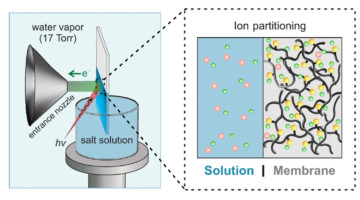
Researchers performed the first direct measurement of the Donnan electrical potential, which arises from an imbalance of charges at membrane-solution interfaces. Considered unmeasurable for over a century, the Donnan potential is relevant to a wide range of fields, from cell biology to energy storage and water desalination. Read more »![]()
![]()
Gas-phase synthesis of racemic helicenes and their potential role in the enantiomeric enrichment of sugars and amino acids in meteorites
Molecular-beam experiments with isomer-selective photoionization via a targeted, vinylacetylene-mediated gas-phase reaction of aromatic helicenyl radicals coupled with electronic structure calculations and astrochemical modeling reveal an elegant synthetic route to racemic helicenes – ortho-fused polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), in which benzene building blocks form helically-shaped molecules. Read more »
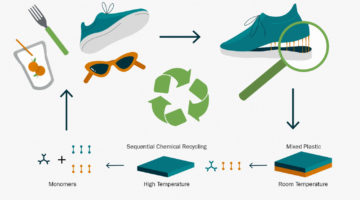
A New Material System for Mixed-Plastic Recycling
Scientists have designed a new material system to overcome one of the biggest challenges in recycling consumer products: mixed-plastic recycling. Their achievement will help enable a much broader range of fully recyclable plastic products and brings into reach an efficient circular economy for durable goods like automobiles. Read more »
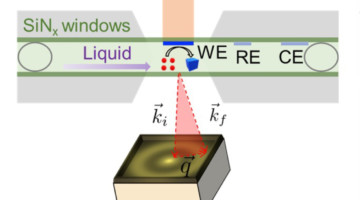
Operando Study of CO2 Reduction by Copper Nanoparticles
Since copper is necessary to catalyze the reduction of CO2, a greenhouse gas, to valuable products, scientists are working hard to improve its selectivity and activity. Now, researchers have developed an operando capability that can help in this effort by simultaneously probing chemical valence and interparticle dynamics. Read more »
Designer Materials to Keep Plastic Out of Landfills
Scientists have designed a new material system to overcome one of the biggest challenges in recycling consumer products: mixed-plastic recycling. Their achievement will help enable a much broader range of fully recyclable plastic products and brings into reach an efficient circular economy for durable goods like automobiles. Read more »
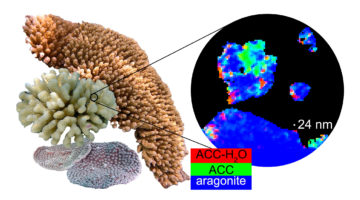
Key to Coral Resilience Is Faster Skeletal Crystallization
In a new study, researchers show that the crystallization rate of coral skeletons differs across species and is correlated with their resilience to ocean acidification. The results have implications for predicting coral reef survival and developing mitigation strategies against having their bony skeletons weakened by ocean acidification. Read more »
Biomineralization: Integrating mechanism and evolutionary history
In this review, Gilbert et al. develop a model for calcium carbonate biomineralization applicable to all phyla. Their model may help elucidate the key genetic components that drive biomineralization and offers insight into the consequences of global climate change on marine organisms. Read more »
Loss of biological control of enamel mineralization in amelogenin-phosphorylation-deficient mice
Amelogenin phosphorylation plays crucial roles in controlling structural, crystallographic, mechanical, and compositional characteristics of dental enamel. Thus, loss of amelogenin phosphorylation leads to a reduction in the biological control over the enamel mineralization process. Read more »
New Device Advances Commercial Viability of Solar Fuels
A Berkeley Lab research team developed a new artificial photosynthesis device component that exhibits remarkable stability and longevity as it selectively converts sunlight and carbon dioxide into two promising sources of renewable fuels—ethylene and hydrogen. Read more »
A Split-Screen View of Solar-Cell Crystallization
Researchers simultaneously monitored both the structure and function of a photovoltaic material as it crystallized from solution. The work raises the prospect of rationally tuning materials for optimal performance in photovoltaics and other light-manipulating devices, including light-emitting diodes, detectors, and lasers. Read more »![]()
![]()
- « Previous Page
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- …
- 7
- Next Page »