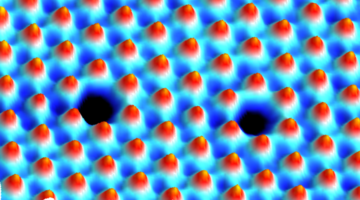
Two studies reveal surprising details on how some atomic defects emerge in transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs), and how those defects shape the material’s electronic properties. The findings could provide a more platform for designing 2D materials for quantum information science and smaller, more powerful optoelectronics. Read more »
Self-Assembling Nanomaterials Are Organized and Tunable
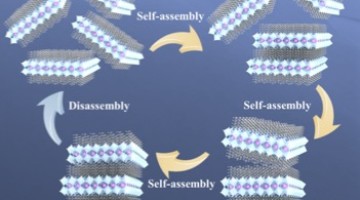
Perovskite superlattices have a wide variety of applications, but they are difficult to synthesize. Researchers have now characterized their self-assembly process to better understand how to create a variety of superlattice materials. Read more »
Controlling Spin in Antiferromagnetic Nanostructures
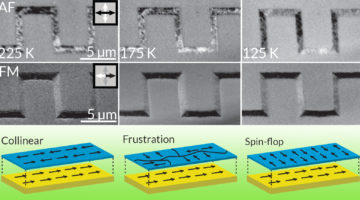
Researchers discovered that the spin configuration of a nanostructured antiferromagnetic material can be affected by the dimensions of features imprinted onto the material. The results suggest that nanoscale patterning can be a viable tool for engineering spin configurations in future antiferromagnetic spintronic devices. Read more »![]()
![]()
Multiple Levels of Chirality from Achiral Molecules
Liquid crystal samples were found to exhibit up to four levels of chirality, despite being made up of achiral molecules. The work sheds light on how molecular properties and competing interactions “propagate” order from the molecular level up to the microscale, leading to complexity similar to that found in biological materials. Read more »
Chemical and Morphological Origins of Improved Ion Conductivity in Perfluoro Ionene Chain Extended Ionomers
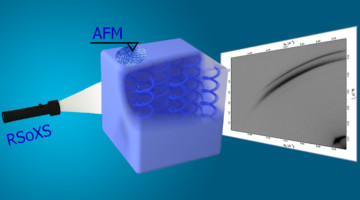
Resonant x-ray scattering and x-ray absorption spectroscopy with elemental sensitivity unravel structural features tied to water–ion domains and discern sulfur-containing groups in sulfonated ionomers, which help delineate chemical factors controlling their phase-separated morphology and governing ion transport. Read more »
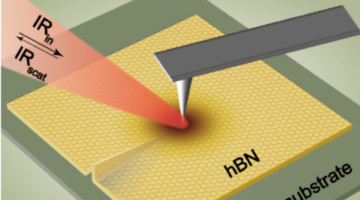
Infrared Nano-Mapping of Local Strain in 2D Materials
Researchers have demonstrated an infrared technique to map and analyze strain in atomically thin crystals of hexagonal boron nitride (hBN) at the nanoscale. This ultrasensitive strain-imaging method could be a promising tool for the examination of low-dimensional materials of interest for electronic and photonic devices. Read more »
Sulfur-linked cyanobiphenyl-based liquid crystal dimers and the twist-bend nematic phase
The synthesis and characterization of cyanobiphenyl-based liquid crystal dimers containing sulfur links between the spacer and mesogenic units are described. Resonant x-ray scattering studies of the twist-bend nematic phase at both the carbon and sulfur absorption edges were performed to determine the critical behaviour of the helical pitch at the transition to the nematic phase. Read more »
Tuning Material Properties with Laser Light
Researchers demonstrated that coupled electronic and magnetic properties in a material can be repeatably tuned using laser light. The results suggest the possibility of creating microelectronic devices that use a laser beam to erase and rewrite bits of information in materials engineered for random-access memory and data storage. Read more »![]()
![]()
Shape transformation and self-alignment of Fe-based nanoparticles
Magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) have widespread applications in biotechnology, materials science, engineering, and environmental studies. Thus, much attention has been paid to their controllable synthesis. Three new functions of iron-based nanoparticles are reported: shape transformation, oxidation prevention, and self-alignment. Read more »
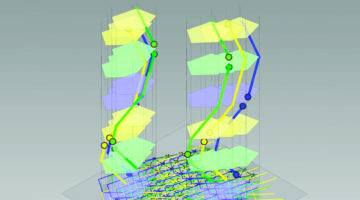
Linking Structure to Behavior in Twisted Liquid Crystals
Researchers untangled connections between structure and behavior in a class of liquid crystals consisting of flexible, chain-like molecules that self-organize into twisting patterns. The study opens up new possibilities for designing novel liquid-crystal molecules that allow greater control of nanoscale behavior for technological applications. Read more »![]()
![]()
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- …
- 26
- Next Page »