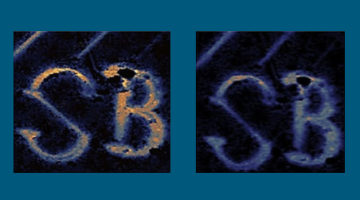
Researchers from Cairo University worked with teams at the ALS to study soil and bone samples dating back 4,000 years. The experiments are casting a new light on Egyptian soil and ancient mummified bone samples that could provide a richer understanding of daily life and environmental conditions thousands of years ago. Read more »
Infrared Nanospectroscopy at Graphene–Liquid Interfaces
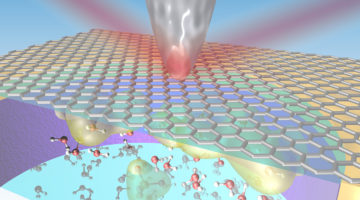
Researchers developed a new infrared approach to probing the first few molecular layers of a liquid in contact with a graphene electrode under operating conditions. The work offers a new way to study the interfaces that are key to understanding batteries, corrosion, and other bio- and electrochemical phenomena. Read more »![]()
![]()
Infrared Nano-Mapping of Local Strain in 2D Materials
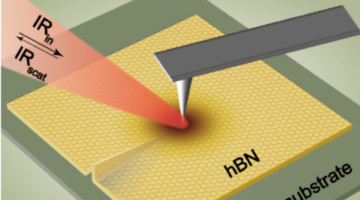
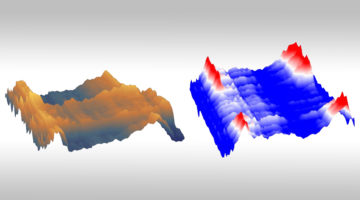
Researchers have demonstrated an infrared technique to map and analyze strain in atomically thin crystals of hexagonal boron nitride (hBN) at the nanoscale. This ultrasensitive strain-imaging method could be a promising tool for the examination of low-dimensional materials of interest for electronic and photonic devices. Read more »
Infrared Light Reveals Microstripes at Insulator-Metal Transition
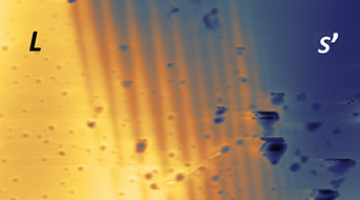
In this study of a current-driven insulator-to-metal transition, a distinctive stripe pattern develops between the insulating and metallic phases. The work reveals remarkable new features of electrically induced insulator-to-metal transitions in materials with potential applications in energy-efficient memory and transistor devices. Read more »![]()
Expanding the Infrared Nanospectroscopy Window
An innovative infrared-light probe with nanoscale spatial resolution has been expanded to cover previously inaccessible far-infrared wavelengths. The ability to investigate heterogeneous materials at nanometer scales and far-infrared energies will benefit a wide range of fields, from condensed matter physics to biology. Read more »![]()
![]()
Near-field infrared nanospectroscopy and super-resolution fluorescence microscopy enable complementary nanoscale analyses of lymphocyte nuclei
Recent super-resolution fluorescence microscopy studies have revealed significantly altered nuclear organization between normal lymphocyte nuclei and those of classical Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Reported here are the first near-field IR imaging of lymphocyte nuclei, and far-field IR imaging results of whole lymphocytes and nuclei from normal human blood. Read more »
Scientists Use Machine Learning to Span Scales in Shale
Machine-learning techniques have been used to integrate fine- and large-scale infrared characterizations of shale—sedimentary rocks composed of minerals and organic matter. Understanding shale chemistry at both the nano and mesoscale is relevant to energy production, climate-change mitigation, and sustainable water and land use. Read more »
Phase Diagram Leads the Way to Tailored Metamaterial Responses
Researchers discovered an innovative way to independently control two optical responses in a single-material system by utilizing the material’s phase diagram. This unique combination of material, methods, and results could lead to a paradigm shift in the design of metamaterial devices that manipulate light. Read more »![]()
![]()
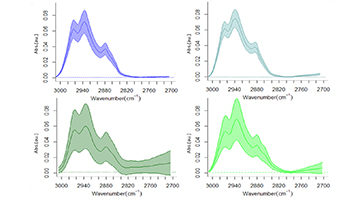
Microbes Linked to Drier Human Skin
Genetic analyses and infrared studies have found that archaea, a type of microbe commonly found in extreme environments, are also found on human skin. The results suggest that an increase in archaea is linked to reduced skin moisture and that they are most abundant in subjects younger than 12 and older than 60. Read more »
What’s On Your Skin? Archaea, That’s What
It turns out your skin is crawling with single-celled microorganisms—and they’re not just bacteria. A study by Berkeley Lab and the Medical University of Graz has found that the skin microbiome also contains archaea, a type of extreme-loving microbe, and that the amount of it varies with age. Read more »