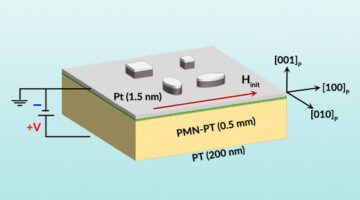
Researchers learned how the size, shape, and orientation of microstructures affect how they switch magnetization directions in response to an applied voltage. The work advances our understanding of strain-responsive composite materials for use in energy-efficient electronic applications such as memory devices, sensors, and actuators. Read more »![]()
![]()
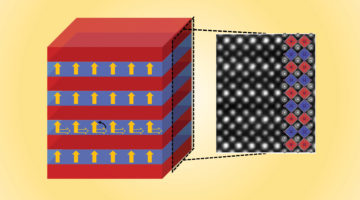
Controlling Magnetization Vector Depth Profiles of La0.7Sr0.3CoO3/La0.7Sr0.3MnO3 Exchange Spring Bilayers via Interface Reconstruction
Polarized neutron reflectometry was combined with soft x-ray magnetic spectroscopy to quantify the changes in the magnetic and chemical depth profiles in La0.7Sr0.3CoO3/La0.7Sr0.3MnO3 bilayers, confirming the formation of interfacial layers with distinct magnetization and chemical density. Read more »
A New Way to Tune Emergent Magnetism
Perpendicular magnetic anisotropy (PMA)—where magnetic moments in a thin film preferentially point out of the plane of the film—is an emergent phenomenon of both fundamental and technological interest. A combination of x-ray techniques demonstrate how to tune PMA in transition-metal oxide multilayers. Read more »![]()
![]()
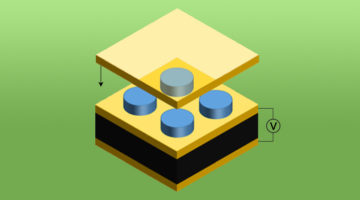
Electrical Switching of Magnetic Vortex Circulation
Photoemission electron microscopy (PEEM) experiments have demonstrated that the circulation direction of a magnetic vortex can be switched by the application of an electric field, opening the door to digital devices with more streamlined system designs, improved performance, and greater energy efficiency. Read more »![]()
![]()
A Multifunctional Material with Electric-Field Control
Three distinct crystalline phases with different electronic, magnetic, and optical properties were reversibly induced in a material through the insertion and extraction of ions by an electric field at room temperature. Such multifunctional materials are desirable for many applications, from smart windows to spintronics. Read more »![]()
![]()
Magnetism Emerges at Wonky Interfaces
Researchers have found a new way to control magnetism at the atomic level that will serve as a model for studying emergent phenomena in other systems. The ability to engineer and tune properties on such small length scales can (eventually) enable us to design exciting new magnetic devices. Read more »
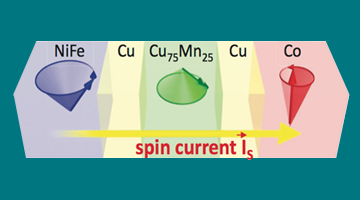
How to Directly Probe ac Spin Currents
Scientists working at the ALS have made the first unambiguous, direct measurements of ac spin currents flowing through nanostructured metal layers. The work represents a crucial step toward the development of future spintronic devices that are smaller, faster, and more energy efficient. Read more »![]()
![]()
Antiferromagnetic Spins Do The Twist
At ALS Beamline 4.0.2, researchers have found that the spins in an antiferromagnetic nanolayer perform a version of “The Twist,” turning one way and then the other, challenging a model that has been a cornerstone of exchange-bias theory for 27 years.
Read more »