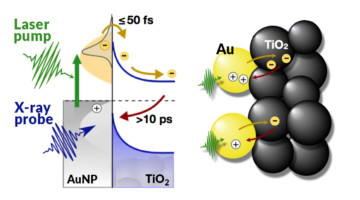
Using time-resolved experiments at the ALS, researchers found a way to count electrons moving back and forth across a model interface for photoelectrochemical cells. The findings provide real-time, nanoscale insight into the efficiency of nanomaterial catalysts that help turn sunlight and water into fuel through artificial photosynthesis. Read more »![]()
![]()
The Bottleneck Step of a Complex Catalytic Reaction
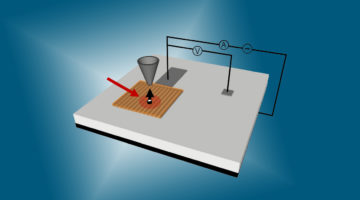
The rate-limiting step in catalysis involving oxygen uptake was identified through analysis of the reaction pathways and observations performed under operating conditions. The work lays the foundation for improving the efficiency of energy conversion and storage devices such as fuel cells, catalytic reactors, and batteries. Read more »![]()
![]()
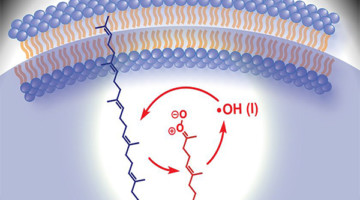
Criegee Intermediates Play Unexpected Role in Cell Chemistry
Researchers employed mass spectrometry to illuminate lipid nanodroplets under ultraviolet light. The results unexpectedly showed that hydroxyl radicals cause damage to cells via the formation of Criegee intermediates: molecules first proposed in 1975 to explain how pollutants react with the ozone layer in our atmosphere. Read more »
Scientists Discover New Clue Behind Age-Related Diseases and Food Spoilage
Scientists at Berkeley Lab have made a surprising discovery that could help explain our risk for developing chronic diseases or cancers as we get older, and how our food decomposes over time. The findings point to an unexpected link between the ozone chemistry in our atmosphere and our cells’ hardwired ability to ward off disease. Read more »
Probing the Evolution of Photovoltaic Films during the Spin-Coating Process
A new, in-beamline spin-coating platform enabled researchers to probe the structure of a promising photovoltaic material in the crucial early stages of processing. The results demonstrate the power of multimodal in situ techniques as promising tools for optimizing synthesis parameters and, thus, device performance. Read more »
Here Comes the Sun: A New Framework for Artificial Photosynthesis
Scientists have long sought to mimic the process by which plants make their own fuel using sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water through artificial photosynthesis devices, but exactly how catalysts work to generate renewable fuel remains a mystery. Now, a study has uncovered new insight into how to better control cobalt oxide, one of the most promising catalysts for artificial photosynthesis. Read more »
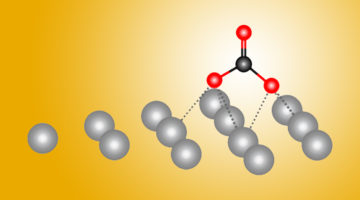
A New Path to Carbon Dioxide Transformation
Combining ALS experiments with quantum-mechanical calculations, scientists found dramatic differences in how carbon dioxide (CO2) reactions begin on silver as opposed to copper. Both metals help transform CO2—a greenhouse gas—into more useful forms, and this new atomic-level data could help make the process more efficient. Read more »![]()
![]()
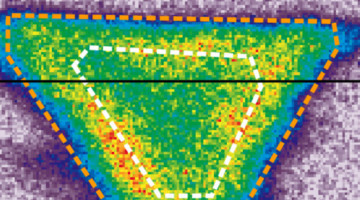
A Nanoscale View of Defect Effects on Band Structure
In the first comprehensive study at the ALS involving nanoARPES, researchers probed the electronic effects of defects in monolayer tungsten disulfide at the nanoscale. The extremely small scale of the measurements makes nanoARPES a great discovery tool that will be particularly useful for understanding new materials as they are invented. Read more »
Gas‐Phase Synthesis of Triphenylene (C18H12)
The cover image shows the triphenylene molecule as a potential precursor to two‐dimensional graphite nanosheets in the interstellar medium. The barrier‐less, exoergic nature of the reaction reveals a versatile reaction mechanism that may drive molecular mass growth processes in cold environments in deep space. Read more »
The Smoking Gun of Soot Formation
Scientists identified a mechanism for the formation of soot involving a series rapid chemical reactions rather than the typical condensation of particles from gas. The results are critical to developing methods for controlling emissions responsible for millions of deaths annually, severe degradation of air quality, and enhanced global warming. Read more »![]()
![]()
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- Next Page »