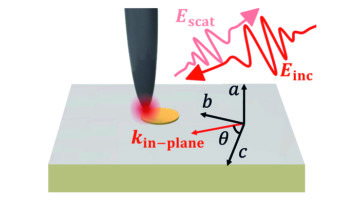
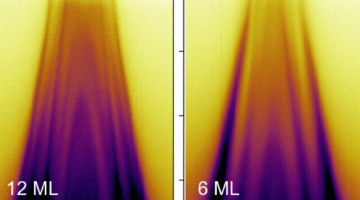
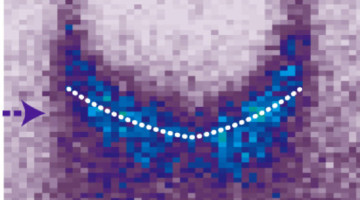
Scattering-type scanning near-field optical microscopy (s-SNOM) focuses infrared light to dimensions below the diffraction limit, measuring properties with components perpendicular to the sample surface. Researchers have now devised a way to probe components parallel to the sample, where the technique has been less sensitive. Read more »
ALS Work Using Spectroscopy
These techniques are used to study the energies of particles that are emitted or absorbed by samples that are exposed to the light-source beam and are commonly used to determine the characteristics of chemical bonding and electron motion.
Autonomous Data Acquisition for Scientific Discovery
Researchers at large scientific facilities such as the ALS have applied a robust machine-learning technique to automatically optimize data gathering for a variety of experimental techniques. The work promises to enable experiments with large, complex datasets to be run more quickly, efficiently, and with minimal human intervention. Read more »![]()
![]()
This Exotic Particle Had an Out-of-Body Experience; These Scientists Took a Picture of It
Scientists have taken the clearest picture yet of electronic particles that make up a mysterious magnetic state called a quantum spin liquid (QSL), in which electrons decompose into spin-like particles (spinons) and charge-like particles (chargons). The achievement could facilitate the development of superfast quantum computers and energy-efficient superconductors. Read more »
David Prendergast Wins 2021 Shirley Award
David Prendergast, an internationally recognized computational scientist whose first-principles calculations of x-ray spectra have helped with the interpretation of countless experiments done at the ALS, has been awarded the 2021 Shirley Award for Outstanding Scientific Achievement by the ALS Users’ Executive Committee. Read more »
Main Attraction: Scientists Create World’s Thinnest Magnet
A one-atom-thin 2D magnet that operates at room temperature could lead to new applications in computing and electronics—such as high-density, compact spintronic memory devices—and new tools for the study of quantum physics. X-ray experiments at the ALS characterized the material’s magnetic parameters under high temperature. Read more »
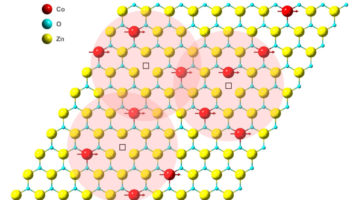
Tuning Semimetallicity Using Thin Films and Interfaces
With support from ALS data, scientists gained new insight into a semimetal’s unusual electronic behavior. The work lays out a basic strategy for engineering the band structures of semimetallic compounds using dimensional confinement and reveals a new way of creating two-dimensional electron/hole gases by exploiting interfacial bonding. Read more »![]()
![]()
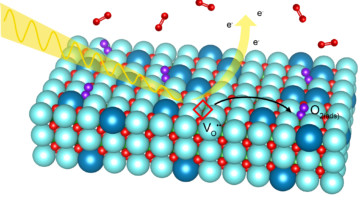
Scientists Uncover a Different Facet of Fuel-Cell Chemistry
Solid oxide fuel cells are a promising technology for cleanly converting chemical energy to electrical energy. To improve the efficiency of these devices, researchers studied a model electrode material in a new way—by exposing a different facet of its crystal structure to oxygen gas at operating pressures and temperatures. Read more »
Graphene Outperforms Metal Junctions for 2D Semiconductors
Researchers found that graphene performs ten times better than metal in transmitting a photoinduced current across interfaces with 2D semiconductors. Nanoscale-resolution band-structure measurements provided a deeper understanding of charge transport in these systems and will help in engineering more efficient contacts. Read more »
X-Ray Study Recasts Role of Battery Material from Cathode to Catalyst
Researchers used the ALS to learn about a lithium-rich battery material that has been the subject of much study for its potential to extend the range of electric vehicles and the operation of electronic devices. Through a fundamental spectroscopic study, they not only clarified the reaction mechanism of this material, but also found a conceptually different use of it as a catalyst. Read more »
Hybridized Radial and Edge Coupled 3D Plasmon Modes in Self-Assembled Graphene Nanocylinders
The researchers report hybridized 3D plasmon modes stemming from 3D graphene nanostructures, resulting in non-surface-limited (volumetric) field enhancements and a four orders of magnitude stronger field at the openings of cylinders than in rectangular 2D graphene ribbons. Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- …
- 30
- Next Page »