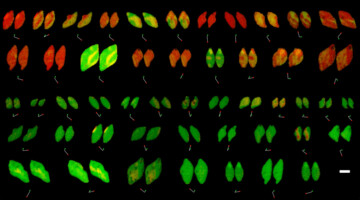
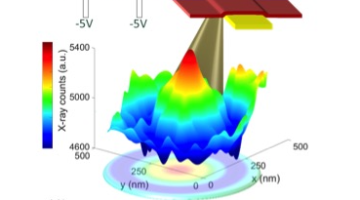
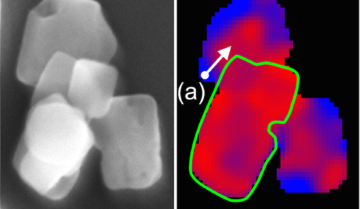
Using a type of machine learning called “computer vision” to mine data from x-ray movies, researchers made new discoveries about the reactivity of a material in rechargeable batteries. The results suggest that optimizing the carbon layer thickness on the electrode surface could help researchers to design more efficient batteries. Read more »
Will Chueh to Receive the 2023 Shirley Award
Will Chueh of Stanford University is the 2023 winner of the Shirley award for Outstanding Scientific Achievement at the ALS. His selection recognizes Chueh’s deep contributions in operando soft x-ray spectromicroscopy for imaging electrochemical redox phenomena—images and movies for battery and electrocatalytic reactions. Read more »
Reversible Room-Temperature Fluoride-Ion Insertion in a Tunnel-Structured Transition Metal Oxide Host
Fluoride ions show promise as charge carriers in batteries but have limited cyclability. Here we show the reversible and homogeneous topochemical insertion/deinsertion and bulk diffusion of F ions within the one-dimensional tunnels of submicrometer-sized FeSb2O4 particles at room temperature. Read more »
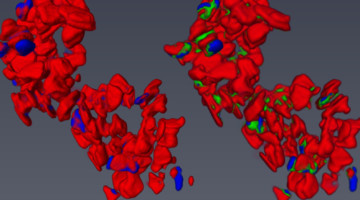
3D Localization of Nanoscale Battery Reactions
A new tool lets researchers pinpoint the locations of chemical reactions happening inside batteries in three dimensions at the nanoscale level. Combining ptychography, tomography, and spectroscopy, Nanosurveyor 1 is a multidimensional tool providing novel insight into the design of next-generation batteries and devices. Read more »
From Moon Rocks to Space Dust: Berkeley Lab’s Extraterrestrial Research
Berkeley Lab has a well-storied expertise in exploring samples of extraterrestrial origin. This research—which has helped us to understand the makeup and origins of objects within and beyond our solar system—stems from long-standing core capabilities in structural and chemical analyses and measurement at the microscale and nanoscale. Read more »
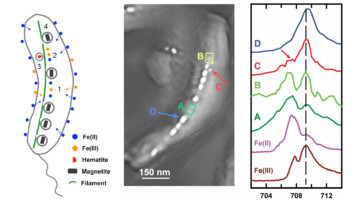
Ptychography of a Bacterium’s Inner Compass
Magnetotactic bacteria (MTB) synthesize chains of magnetic nanocrystals (magnetosomes) that interact with the Earth’s magnetic field like an inner compass needle, simplifying their search for optimum environments. Ptychographic spectra of magnetosomes from a marine MTB provides insight into how these inner compasses form. Read more »
Industrial-Academic Collaboration Gives Nanoscale Insight into Batteries
An industrial collaboration between Hummingbird Scientific and a team of researchers from the ALS, SLAC, Berkeley Lab, Stanford University, and other institutions has resulted in a new x-ray microscopy platform that gives scientists the ability to image nanoscale changes inside lithium-ion battery particles in real time as they charge and discharge. Insights obtained from the imaging platform have already provided surprising new insights and could help researchers improve batteries for electric vehicles as well as smart phones, laptops, and other devices. Read more »![]()
Hewlett Packard Labs Gains Insights with Innovative ALS Research Tools
For the past eight years, Hewlett Packard Labs, the central research organization of Hewlett Packard Enterprise, has been using cutting-edge ALS techniques to advance some of their most promising technological research, including vanadium dioxide phase transitions and atomic movement during memristor operation. Read more »![]()
X-Ray Microscopy Reveals How Crystal Mechanics Drive Battery Performance
Recent findings at the ALS show that small crystal size is key to maintaining a battery’s performance and establish soft x-ray ptychography as an essential tool for studying chemical states in nanoparticles.
Read more »![]()
![]()
Record-Setting Microscopy Illuminates Energy Storage Materials
Using soft x-ray ptychography, researchers at the ALS have demonstrated the highest-resolution x-ray microscopy ever achieved by imaging five-nanometer structures. The researchers used ptychographic imaging to map the chemical composition of lithium iron phosphate nanocrystals, yielding important new insights into a material of high interest for electrochemical energy storage. Read more »![]()
![]()