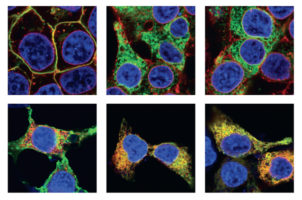
Using FTIR microspectroscopy at the NSLS in Brookhaven and at ALS Beamline 1.4.3, scientists got a first glimpse into the structural changes that result from point mutations in opsin, one of the causes of retinitis pigmentosa. Read more »![]()
ALS Work Using Spectroscopy
These techniques are used to study the energies of particles that are emitted or absorbed by samples that are exposed to the light-source beam and are commonly used to determine the characteristics of chemical bonding and electron motion.
Phonon Polariton Behavior in 2D Materials
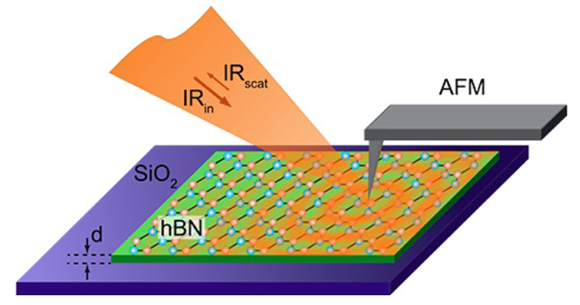
Synchrotron infrared nanospectroscopy (SINS) was used to study the behavior of phonon polaritons in ultrathin crystals of hexagonal boron nitride. The results pave the way towards engineering infrared-light photonic nanodevices and expand our understanding of polariton behavior in low-dimensional nanomaterials. Read more »![]()
![]()
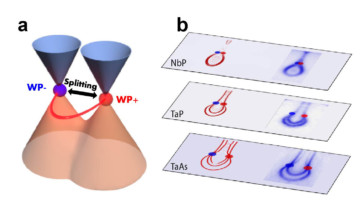
Discovery of Weyl Semimetals May Lead to Novel Future Spintronic Applications
A team of researchers using angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy (ARPES) at ALS Beamline 10.0.1 found intriguing particles in a new phase of quantum matter: topological Weyl semimetals.
Read more »
Tracking the Elusive QOOH Radical
For the first time, researchers directly observed QOOH molecules, a class of highly reactive molecules at the center of the web of ignition chemistry reactions. The data generated will improve the fidelity of combustion models used to create cleaner and more efficient cars and trucks. Read more »![]()
![]()
Spectroscopy of Supercapacitor Electrodes In Operando
X-ray spectroscopy of graphene supercapacitor electrodes under operating conditions reveals changes in electronic structure and bonding. The research could lead to an improvement in the capacity and efficiency of electrical energy storage systems needed to meet the burgeoning demands of consumer, industrial, and green technologies. Read more »![]()
![]()
ALS X-Rays Shine a New Light on Catalysis
Recently a team of Stanford and Berkeley Lab researchers used x-rays at the ALS in a novel way to observe the behavior of electrons during technologically important chemical reactions in metal oxide electrocatalysts. What they learned has upended long-held scientific understanding of how these catalysts work. Read more »![]()
![]()
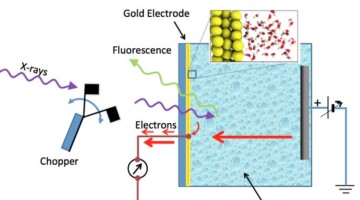
Molecular Structure of Water at Gold Electrodes Revealed
ALS researchers have now made a first-ever observation of the molecular structure of liquid water at a gold surface under different charging conditions. This marks the first time that the scientific community has been able to achieve such high sensitivity in an in situ environment under working electrode conditions. Read more »![]()
![]()
Antiferromagnetic Spins Do The Twist
At ALS Beamline 4.0.2, researchers have found that the spins in an antiferromagnetic nanolayer perform a version of “The Twist,” turning one way and then the other, challenging a model that has been a cornerstone of exchange-bias theory for 27 years.
Read more »
New Technique Gives a Deeper Look into the Chemistry of Interfaces
A new technique developed at the ALS offers sub-nanometer depth resolution of every chemical element to be found at heterogeneous interfaces, such as those in batteries and fuel cells. The technique has relevance to energy research, heterogeneous catalysis, electrochemistry, and atmospheric and environmental science. Read more »![]()
![]()
ALS Director’s Update: Reflections on our Past, Present, and Future
We are looking forward to an exciting and productive year at the ALS, with plans for new beamlines and capabilities coming online, and more users taking advantage of our technical and scientific expertise to produce a record number publications. At the ALS, we are encouraged by this year’s funding and are looking for new ways to focus on our core strengths while expanding partnerships to explore new opportunities. Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- Next Page »