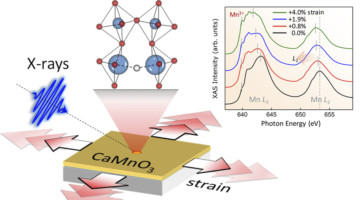
Researchers have demonstrated a novel way to systematically strain-engineer oxygen vacancies in complex transition-metal oxide thin films. The work advances our ability to tailor such defects, small changes in which can lead to dramatic changes in material properties such as conductivity and magnetism. Read more »
ALS Work Using Spectroscopy
These techniques are used to study the energies of particles that are emitted or absorbed by samples that are exposed to the light-source beam and are commonly used to determine the characteristics of chemical bonding and electron motion.
A Seaweed Derivative Could Be Just What Lithium-Sulfur Batteries Need
Lithium-sulfur batteries have great potential as a low-cost, high-energy, energy source for both vehicle and grid applications. However, they suffer from significant capacity fading. Now, scientists have found that carrageenan, a seaweed derivative, acts as a stabilizer, allowing for more cycling and an extended lifetime. Read more »
Researchers Find a Surprise Just Beneath the Surface in Carbon Dioxide Experiment
X-ray experiments, coupled with theoretical work, revealed how oxygen atoms embedded near the surface of a copper sample had a more dramatic effect on the early stages of a reaction with CO2 than accounted for in earlier theories. This work could prove useful in designing new catalysts for converting CO2 into liquid fuels and other products. Read more »
Bacterial Symbiont Sequesters Arsenic and Barium in Sponges
Researchers used x-ray fluorescence, spectroscopy, and diffraction to study how populations of symbiotic bacteria can act as a detox organ in a host with no organs. The bacteria, members of the species Entotheonella, accumulate and mineralize large quantities of arsenic and barium in sponges. Read more »
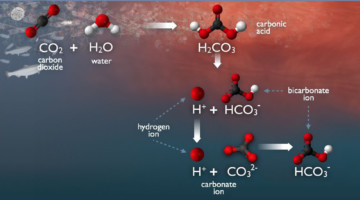
APXPS Finds Carbonate Reversal at Liquid Interfaces
Aqueous carbonate systems are central to many processes essential to life, from the blood buffer system to the global carbon cycle. Using APXPS, researchers probed the concentration of carbonates near an interface, finding a surprising reversal in the expected abundances as a function of depth. Read more »![]()
![]()
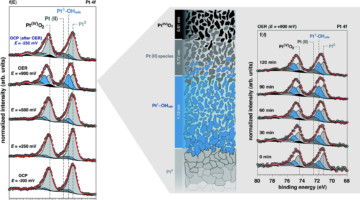
A Closer Look at a Working Platinum/Electrolyte Interface
Ambient-pressure studies of the interface between a platinum electrode and an alkaline electrolyte revealed the molecular-level chemistry, structure, and dynamics of the platinum surface as a function of applied potential, highlighting differences between thermodynamic predictions and the actual surface composition. Read more »
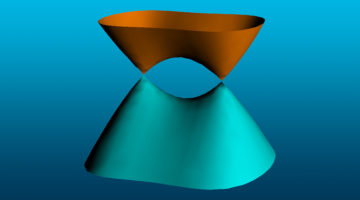
Strain Turns Tin into a 3D Topological Dirac Semimetal
A small amount of compressive strain turns a nonmetallic form of tin into a 3D topological Dirac semimetal—a kind of “supermetal” with very high electron mobility. With its rich topological phase diagram, the material shows promise for both novel physics and eventual device applications. Read more »![]()
![]()
Modulating Infrared Light with 2D Black Phosphorus
Two-dimensional materials represent a promising new frontier in the field of optoelectronics. Most progress so far, however, has been in the visible-light range. Now, at the ALS, researchers have measured the infrared transmission spectra of ultrathin samples of black phosphorus under an applied electric field. Read more »![]()
![]()
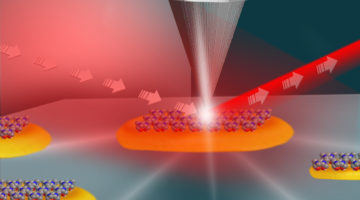
Mapping Catalytic Reactions on Single Nanoparticles
A new study confirms that structural defects and jagged surfaces at the edges of platinum and gold nanoparticles are key hot spots for chemical reactivity. The experiments should help researchers customize the structural properties of catalysts to make them more effective in fostering chemical reactions. Read more »![]()
![]()
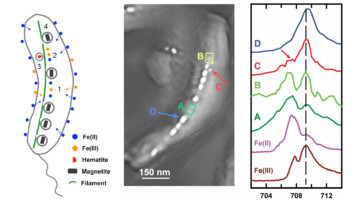
Ptychography of a Bacterium’s Inner Compass
Magnetotactic bacteria (MTB) synthesize chains of magnetic nanocrystals (magnetosomes) that interact with the Earth’s magnetic field like an inner compass needle, simplifying their search for optimum environments. Ptychographic spectra of magnetosomes from a marine MTB provides insight into how these inner compasses form. Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- …
- 30
- Next Page »