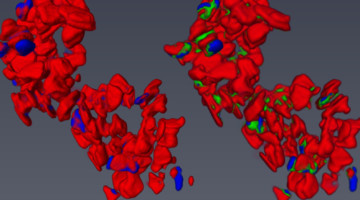
A new tool lets researchers pinpoint the locations of chemical reactions happening inside batteries in three dimensions at the nanoscale level. Combining ptychography, tomography, and spectroscopy, Nanosurveyor 1 is a multidimensional tool providing novel insight into the design of next-generation batteries and devices. Read more »
ALS Work Using Microscopy/Imaging
These techniques use the light-source beam to obtain pictures with fine spatial resolution of the samples under study and are used in diverse research areas such as cell biology, lithography, infrared microscopy, radiology, and x-ray tomography.
From Moon Rocks to Space Dust: Berkeley Lab’s Extraterrestrial Research
Berkeley Lab has a well-storied expertise in exploring samples of extraterrestrial origin. This research—which has helped us to understand the makeup and origins of objects within and beyond our solar system—stems from long-standing core capabilities in structural and chemical analyses and measurement at the microscale and nanoscale. Read more »
Non-Crystal Clarity: Scientists Find Ordered Magnetic Patterns in Disordered Magnetic Material
Scientists have confirmed the presence chirality, or handedness, in nanometers-thick samples of amorphous (noncrystalline) multilayer materials. The chirality—which potentially could be exploited to transmit and store data in a new way—was observed in the domain walls between neighboring regions of opposite spin. Read more »
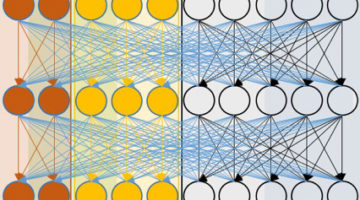
Scientists Use Machine Learning to Span Scales in Shale
Machine-learning techniques have been used to integrate fine- and large-scale infrared characterizations of shale—sedimentary rocks composed of minerals and organic matter. Understanding shale chemistry at both the nano and mesoscale is relevant to energy production, climate-change mitigation, and sustainable water and land use. Read more »
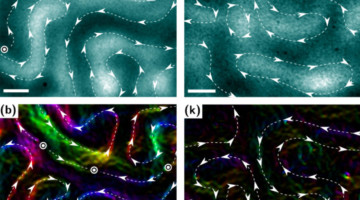
Imaging Magnetic Microstructure Response to Substrate Strain
A ferromagnetic thin film on a piezoelectric substrate offers a way to control magnetization in ultralow-power devices by relying on coupling between the piezoelectric and ferromagnetic components. At the ALS, researchers were able to image the electrically induced magnetic behavior and correlate it with the piezo-strain driving it. Read more »
Ingredients for Life Revealed in Meteorites
X-ray absorption spectroscopy and other techniques were used to measure the organic chemical components in a pair of meteorites that crashed to Earth in 1998. The study treads new ground in solar system history and asteroid geology, surfacing exciting possibilities for the existence of life elsewhere in Earth’s neighborhood. Read more »![]()
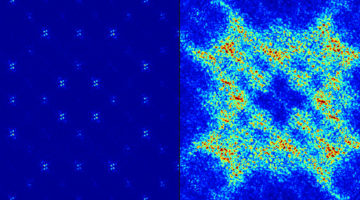
Tuning Magnetic Frustration in a Dipolar Trident Lattice
Researchers designed and fabricated a nanomagnet array in which competing (“frustrated”) magnetic interactions can be directly tuned. Frustrated interactions are key to a wide range of phenomena, from protein folding and magnetic memory to fundamental studies of emergent exotic states. Read more »![]()
![]()
The Microstructure of a Parrotfish Tooth Contributes to Its Toughness
Parrotfish chew on coral, producing hundreds of pounds of sand each year. Mapping the microstructure of parrotfish teeth, scientists found bundles of crystals interwoven like chain mail. The results provide a blueprint for creating ultra-durable materials for mechanical components that undergo repetitive contact, movement, and abrasion. Read more »
A Path to a Game-Changing Battery Electrode
If you add more lithium to the positive electrode of a lithium-ion battery, it can store much more charge in the same amount of space, theoretically powering an electric car 30 to 50 percent farther between charges. But these lithium-rich cathodes quickly lose voltage, and years of research have not been able to pin down why—until now. Read more »![]()
Coral Exoskeleton Growth Begins Inside Living Tissue
Researchers have discovered some good news regarding corals: the mechanism by which their exoskeletons grow may help them resist the effects of ocean acidification. The discovery, made with PEEM studies, has ramifications not only for the health of coral reefs, but for applications such as 3D printing as well. Read more »![]()
![]()
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- …
- 19
- Next Page »