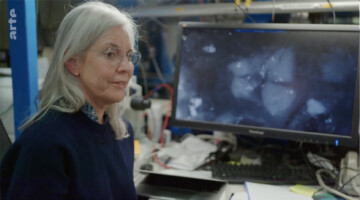
A study on the remarkable durability of 2000-year old Roman concrete, by ALS user Marie Jackson with ALS beamline scientist Nobumichi Tamura, was recently highlighted in “Miracle Materials,” a science documentary produced by a German-French company, Gruppe 5, for airing on the Eurpean public service channel, ARTE. Read more »
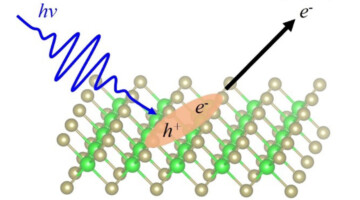
Electronic transport and polarization-dependent photoresponse in few-layered hafnium trisulfide (HfS3) nanoribbons
We report on the electrical and optoelectronic characterization of field-effect transistor (FET) devices based on few-layered HfS3 nanoribbons. The results support the contention that in the presence of light, the photocarriers include both electrons and holes, enhancing the photocurrent of devices. Read more »
Making Renewable, Infinitely Recyclable Plastics Using Bacteria
Scientists engineered microbes to make the ingredients for recyclable plastics—replacing finite, polluting petrochemicals with sustainable alternatives. The new approach shows that renewable, recyclable plastics are not only possible, but also outperform those from petrochemicals. Read more »
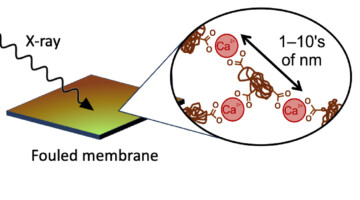
Keeping Water-Treatment Membranes from Fouling Out
When you use a membrane for water treatment, junk builds up on the membrane surface—a process called fouling—which makes the treatment less efficient. In this work, researchers studied how membranes are fouled by interactions between natural organic matter and positively charged ions commonly found in water. Read more »
A Molecular-Scale Understanding of Misorientation Toughening in Corals and Seashells
Researchers reveal that the toughness of polycrystalline seashells and coral skeletons is increased by small misorientation of adjacent crystals. The findings pave the way toward bioinspired materials with tunable toughness. Read more »
Excitons Dance the Two-Step in a 2D Material
Excitonic insulators are a rare form of macroscopic quantum state that can be realized at a high temperature, which can be useful for quantum information science. At the ALS, researchers found that in a 2D material, a novel two-step “folding” behavior in the ARPES data signals the existence of an intermediate exciton gas state. Read more »
Chiral Twists and Turns Lead Way to New Materials
Researchers found that, in crystals with structural chirality (left- or right-handedness), tuning the electronic behavior reveals hidden chiral phases and singularities. The results provide a new way to predict, test, and manipulate novel materials that exhibit desirable properties for next-generation electronic and spintronic devices. Read more »![]()
![]()
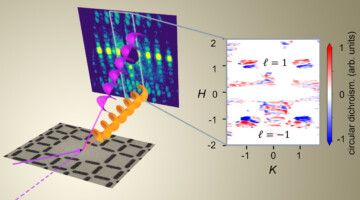
Spiraling Beams Differentiate Antiferromagnetic States
Using spiraling x-ray beams, researchers differentiated between energetically equivalent (“degenerate”) states in an antiferromagnetic lattice. The work shows the potential of these beams to probe properties that would otherwise be inaccessible, to better understand phenomena of fundamental interest and for applications such as spintronics. Read more »![]()
![]()
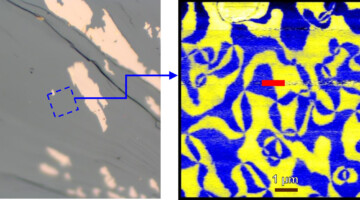
Probing Walls between Electrically Polarized Domains
Researchers used infrared light to investigate the properties of the domain walls that separate electrically polarized (ferroelectric) regions in a rare-earth ferrite material. An understanding of domain-wall behavior is relevant to the development of advanced logic and memory applications for ultralow-power digital devices. Read more »![]()
![]()
Sub-4 nm mapping of donor–acceptor organic semiconductor nanoparticle composition
We report, for the first time, sub-4 nm mapping of donor : acceptor nanoparticle composition in eco-friendly colloidal dispersions for organic electronics. This technology shows great promise for the optimization of organic semiconductor blends for organic electronics and photocatalysis and has further applications in organic core–shell nanomedicines. Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- …
- 26
- Next Page »