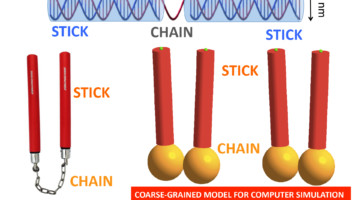
Researchers designed DNA sequences that self-assemble into a nanoparticle about 50 nm long, composed of two double-stranded DNA duplexes linked together by a single-stranded DNA filament. The nanoparticle resembles nunchaku—a traditional weapon of several martial arts—but 30 million times smaller. Read more »
ALS Work Using Scattering/Diffraction
These techniques make use of the patterns of light produced when x-rays are deflected by the closely spaced lattice of atoms in solids and are commonly used to determine the structures of crystals and large molecules such as proteins.
Evolutionary drivers of thermoadaptation in enzyme catalysis
With early life likely to have existed in a hot environment, enzymes had to cope with an inherent drop in catalytic speed caused by lowered temperature. Here, researchers characterize the molecular mechanisms underlying thermoadaptation of enzyme catalysis in adenylate kinase using ancestral sequence reconstruction spanning 3 billion years of evolution. Read more »
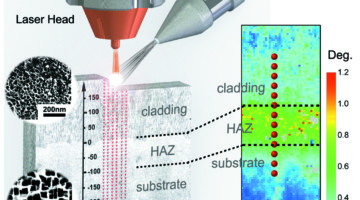
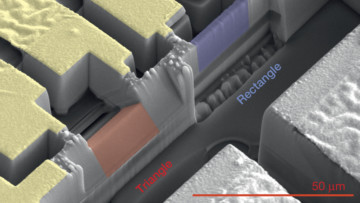
X-Rays Help Evaluate Quality of 3D-Printed Repairs
Laser 3D printing is a promising way to repair machine parts (such as jet-engine turbine blades) made of single-crystal superalloys. But microstructural inhomogeneities created by the high-power laser are a major reliability concern, so researchers employed x-ray Laue microdiffraction to probe the microstructure. Read more »
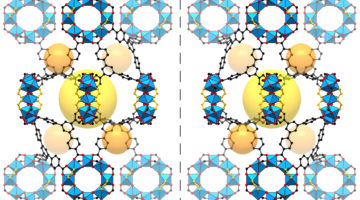
A New Way to Determine the 3D Structure of Molecules
Researchers have created a sort of nanoscale display case that enables new atomic-scale views of hard-to-study chemical and biological samples. The work could help to reveal new structural details for a range of challenging molecules by stabilizing them inside sturdy structures known as metal-organic frameworks (MOFs). Read more »![]()
![]()
Glowing Crystals Can Detect, Cleanse Contaminated Drinking Water
Tiny, glowing crystals designed to detect and capture heavy-metal toxins such as lead and mercury could prove to be a powerful new tool in locating and cleaning up contaminated water sources. The crystals function like miniature, reusable sensors and traps, and are known as luminescent metal-organic frameworks, or LMOFs. Read more »
Solar Cells Get Boost with Integration of Water-Splitting Catalyst onto Semiconductor
Scientists have found a way to engineer the atomic-scale chemical properties of a water-splitting catalyst for integration with a solar cell, and the result is a big boost to the stability and efficiency of artificial photosynthesis. Read more »
A Molecular View of Sperm–Egg Fusion
Researchers have uncovered the first interactions between the human sperm and egg—the initial steps in the creation of human life. The discovery lays a foundation to better understand fertilization and could lead to the development of non-hormonal contraceptives. Read more »
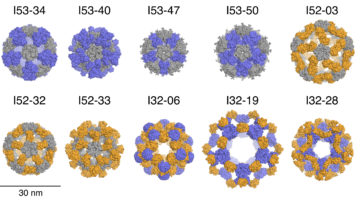
Designed Protein Nanocages Inspired by Nature
Inspired by protein molecules observed in nature, researchers have now engineered ten large, 120-subunit, two-component protein complexes. These designed nanomaterials are attractive starting points for new approaches to targeted drug delivery, vaccine design, and bioenergy. Read more »
Scientists Find Twisting 3-D Raceway for Electrons in Nanoscale Crystal Slices
Researchers have observed, for the first time, an exotic 3-D racetrack for electrons in ultrathin slices of a tiny crystal they made at Berkeley Lab. Read more »
Molecular Switch Triggers Bacterial Pathogenicity
Using an array of high-powered x-ray imaging techniques at the ALS, scientists have revealed for the first time the molecular steps that turn on bacteria’s pathogenic genes. The study could open up new avenues in the development of drugs to prevent or treat bacterial infection. Read more »![]()
![]()
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- …
- 39
- Next Page »