Printable plastic solar cells are a potential source of inexpensive renewable energy, but the transition from lab to factory results in decreased efficiency. Now, for the first time, a miniature solar-cell printer installed in a beamline allows researchers to use x-ray diffraction and scattering to figure out why. Read more »![]()
![]()
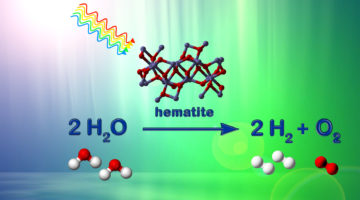
Two Electron Holes in Hematite Facilitate Water Splitting
Hematite is a promising electrode material for solar-powered water splitting—an important reqirement for producing hydrogen fuel with zero emissions. At Beamline 7.0.1, researchers have gained a better understanding of hematite’s electronic structure through soft x-ray spectroscopy performed in situ and “operando.” Read more »![]()
![]()
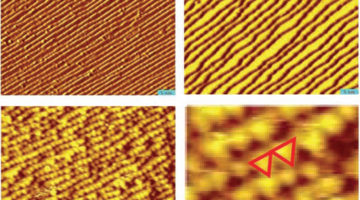
Platinum Nanoclusters Out-Perform Single Crystals
Researchers have found that under high pressure—comparable to the pressures at which many industrial technologies operate—platinum surfaces can change their structure dramatically in response to the presence of high-coverage reactants. Read more »![]()
![]()
Nanoscale Chemical Imaging of a Working Catalyst
Researchers identified the chemical species present for an iron-based Fischer–Tropsch synthesis catalyst and to image their distribution on the nanoscale. When developed further, this new tool may give chemists the ability to design and tailor catalysts for maximum selectivity and efficiency in a wide range of chemical processes. Read more »![]()
![]()
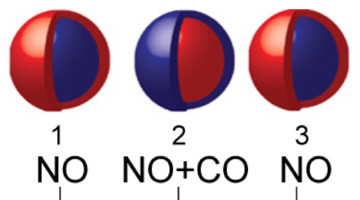
Reaction-Driven Restructuring of Bimetallic Nanoparticle Catalysts
Researchers have used an ambient-pressure x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (APXPS) apparatus to demonstrate that bimetallic nanoparticle catalysts can undergo profound structural and chemical changes in response to reactive environments at ambient pressures, thereby opening the way for engineering catalysts with enhanced activity and selectivity. Read more »![]()
![]()
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 14
- 15
- 16