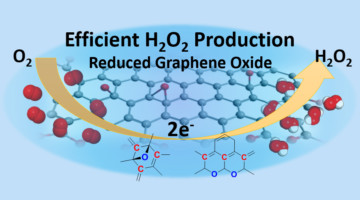
Scientists characterized a graphene-based electrocatalyst that potentially makes the production of hydrogen peroxide more selective, efficient, and cost effective. Hydrogen peroxide is an important commodity chemical with growing demand in many areas, including the electronics industry, wastewater treatment, and paper recycling. Read more »![]()
![]()
Clarifying the Working Principle of a High-Capacity Battery Electrode
Operando x-ray absorption spectroscopy experiments revealed the electrochemical reaction mechanism of molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) electrodes in lithium-ion battery cells. The work unambiguously clarifies that the MoS2 conversion reaction is not reversible and that the Li2S formed is converted to sulfur in the first charge process. Read more »
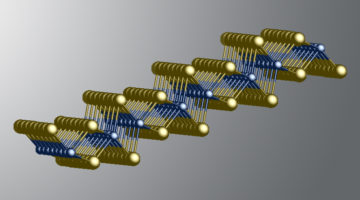
X-Ray Handedness Reveals Handedness of Electronic Vortices
Electronic vortex structures have been found to emerge from engineered samples of alternating complex-oxide layers. Resonant soft x-ray diffraction (RSXD) studies using circularly polarized x-rays revealed the vortices’ left- and right-handedness. The intriguing results open the door to electrically controllable chiral devices. Read more »
Fuel from the Sun: Insight into Electrode Performance
The mechanisms limiting the performance of hematite electrodes—potentially key components in producing fuel from the sun—have been clarified in interface-specific studies under realistic operating conditions, bringing us a step closer to storing solar energy in chemical fuels. Read more »![]()
![]()
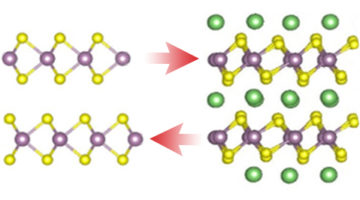
Researchers Confirm New 2D Topolgical Insulator
Researchers have established that a particularly stable form of WTe2 is a two-dimensional topological insulator, confirming recent predictions. The findings should provide new opportunities for fundamental studies of topological phenomena and for next-generation spintronic applications. Read more »![]()
![]()
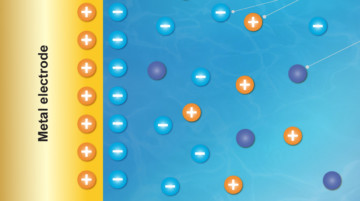
Tender X-Rays Map the Double-Layer Potential
In a first-of-its-kind experiment, ALS researchers demonstrated a new, direct way to study the inner workings of a phenomenon in chemistry known as an “electrochemical double layer” that forms where liquids meet solids—where battery fluid meets an electrode, for example. Read more »![]()
![]()
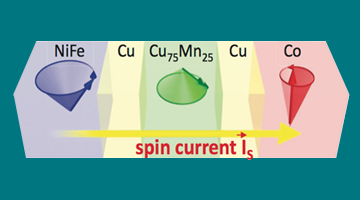
How to Directly Probe ac Spin Currents
Scientists working at the ALS have made the first unambiguous, direct measurements of ac spin currents flowing through nanostructured metal layers. The work represents a crucial step toward the development of future spintronic devices that are smaller, faster, and more energy efficient. Read more »![]()
![]()
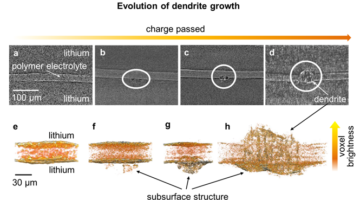
ALS Technique Gives Novel View of Lithium Battery Dendrite Growth
Lithium-ion batteries, popular in today’s electronic devices, could gain significant energy density if their graphite anodes were replaced with lithium metal anodes. But there’s a major concern with substituting lithium—when the battery cycles, microscopic fibers of the lithium anodes (“dendrites”) form on the surface of the lithium electrode and spread across the electrolyte until they reach the other electrode, possibly leading to short circuiting. Researchers have recently discovered that the x-ray microtomography capabilities at ALS Beamline 8.3.2 can give them a novel view of dendrite growth that’s likely to provide the insight needed to stop it. Read more »![]()
The Molecular Ingenuity of a Unique Fish Scale
ALS research has shown how the scales of a freshwater fish found in the Amazon Basin can literally re-orient themselves in real time to resist force, in essence creating an adaptable body armor. Read more »![]()
![]()
Platinum Nanoclusters Out-Perform Single Crystals
Researchers have found that under high pressure—comparable to the pressures at which many industrial technologies operate—platinum surfaces can change their structure dramatically in response to the presence of high-coverage reactants. Read more »![]()
![]()
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- Next Page »