When the lattice-matched 2D perovskite BA2FAPb2I7 (red) is incorporated into a yellow-phase FAPbI3 matrix (yellow), the 2D crystallites present a perovskite-like surface, which serves as a template for the FAPbI3 to convert to its photoactive phase (black). The resulting phase-stabilized FAPbI3 shows substantially improved optoelectronic properties and exceptional stability under 85°C and sunlight. Read more »
How Bulky Molecules Improve Next-Generation Solar Cells
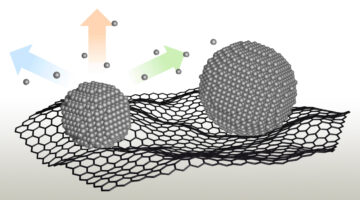
Adding “bulky” organic molecules earlier in solar-film synthesis slows crystal growth, leading to the formation of a protective surface layer that improves durability and efficiency. These next-gen materials could revolutionize solar-cell technology, offering increased efficiency, lower cost, lighter weight, and flexible solar modules. Read more »![]()
![]()
Surtsey Volcano: A Rare Window into Earth’s Oceanic Crust
Surtsey, a very young oceanic island in Iceland, emerged through explosive volcanic activity in 1963. Utilizing various techniques, including x-ray microdiffraction at the ALS, researchers gained unique insights into the transformation of volcanic glass to form mineral cements in the basaltic rock of underwater volcanoes. Read more »
New Insights Lead to Better Next-Gen Solar Cells
Perovskites show great promise to reduce the costs of solar power but are not yet durable enough to be commercially viable. Researchers used simultaneous characterization techniques to understand why a simplified fabrication process works so well, providing key insights to nudge perovskites closer to commercialization. Read more »
Tracking Platinum Movement on Fuel-Cell Electrodes
Researchers tracked the movement of the platinum nanoparticles that catalyze reactions in polymer electrolyte fuel cells (PEFCs) and correlated this movement with nanoparticle degradation. The results yielded solutions that can immediately reduce platinum waste in emission-free heavy-duty fuel-cell vehicles. Read more »![]()
![]()
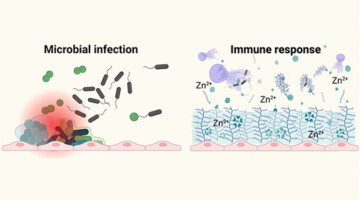
Immune Response Spurs Growth of “Soft” Kidney Stones
Matrix stones are an unusual type of soft kidney stone closely associated with the presence of bacteria from unchecked urinary tract infections. Researchers conducted a comprehensive study of surgically extracted matrix stones, work that highlights how host defense mechanisms against microbes can simultaneously encourage harmful stone formation. Read more »
Organic Matrix Derived from Host–Microbe Interplay Contributes to Pathological Renal Biomineralization
A composite image of a rare form of kidney stone, illustrating extensive organic filamentous networks abundant with immune response-related proteins such as calprotectin (displayed in red), myeloperoxidase (in yellow), and DNA molecules (in blue). Originating from intricate host-microbe interplay, these organic networks promote the heterogeneous nucleation and precipitation of inorganic particulates. Read more »
ALS Work on Roman Concrete Highlighted in German-French Documentary
A study on the remarkable durability of 2000-year old Roman concrete, by ALS user Marie Jackson with ALS beamline scientist Nobumichi Tamura, was recently highlighted in “Miracle Materials,” a science documentary produced by a German-French company, Gruppe 5, for airing on the Eurpean public service channel, ARTE. Read more »
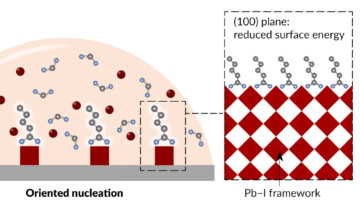
Coaxing Molecules to Stand Tall for Better Solar Cells
Multimodal probes revealed a way to prevent the formation of undesirable phases in a perovskite-type compound that shows promise for the efficient harvesting of light for solar cells. The work led to new fabrication protocols that resulted in devices with improved power-conversion efficiencies and operational stability. Read more »![]()
![]()
In Situ and Operando Characterizations of Metal Halide Perovskite and Solar Cells: Insights from Lab-Sized Devices to Upscaling Processes
The performance and stability of metal halide perovskite solar cells strongly depend on precursor materials and deposition methods adopted during the perovskite layer preparation. This review presents an update of studies conducted in situ using a wide range of structural, imaging, and spectroscopic techniques, involving the formation/degradation of halide perovskites. Read more »
- 1
- 2
- 3
- …
- 5
- Next Page »