized from scratch, characterizing how these building blocks assemble on mica. Read more »
A Citizen-Science Computer Game for Protein Design
Using the computer game, “Foldit,” nonexpert citizen scientists designed new proteins whose structures, verified at the ALS, were equivalent in quality to and more structurally diverse than computer-generated designs. The work shows the potential of using crowd-based creativity in the design of new proteins for fighting illness and disease. Read more »![]()
![]()
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- …
- 24
- Next Page »