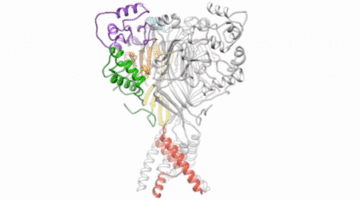
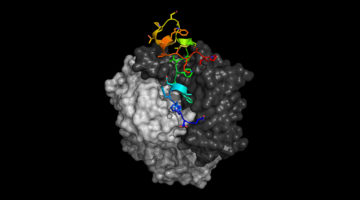
Researchers used x-ray data to define the structure of a closed protein gate important for neuronal signaling. Comparing the closed gate with previously known structures of the same gate when open, researchers now have a comprehensive picture of proton-dependent channels in neurons. Read more »
ALS Work Using Scattering/Diffraction
These techniques make use of the patterns of light produced when x-rays are deflected by the closely spaced lattice of atoms in solids and are commonly used to determine the structures of crystals and large molecules such as proteins.
Structures Reveal New Target for Malaria Vaccine
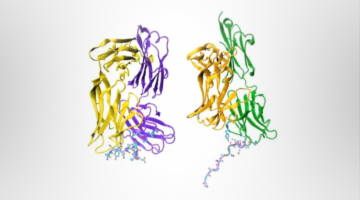
Researchers isolated human-derived antibodies that protect against malaria, and protein-structure studies revealed the antibodies’ site of attack. The discovery paves the way for the development of a more effective and practical human vaccine for malaria, which is responsible for half a million deaths every year. Read more »![]()
![]()
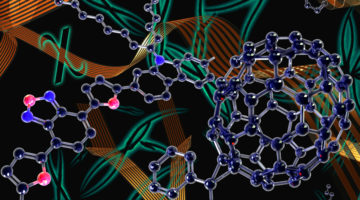
Molecular Anvils Trigger Chemical Reactions
“Molecular anvils” (diamondoids) were used to trigger chemical reactions using pressure, yielding products that differ from those produced in conventionally driven reactions with the same reactants. The discovery opens up new possibilities for the high-specificity synthesis of valuable but challenging molecules in an environmentally friendly process. Read more »![]()
![]()
From Moon Rocks to Space Dust: Berkeley Lab’s Extraterrestrial Research
Berkeley Lab has a well-storied expertise in exploring samples of extraterrestrial origin. This research—which has helped us to understand the makeup and origins of objects within and beyond our solar system—stems from long-standing core capabilities in structural and chemical analyses and measurement at the microscale and nanoscale. Read more »
Rational Optimization of Organic Solar-Cell Materials
Researchers have established a new quantitative model that connects molecular interactions in organic solar-cell materials to device performance. The work suggests a way to quickly identify ideal material mixtures and processing methods, bypassing trial-and-error strategies and minimizing labor-intensive synthesis. Read more »![]()
![]()
Respiratory Virus Study Points to Likely Vaccine Target
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) causes serious respiratory disease in infants and older adults, but no vaccine is yet available. Researchers have now determined the molecular structures of human antibodies bound to an RSV surface protein, providing a promising route for designing a vaccine effective against a broad range of RSV strains. Read more »![]()
![]()
Structure-based Design of Pyridone–Aminal eFT508 Targeting Dysregulated Translation by Selective Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase Interacting Kinases 1 and 2 (MNK1/2) Inhibition
Dysregulated translation drives key hallmarks of cancer and is controlled by Phase 2 candidate eFT508 binding to the MNK protein, exploiting stereoelectronic interactions, critical to the compound’s selectivity and potency. Read more »
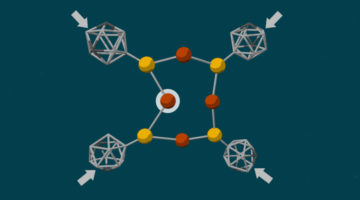
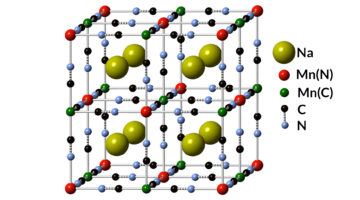
Monovalent Manganese for High-Performance Batteries
Scientists have detected a novel chemical state of the element manganese that was first proposed about 90 years ago. The discovery enables the design of a high-performance, low-cost battery that, according to its developers, outperforms Department of Energy goals on cost and cycle life for grid-scale energy storage. Read more »![]()
![]()
Imaging Magnetic Microstructure Response to Substrate Strain
A ferromagnetic thin film on a piezoelectric substrate offers a way to control magnetization in ultralow-power devices by relying on coupling between the piezoelectric and ferromagnetic components. At the ALS, researchers were able to image the electrically induced magnetic behavior and correlate it with the piezo-strain driving it. Read more »
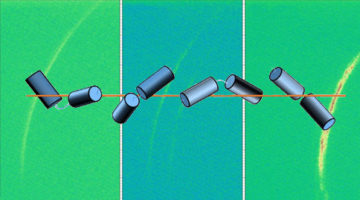
Twisted Structures Emerge from Achiral Molecules
The spontaneous formation of chiral structures from achiral molecules could shed light on the origin of biological homochirality—how one type of chirality dominated the other in certain biological molecules. Here, resonant soft x-ray scattering (RSoXS) has been used to explore helical phases that emerge from achiral asymmetric dimers. Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- …
- 39
- Next Page »