Researchers detected the signatures of ancient magnetic fields imprinted in the ferromagnetic grains of meteorites that originated from the same parent body. The results, combined with radioisotopic dating of the samples, support an extended time frame for the cooling of molten protoplanetary cores. Read more »
ALS Work Using Microscopy/Imaging
These techniques use the light-source beam to obtain pictures with fine spatial resolution of the samples under study and are used in diverse research areas such as cell biology, lithography, infrared microscopy, radiology, and x-ray tomography.
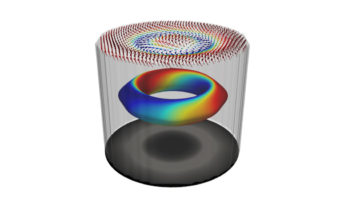
The Spintronics Technology Revolution Could Be Just a Hopfion Away
Scientists have long treated skyrmions as merely 2D objects. Recent studies, however, have suggested that 2D skyrmions could actually be the genesis of a 3D spin pattern called hopfions. Now, a team of researchers has reported the first demonstration and observation of 3D hopfions emerging from skyrmions at the nanoscale in a magnetic system. Read more »
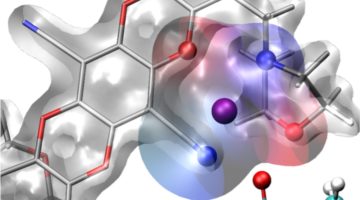
Designing Selective Membranes for Batteries Using a Drug Discovery Toolbox
Researchers designed a polymer membrane with molecular cages built into its pores that hold positively charged ions from a lithium salt. These “solvation cages” increased lithium-ion flow by an order of magnitude and could allow high-voltage battery cells to operate at higher power and more efficiently, important for both electric vehicles and aircraft. Read more »
X-Ray Experiments, Machine Learning Could Trim Years Off Battery R&D
Scanning transmission x-ray microscopy at the ALS’s COSMIC beamline contributed to a battery study that used an innovative approach to machine learning to speed up the learning curve about a process that shortens the life of fast-charging lithium batteries. It represents the first time this brand of “scientific machine learning” was applied to battery cycling. Read more »
Coral Skeleton Reveals Hidden Structures under Multimodal Scrutiny
A powerful new microscope combining ptychography with x-ray linear dichroism provides nanoscale insight into the biomineral strength and resilience of a coral skeleton. The technique’s previously unachievable spatial resolution and contrast will open up new lines of research for users of x-ray microscopy at the ALS. Read more »
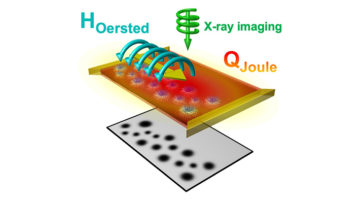
Skyrmion Creation and Annihilation Made Simple
Researchers developed a simple approach to writing and deleting skyrmions on demand, using heat and magnetic fields generated by an electrical current, by-products normally considered problematic. The ubiquitous character of these effects, coupled with simplicity of design, offers much-needed scalability and broad applicability. Read more »
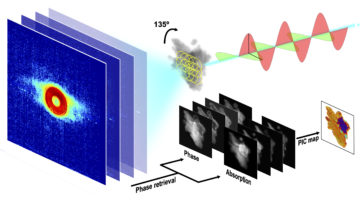
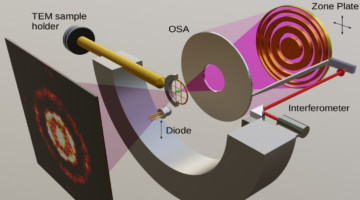
A COSMIC Approach to Nanoscale Science
COSMIC, a multipurpose x-ray instrument, has made headway since its launch less than two years ago, with groundbreaking contributions in fields ranging from batteries to biominerals. Its capabilities include world-leading microscopy resolution, extreme chemical sensitivity, and ultrafast scanning speed. Read more »
To Speed Discovery, Infrared Microscopy Goes “Off the Grid”
Researchers developed a highly efficient way to collect infrared microscopy data that avoids the use of slow, grid-based raster scans. The method substantially reduces image-acquisition times by autonomously increasing sampling density in regions of interest, facilitating infrared spectromicroscopy of biochemical processes in real time. Read more »
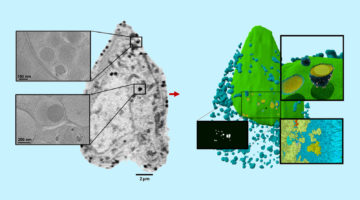
3D Whole-Cell Mapping of Insulin Secretion
Researchers used soft x-ray tomography to gain a 3D whole-cell view of how insulin-producing pancreatic cells react upon exposure to glucose and a diabetes drug. The approach enables direct quantification of intracellular responses before, during, and after cell stimulation, providing new insights into how drugs alter cell function. Read more »![]()
![]()
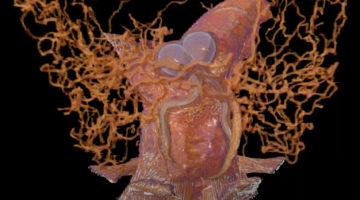
A Detailed Look Inside Tsetse Flies
To better understand the unique reproductive biology of tsetse flies, which are carriers of the parasites that cause a deadly infection known as African sleeping sickness, researchers explored the intact organs and tissues of tsetse flies using a powerful 3D x-ray imaging technique at Berkeley Lab’s Advanced Light Source. Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- …
- 19
- Next Page »