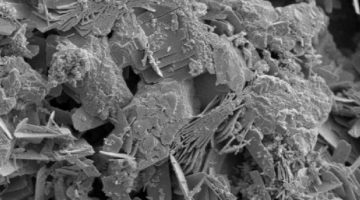
Researchers used x-ray microdiffraction to trace the complex sequences of crystal growth in concrete from ancient Roman pier and breakwater sites. The results indicate that minerals continue to form over millennia as seawater percolates through, reinforcing the cementing matrix in a kind of regenerative process. Read more »
New Studies of Ancient Concrete Could Teach Us to Do as the Romans Did
A new look inside 2,000-year-old concrete—made from volcanic ash, lime (the product of baked limestone), and seawater—has provided new clues to the evolving chemistry and mineral cements that allow ancient harbor structures to withstand the test of time. Read more »
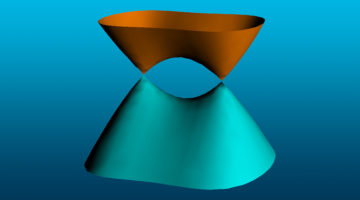
Strain Turns Tin into a 3D Topological Dirac Semimetal
A small amount of compressive strain turns a nonmetallic form of tin into a 3D topological Dirac semimetal—a kind of “supermetal” with very high electron mobility. With its rich topological phase diagram, the material shows promise for both novel physics and eventual device applications. Read more »![]()
![]()
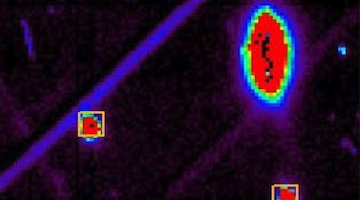
New Insights into Nanoscale Deformation
A group of scientists used Laue x-ray microdiffraction at the ALS to probe plastic deformation mechanisms at the nanoscale. Their findings may overturn conventional theory and reshape our understanding of the mechanical behavior of a host of nanocrystalline metals. Read more »
Ancient Ocean Temperatures Recorded in Mother-of-Pearl
Researchers have shown that the thickness of the nacre, or mother-of-pearl, that lines the insides of mollusk shells can be used to estimate ocean temperatures as far back as the early Jurassic period. X-ray studies of modern and ancient shells help establish the method’s feasibility. Read more »
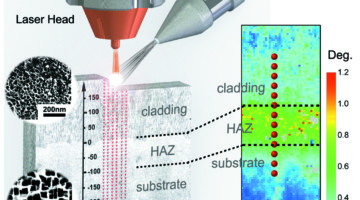
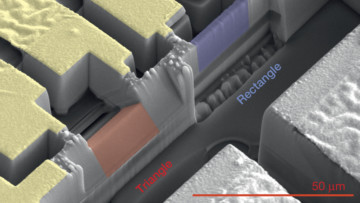
X-Rays Help Evaluate Quality of 3D-Printed Repairs
Laser 3D printing is a promising way to repair machine parts (such as jet-engine turbine blades) made of single-crystal superalloys. But microstructural inhomogeneities created by the high-power laser are a major reliability concern, so researchers employed x-ray Laue microdiffraction to probe the microstructure. Read more »
Scientists Find Twisting 3-D Raceway for Electrons in Nanoscale Crystal Slices
Researchers have observed, for the first time, an exotic 3-D racetrack for electrons in ultrathin slices of a tiny crystal they made at Berkeley Lab. Read more »
Improving Alloy Memory by Tuning Material Composition
Shape memory alloys can “remember” their original form and return to it repeatedly when heated. To gain structural insight into a new alloy capable of sustaining millions of cycles without failure, researchers performed x-ray Laue microdiffraction at ALS Beamline 12.3.2. Read more »
Quantitative Microstructural Imaging by Scanning Laue X-ray Micro- and Nanodiffraction
Synchrotron Laue x-ray microdiffraction turns 20 this year. The June 2016 issue of MRS Bulletin is dedicated to synchrotron radiation research in materials science and features a review article on the current capabilities, latest technical developments, and emerging applications of Laue x-ray micro- and nanodiffraction co-authored by ALS beamline scientist Nobumichi Tamura. The cover image shows a Laue x-ray microdiffraction pattern from a sea urchin tooth taken on Beamline 12.3.2. Read more »
Conduction Along Magnetic Interfaces could Improve Memory Devices
Scientists have provided the first direct evidence of a controversial phenomenon: the boundaries between magnetic regions in an electrical insulator can become electrically conductive. This discovery can potentially lead to improvements in future memory storage devices. Read more »