Microscope image of a microfluidic nozzle producing a liquid heterostructure: a layered flat liquid sheet with outer toluene layers and an inner water layer. The colored bands arise from thin film interference, indicating the presence of buried liquid‒liquid interfaces and submicron layer thicknesses. Read more »
ALS Work Using Scattering/Diffraction
These techniques make use of the patterns of light produced when x-rays are deflected by the closely spaced lattice of atoms in solids and are commonly used to determine the structures of crystals and large molecules such as proteins.
Structures Signal Fresh Targets for Anticancer Drugs
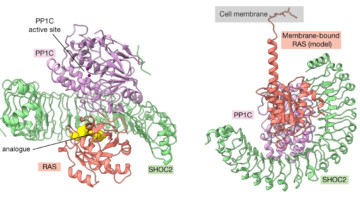
Researchers from Genentech used a suite of methods, including small-angle x-ray scattering, to learn how an assembly of three proteins works together to transmit signals for cell division. The work reveals new targets for the development of drugs that fight certain types of cancer, including lung, colorectal, and pancreatic cancer. Read more »![]()
![]()
A New Material System for Mixed-Plastic Recycling
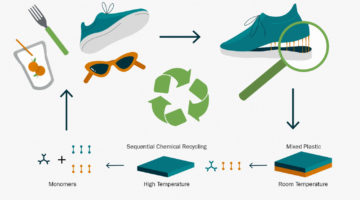
Scientists have designed a new material system to overcome one of the biggest challenges in recycling consumer products: mixed-plastic recycling. Their achievement will help enable a much broader range of fully recyclable plastic products and brings into reach an efficient circular economy for durable goods like automobiles. Read more »
Scientists Grow Lead-Free Solar Material With a Built-In Switch
A new ferroelectric material—grown in the lab from cesium germanium tribromide (CGB)—opens the door to an easier approach to making solar cell devices. Unlike conventional solar materials, CGB crystals are inherently polarized, where one side of the crystal builds up positive charges and the other side builds up negative charges, no doping required. Read more »
An Expanded Set of DNA Building Blocks for 3D Lattices
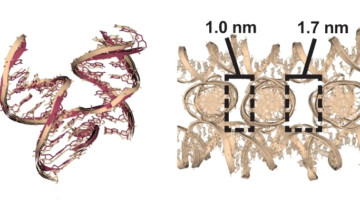
Researchers studied 36 DNA-based molecular junctions and discovered factors that yield superior self-assembled 3D lattice structures. The work expands the set of building blocks for lattices that can scaffold molecules into regular arrays, from proteins for structure studies to nanoparticles for nano-antennas and single-particle sensors. Read more »![]()
![]()
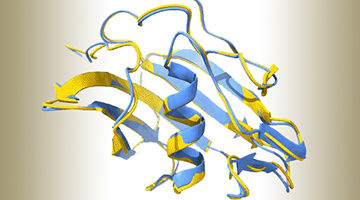
Protein Structures Aren’t Set in Stone
A group of researchers studying the world’s most abundant protein, an enzyme involved in photosynthesis called rubisco, showed how evolution can lead to a surprising diversity of molecular assemblies that all accomplish the same task. The findings reveal the possibility that many of the proteins we thought we knew actually exist in other, unknown shapes. Read more »
Deep-Learning AI Program Accurately Predicts Key Rotavirus Protein Fold
Rotaviruses are the major causative agents of gastroenteritis worldwide. Attempts to design vaccines are complicated by the rotaviruses’ enormous genetic and immunological diversity. At the ALS, researchers validated the novel structure of a key rotavirus protein, predicted using AlphaFold2, a deep-learning artificial-intelligence program. Read more »
Versatile Sequential Casting Processing for Highly Efficient and Stable Binary Organic Photovoltaics
Ideal bulk heterojunction morphology is critical in organic solar cells (OSCs). Here, researchers show how sequential casting improves device performance in both fullerene- and nonfullerene-based systems, in which the donor and acceptor are deposited sequentially. The film spin-coating method is analogous to the traditional Chinese pancake-making process. Read more »
Ionic Conduction Mechanism and Design of Metal–Organic Framework Based Quasi-Solid-State Electrolytes
This cover image demonstrates the critical role of the solvent in the ion motion of intrinsically anionic metal–organic framework (MOF)–based quasi-solid-state electrolytes (QSSEs). Using hybrid theoretical and experimental approaches, we have identified solvent-assisted hopping as the dominant pathway for Li+ conduction in such materials, exemplified by MOF-688. Read more »
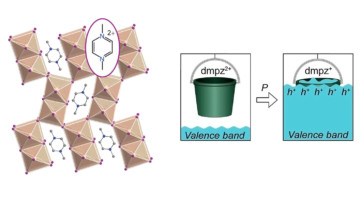
Hybrid Semiconductors Perform Under Pressure
Researchers found that compressing hybrid (organic–inorganic) semiconductors significantly boosts their conductivity. The work demonstrates a novel doping mechanism in which the material’s organic molecules serve as charge reservoirs for tuning charge-carrier concentration, with promising applications in solar cells, lasers, and LEDs. Read more »![]()
![]()
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- …
- 39
- Next Page »