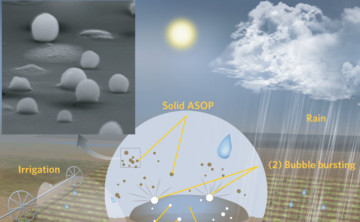
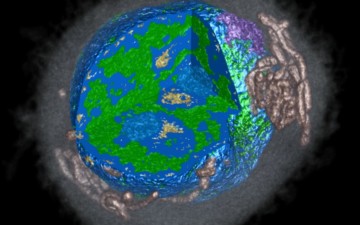
Rain’s reputation for cleansing the air may come with a caveat after new findings, including STXM and NEXAFS data, show that raindrops play a role in generating airborne organic particles. The findings could influence how scientists model our planet’s climate and future. Read more »
ALS Work Using Microscopy/Imaging
These techniques use the light-source beam to obtain pictures with fine spatial resolution of the samples under study and are used in diverse research areas such as cell biology, lithography, infrared microscopy, radiology, and x-ray tomography.
Getting to the Root of Grapevine Hydraulics
In grapevines, “root pressure” was assumed to play a role in recovering from embolisms (blockages) in a plant’s water-transport systems during drought conditions. To clarify this, researchers used ALS Beamline 8.3.2 to obtain 3D microtomographic images of grapevine stem segments detached from roots and leaves. Read more »
Mapping the Topology of the Human Genome
To determine how a gene will function, we need to know the spatial arrangement of the genome in the nucleus. Researchers have made a significant advance in determining this 3D organization by combining modeling and probabilistic calculations with minimally perturbing imaging techniques. Read more »
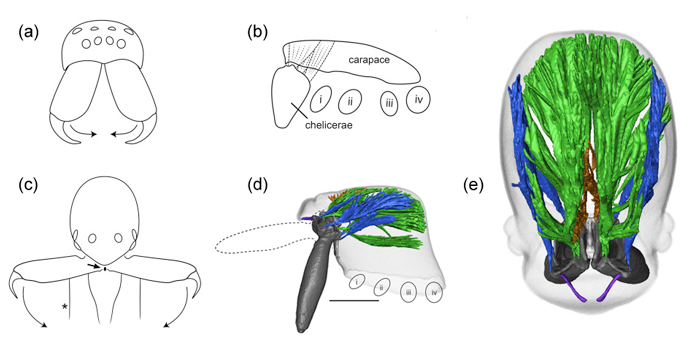
Power-Amplified Predatory Strikes in Trap-Jaw Spiders
Using a combination of high-speed video, molecular phylogenetic analysis, and x-ray microtomography of a family of tiny trap-jaw spiders, researchers discovered that power-amplified predatory strikes evolved four times independently, once the basic trap-jaw body plan was in place. Read more »
Hewlett Packard Labs Gains Insights with Innovative ALS Research Tools
For the past eight years, Hewlett Packard Labs, the central research organization of Hewlett Packard Enterprise, has been using cutting-edge ALS techniques to advance some of their most promising technological research, including vanadium dioxide phase transitions and atomic movement during memristor operation. Read more »![]()
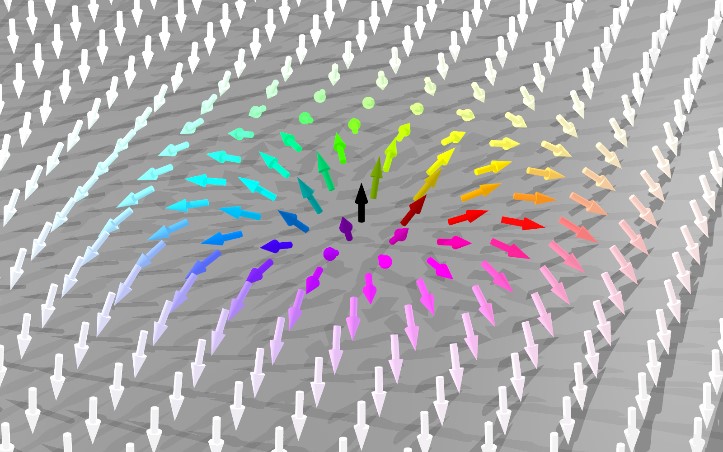
Driving Skyrmions Along a Racetrack
Researchers have demonstrated the ability to generate stable skyrmion lattices and to drive trains of individual skyrmions by short current pulses along a magnetic racetrack at speeds exceeding 100 m/s, as required for spintronic applications. Read more »
Manganese Reduction-Oxidation Drives Plant Debris Decomposition
ALS research has shown that manganese reduction-oxidation (redox) reactions are an important factor in controlling the rate of plant debris decomposition. Understanding the role of manganese will help build better models to predict how litter decomposition rates—and thus nutrient cycling and the ecosystem carbon balance—may behave in future climate scenarios. Read more »![]()
![]()
New Hope for Retinitis Pigmentosa Patients
Using FTIR microspectroscopy at the NSLS in Brookhaven and at ALS Beamline 1.4.3, scientists got a first glimpse into the structural changes that result from point mutations in opsin, one of the causes of retinitis pigmentosa. Read more »![]()
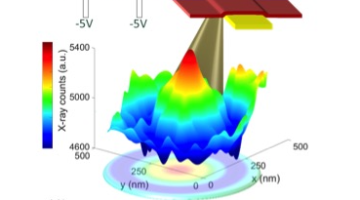
ALS, Molecular Foundry, and aBeam Technologies Collaborate to Make Metrology History
A collaboration between Bay Area company aBeam Technologies, the ALS, and the Molecular Foundry is bringing cutting-edge metrology instrumentation to the semiconductor market, which will enable a new level of quality control. Read more »![]()
Decoding Ancient Ocean Acidification Signals from Plankton Shells
Ancient plankton shells can record the physical and chemical state of the ocean in which they grew. Decoding these signals can reveal changes in global climate, atmospheric CO2, and the acidity of the oceans in deep geologic time.