In this work, researchers demonstrated a macromolecular scaffold that combines an 8-coordinate synthetic ligand and a mammalian protein to characterize the solution and solid-state behavior of the longest-lived actinium isotope. The information could help design better cancer treatments. Read more »
Protein Assemblies Show Surprising Variability
Protein-structure studies performed in part at the ALS helped researchers discover that the protein assemblies in a key carbon-cycling enzyme can rearrange with surprising ease. The findings raise the prospect of genetically tuning the protein in agricultural plant species to produce more productive and resource-efficient crops. Read more »![]()
![]()
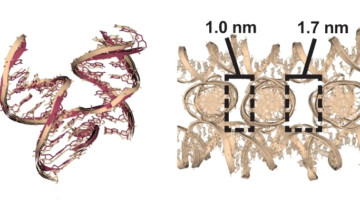
An Expanded Set of DNA Building Blocks for 3D Lattices
Researchers studied 36 DNA-based molecular junctions and discovered factors that yield superior self-assembled 3D lattice structures. The work expands the set of building blocks for lattices that can scaffold molecules into regular arrays, from proteins for structure studies to nanoparticles for nano-antennas and single-particle sensors. Read more »![]()
![]()
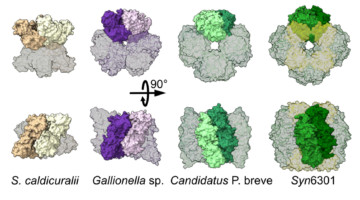
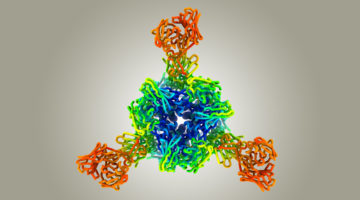
Protein Structures Aren’t Set in Stone
A group of researchers studying the world’s most abundant protein, an enzyme involved in photosynthesis called rubisco, showed how evolution can lead to a surprising diversity of molecular assemblies that all accomplish the same task. The findings reveal the possibility that many of the proteins we thought we knew actually exist in other, unknown shapes. Read more »
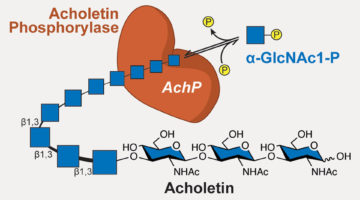
Bacterial Enzyme Produces Biodegradable Polymer
Researchers discovered a bacterial enzyme that synthesizes a biopolymer whose repeating units are linked together in way that had not been previously observed. The new polymer is biodegradable and may be biocompatible, with potential for applications ranging from medical therapeutics to eco-friendly plastic alternatives. Read more »![]()
![]()
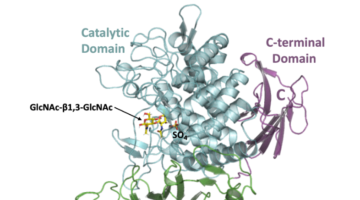
Newly Discovered Bacterial Enzyme Produces Useful Biopolymer
Researchers identified a bacterial enzyme that produces a novel biopolymer. The polymer, dubbed acholetin, is a chain of sugar molecules known as a polysaccharide. Acholetin is similar in structure to chitin, the major component of insect exoskeletons, and holds promise as a useful biomaterial because of its biodegradability and biocompatibility. Read more »
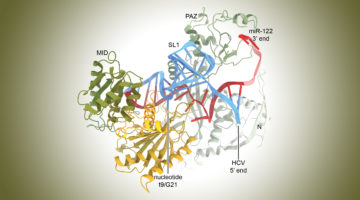
Molecular Hijacking of a MicroRNA by the Hepatitis C Virus
The hepatitis C virus (HCV), which attacks the liver, is known to repurpose host-cell components known as microRNAs—short RNA strands that act to silence gene expression. Now, the molecular structure of an HCV site bound to a microRNA complex revealed how their interactions shield the virus from the host cell’s protective response. Read more »
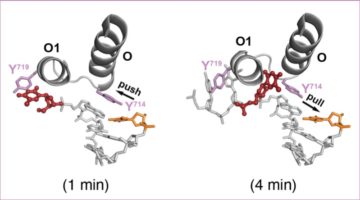
DNA Synthesis: Flip It and Reverse It
What if the current model for DNA synthesis were flipped on its head? Using time-resolved x-ray crystallography, researchers gained new insights into this essential biological process, revealing that two steps in the synthesis pathway are, in reality, reversed. Read more »
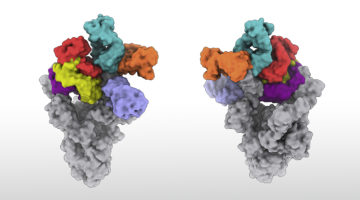
Researchers Set Sights on Another COVID-19 Target
Early in the COVID-19 pandemic, it was quickly established that the receptor binding domain (RBD) of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein is a prime target for neutralizing antibodies. Now, scientists have found a second region of the spike protein that is targeted by dozens of antibodies, some of which exhibit ultrapotent neutralizing activity. Read more »
Guiding Target Selection for COVID-19 Antibody Therapeutics
Protein-structure studies helped demonstrate that the primary target of antibody-based COVID-19 immunity is the part of the virus’s spike protein that can most easily mutate. The work anticipated the rise of SARS-CoV-2 variants and guides the selection of antibody therapeutics that are likely to be more resistant to immune escape. Read more »![]()
![]()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- …
- 6
- Next Page »