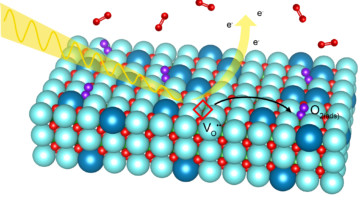
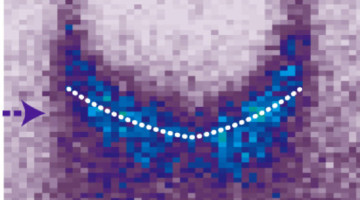
Solid oxide fuel cells are a promising technology for cleanly converting chemical energy to electrical energy. To improve the efficiency of these devices, researchers studied a model electrode material in a new way—by exposing a different facet of its crystal structure to oxygen gas at operating pressures and temperatures. Read more »
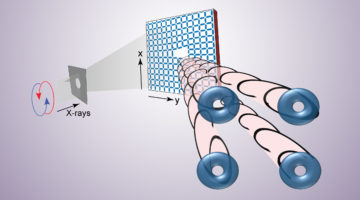
Artificial Spin Ice Toggles Twist in X-Ray Beams on Demand
ALS studies helped scientists understand how a nanoscale magnetic lattice (an artificial spin ice) acts as a toggle switch for x-ray beams with spiral character. The findings represent an important step toward the development of a versatile new tool for probing or controlling exotic phenomena in electronic and magnetic systems. Read more »![]()
![]()
Single-Domain Multiferroic Array-Addressable Terfenol-D (SMArT) Micromagnets for Programmable Single-Cell Capture and Release
Researchers develop programmable multiferroic micromotors that enable single-cell manipulation based on time-dependent functions of individual cells, such as cell secretion. Smart programmable multiferroic materials lay the groundwork for large-scale automated single-cell sorting and enable a broad spectrum of biotechnology applications. Read more »
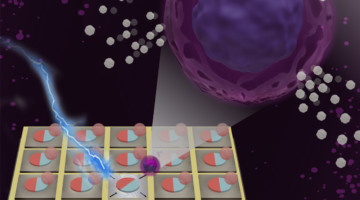
Programmable Micromagnets for Single-Cell Sorting
Researchers demonstrated that electrically induced mechanical strain can control the magnetic state of tiny magnets used to sort biological cells. The work lays the foundation for a programmable, single-cell sorting platform to support a wide variety of biotechnology applications, including personalized cancer treatments. Read more »![]()
![]()
Graphene Outperforms Metal Junctions for 2D Semiconductors
Researchers found that graphene performs ten times better than metal in transmitting a photoinduced current across interfaces with 2D semiconductors. Nanoscale-resolution band-structure measurements provided a deeper understanding of charge transport in these systems and will help in engineering more efficient contacts. Read more »
To Design Truly Compostable Plastic, Scientists Take Cues From Nature
Researchers have designed an enzyme-activated compostable plastic that could diminish microplastics pollution and holds great promise for plastics upcycling. The material can be broken down to its building blocks—small individual molecules called monomers—and then reformed into a new compostable plastic product. Read more »
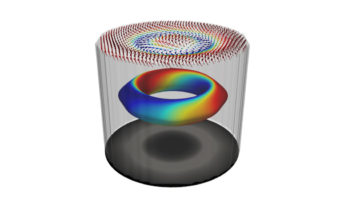
The Spintronics Technology Revolution Could Be Just a Hopfion Away
Scientists have long treated skyrmions as merely 2D objects. Recent studies, however, have suggested that 2D skyrmions could actually be the genesis of a 3D spin pattern called hopfions. Now, a team of researchers has reported the first demonstration and observation of 3D hopfions emerging from skyrmions at the nanoscale in a magnetic system. Read more »
Hybridized Radial and Edge Coupled 3D Plasmon Modes in Self-Assembled Graphene Nanocylinders
The researchers report hybridized 3D plasmon modes stemming from 3D graphene nanostructures, resulting in non-surface-limited (volumetric) field enhancements and a four orders of magnitude stronger field at the openings of cylinders than in rectangular 2D graphene ribbons. Read more »
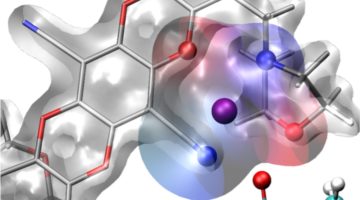
Designing Selective Membranes for Batteries Using a Drug Discovery Toolbox
Researchers designed a polymer membrane with molecular cages built into its pores that hold positively charged ions from a lithium salt. These “solvation cages” increased lithium-ion flow by an order of magnitude and could allow high-voltage battery cells to operate at higher power and more efficiently, important for both electric vehicles and aircraft. Read more »
Chiral Spin Textures in Amorphous Iron–Germanium Thick Films
Robert Streubel and co‐workers report the formation of topological magnetization vector fields in disordered materials with local inversion symmetry breaking, harnessing high‐resolution Lorentz microscopy, quantitative x‐ray microspectroscopy, and coherent scattering. The image shows the reconstructed in‐plane magnetic induction of closely packed Bloch skyrmions embedded into helical spins. Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- …
- 26
- Next Page »