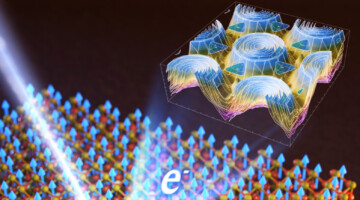
Exactly how does coral make its skeleton, a sea urchin grow a spine, or an abalone form the mother-of-pearl in its shell? A new study at the ALS revealed that this process of biomineralization, which sea creatures use to lock carbon away in their bodies, is more complex and diverse than previously thought. Read more »
Room-Temperature 2D Magnet: Electronic-Structure Insights
Researchers found that small changes in how electron spins interact with each other can make a big difference in the magnetic transition temperatures of 2D magnets. Understanding such factors can help create better magnetic materials for information storage, sensors, medical imaging, and energy-efficient computing. Read more »![]()
![]()
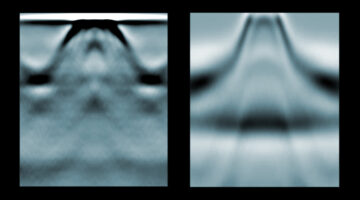
Big Twist Leads to Tunable Energy Gaps in a Bilayer Stack
Researchers found that twisting 2D layers at atypically large angles opens up potentially useful energy gaps in the material’s band structure. The results suggest a new way to tune materials for optoelectronic applications and provide a platform for exploring novel “moiré” phenomena beyond those observed at small twist angles. Read more »![]()
![]()
Magnetically Selective Versatile Transport of Microrobotic Carriers
Field-driven transport systems offer the possibility of biofunctionalized carriers for microrobotics, biomedicine, and cell delivery. Here, researchers show how magnetic fields may selectively manipulate and drive microrobotics along a patterned micromagnet. Different-sized magnetic carriers move in multiple directions, including selective rotation and bidirectional movement. Such steering systems can direct the delivery of drugs or cells into artificial microvascular channels. Read more »
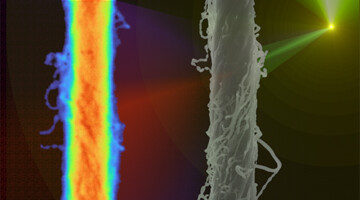
How Processing Affects Structure in Composite Nanotube Yarns
Using the ALS, researchers found quantitative correlations between processing parameters and the structure of ultrafine, polymer-reinforced carbon-nanotube fibers. The work will facilitate the production of high-strength materials, including those needed for positioning target capsules for fusion research at the National Ignition Facility. Read more »![]()
![]()
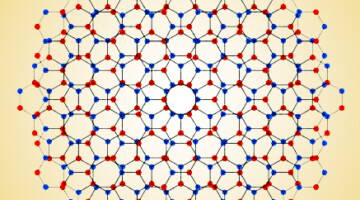
Flat Bands Signal Electrons Trapped in 3D
Researchers found flat electronic band structures—known hallmarks of electrons trapped in two dimensions—but in a material that extends this phenomenon to three dimensions. The work opens up a material framework for exploring superconductivity and other exotic states in three dimensions for advanced electronic applications. Read more »![]()
![]()
Building a Two-Dimensional Magnet One Atom at a Time
Researchers synthesized a new two-dimensional ferromagnet and measured how its electronic and magnetic properties evolve with increasing thickness and temperature. Such atomically thin magnetic materials with tunable magnetic properties would be very useful in next-generation microelectronic and spintronic applications. Read more »
Accelerating Sustainable Semiconductors With ‘Multielement Ink’
Scientists have developed “multielement ink”—the first “high-entropy” semiconductor that can be processed at low temperature or room temperature. The new semiconducting material could accelerate the sustainable production of next-gen microelectronics, photovoltaics, solid state lighting, and display devices. Read more »
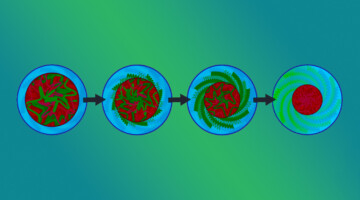
Insight into How Thermoresponsive Nanomaterials Work
By combining soft x-ray scattering with electron microscopy, researchers learned how nanoscale polymer assemblies in solution restructure in response to heating. The approach can be generalized to many complex, solution-phase, nanoscale processes, and holds promise for driving advances in applications from drug delivery to catalysis. Read more »![]()
![]()
Will Chueh to Receive the 2023 Shirley Award
Will Chueh of Stanford University is the 2023 winner of the Shirley award for Outstanding Scientific Achievement at the ALS. His selection recognizes Chueh’s deep contributions in operando soft x-ray spectromicroscopy for imaging electrochemical redox phenomena—images and movies for battery and electrocatalytic reactions. Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- …
- 26
- Next Page »