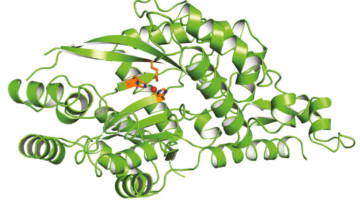
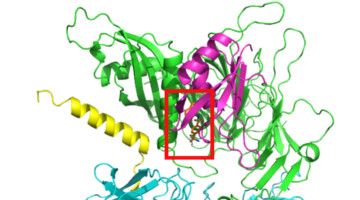
Saldivia et al. identify CLK1 as the target for the amidobenzimidazoles series of compounds. Inhibition of this protein kinase impairs inner kinetochore recruitment, causing cell-cycle arrest and cell death in trypanosomal pathogens such as Trypanosoma brucei. Read more »
Missing Lysine Link Could Improve Plant-Based Nutrition
To engineer crops with higher levels of the important amino acid, lysine, researchers solved the structure of an enzyme that helps break down lysine in plants. A fuller understanding of the factors affecting lysine levels should aid in the successful development of stable high-lysine crops to combat malnutrition globally. Read more »
Structural Features Mediating Zinc Binding and Transfer in the AztABCD Zinc Transporter System
Zinc homeostasis is critical for bacterial survival and virulence. Extracellular zinc-binding proteins play an important role in this process. This work assesses the role of several flexible or unstructured sequences in zinc binding and transfer from proteins AztD to AztC. The results provide insights into the dynamic nature of these processes and support a previously proposed structural model of transfer. Read more »
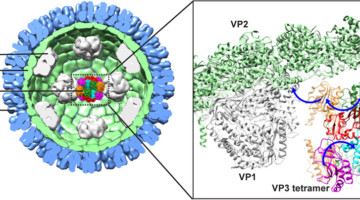
Rotavirus VP3 Is a Multifunctional Capping Machine
Rotavirus, a major cause of infantile gastroenteritis, is responsible for the deaths of about 200,000 children per year. Although vaccines are available, the virus still circulates, and a fuller understanding of the viral structures is needed. Here, scientists investigate the structure and function of the last unsolved rotavirus structural protein. Read more »
Evaluation of Free Energy Calculations for the Prioritization of Macrocycle Synthesis
Free energy perturbation methods represent a paradigm shift in drug discovery, where computational methods inform benchtop activities. Macrocycles are highly constrained molecules, often resulting in nonintuitive structure–activity relationships requiring lengthy synthetic routes. Free energy perturbation methods can be used to predict potency, guiding synthetic chemistry efforts to de-risk complex synthesis. Read more »
Antibody from SARS Survivor Neutralizes SARS-CoV-2
Using structural data from the ALS and cryo-electron microscopy, researchers have characterized how an antibody binds to and neutralizes SARS-CoV-2. This work provides the basis for therapeutic and vaccine development for the SARS-CoV-2 virus, which is responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic. Read more »![]()
![]()
On-Off Switch for Regulating Tumor-Cell Growth
The mechanisms that affect the regulation of cell growth in certain tumor cells were revealed by a Genentech study of enzyme structures, conducted in part at the ALS. The work establishes a framework for the rational discovery of new therapeutics to improve upon currently existing treatments for certain cancers. Read more »![]()
![]()
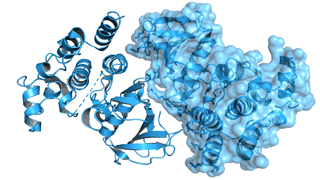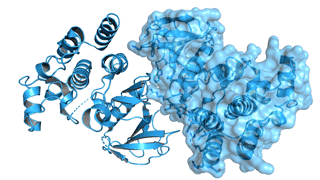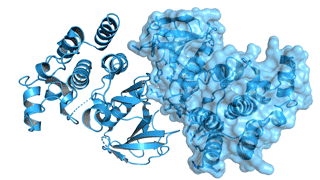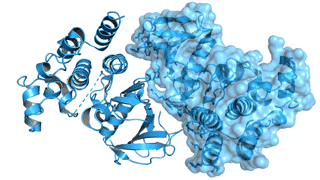
How a Cancer Drug Targets Proteins for Degradation
Protein structures obtained by Novartis researchers helped reveal how a cancer drug promotes the degradation of proteins essential to cell proliferation. A detailed understanding of the drug’s mechanism of action is key to determining whether the protein-degradation system can be reprogrammed to degrade different targets. Read more »![]()
X-Ray Experiments Zero in on COVID-19 Antibodies
In the fight against SARS-CoV-2, scientists have been working on identifying neutralizing antibodies that could be used in preventative treatments or as post-exposure therapies. The latest findings, which include data from the ALS, indicate that antibodies from SARS survivors could potently block entry of SARS-CoV-2 into host cells. Read more »![]()
Study Leads to Firmer Grasp of Biochemical “Reactive Handle”
Protein crystallography provided new insight into a functional group of molecules that, if added to bacterial enzymes, could enable a variety of alterations to the bacteria’s polymer output. Tweaking enzymes to produce these “reactive handles” is a first step toward biosynthesizing diverse polymers with tailored properties. Read more »