The 2024 Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded to David Baker, Demis Hassabis, and John M. Jumper for the development of protein structure prediction and design. At the ALS, Baker leveraged high-throughput small-angle x-ray scattering (SAXS) and protein crystallography capabilities to design novel proteins and pave a new pathway for science, technology, and the environment. Read more »
Computer-Aided Protein Design for New Biomaterials
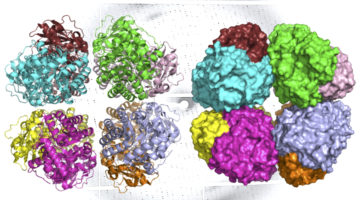
Using a computer-based approach, researchers designed porous protein crystals that were revealed to be stable, tunable, and atomically accurate using x-ray scattering and diffraction at the ALS. The work provides a powerful new platform for biological materials engineering and opens up wide applications in biotechnology and medicine. Read more »![]()
![]()
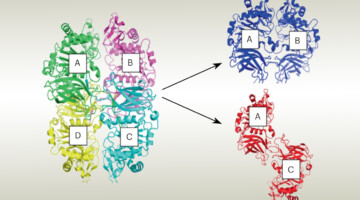
Precisely patterned nanofibres made from extendable protein multiplexes
Superhelical symmetry can be found in helical repeat proteins, and de novo helical repeat proteins are rigid and amenable to stacking in a head-to-tail fashion, which is an important factor in building up coincident symmetries. Now, using cyclic helical repeat proteins, Baker and colleagues generate protein nanostructures—as depicted on the cover—with coincident cyclic and superhelical symmetry axes. Read more »
Plant Enzyme Builds Polymers That Fortify Cell Walls
With data obtained at the ALS, researchers gained insight into how an enzyme orchestrates the synthesis of a pectin polymer that imparts strength and flexibility to plant cell walls. The work could lead to improved biofuel production and guide the design of polymers with tailored functionalities for industrial or biomedical applications. Read more »![]()
![]()
Molecular Switch Triggers Changes in Plant Structure
Using x-ray crystallography, biochemistry, and plant genetics, researchers identified a molecular switch that triggers modifications to plant structure in response to environmental conditions. A greater understanding of this adaptive process will help scientists optimize plants for efficient nutrient uptake and resistance to parasitic species. Read more »![]()
![]()
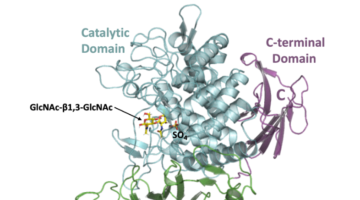
Bacterial Enzyme Produces Biodegradable Polymer
Researchers discovered a bacterial enzyme that synthesizes a biopolymer whose repeating units are linked together in way that had not been previously observed. The new polymer is biodegradable and may be biocompatible, with potential for applications ranging from medical therapeutics to eco-friendly plastic alternatives. Read more »![]()
![]()
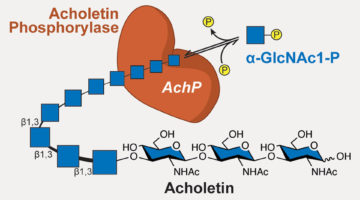
Newly Discovered Bacterial Enzyme Produces Useful Biopolymer
Researchers identified a bacterial enzyme that produces a novel biopolymer. The polymer, dubbed acholetin, is a chain of sugar molecules known as a polysaccharide. Acholetin is similar in structure to chitin, the major component of insect exoskeletons, and holds promise as a useful biomaterial because of its biodegradability and biocompatibility. Read more »
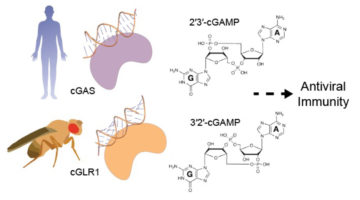
Sounding the Antiviral Alarm: A New Family of Immune-System Sensors
Comparison of enzyme structures from humans and insects revealed a new family of evolutionarily related immune-system sensors, triggered by viral RNA or DNA to produce tailored signals that initiate antiviral action. The results shed new light on the diversity and development of immune defenses in animals. Read more »
Functional and structural characterization of AntR, an Sb(III) responsive transcriptional repressor
Antimony is considered a priority environmental pollutant by the EPA. The ant operon of the antimony-mining bacterium, C. testosterone, confers resistance to Sb(III). The operon is regulated by the product of the first gene in the operon, antR. This is the first report of the structure and binding properties of antR, with high selectivity for environmental antimony. Read more »
Newly Discovered Photosynthesis Enzyme Yields Evolutionary Clues
Scientists have discovered a primitive form of rubisco, a photosynthesis enzyme that has helped shape life on Earth. Detailed information about its structure, determined using complementary techniques at the ALS, will help scientists understand how carbon-fixing organisms oxygenated the atmosphere and how modern plants evolved. Read more »
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- Next Page »