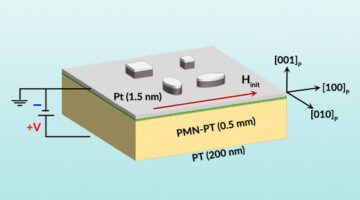
Researchers learned how the size, shape, and orientation of microstructures affect how they switch magnetization directions in response to an applied voltage. The work advances our understanding of strain-responsive composite materials for use in energy-efficient electronic applications such as memory devices, sensors, and actuators. Read more »![]()
![]()
ALS Work Using Spectroscopy
These techniques are used to study the energies of particles that are emitted or absorbed by samples that are exposed to the light-source beam and are commonly used to determine the characteristics of chemical bonding and electron motion.
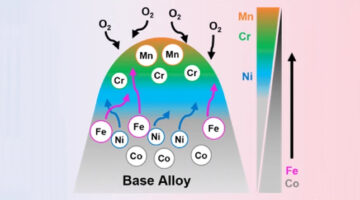
Tracking Oxidation in “High-Entropy” Alloys with Multiple Principal Elements
For extreme applications such as nuclear fusion reactors and high-temperature jet engines, scientists are experimenting with “high-entropy” alloys that consist of many metals mixed together in equal proportions. In this work, researchers begin to unravel how these materials degrade under high-temperature oxidative environments. Read more »![]()
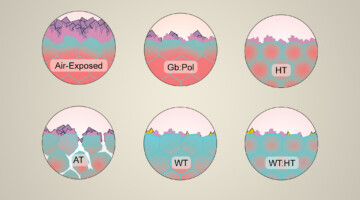
Studying Interfacial Effects in Solid-Electrolyte Batteries
An ambient-pressure probe of a solid electrolyte revealed how surface electrochemical mechanisms lead to poor electrolyte performance and battery failure. The results can help scientists engineer better coatings and interfaces, which are essential for building safer and better-performing batteries, particularly for use in vehicles. Read more »![]()
![]()
Manganese Cathodes Could Boost Lithium-ion Batteries
Rechargeable lithium-ion batteries are used in mobile devices, electric vehicles, and energy storage systems. But supplies of nickel and cobalt, commonly used in the cathodes of these batteries, are limited. New research opens up a potential low-cost, safe alternative in manganese, the fifth most abundant metal in the Earth’s crust. Read more »
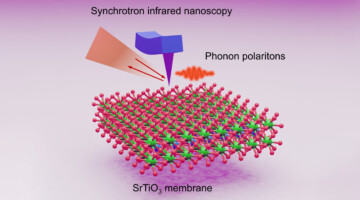
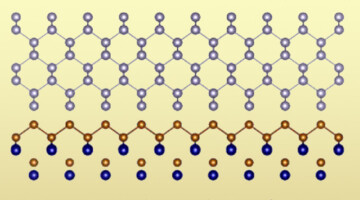
A New Way to “Squeeze” Infrared Wavelengths Down to Size
Researchers demonstrated a new way to confine, or “squeeze,” infrared light by coupling photons with phonons (lattice vibrations) within a certain type of thin film. The work heralds a new class of optical materials for controlling infrared light, with potential applications in photonics, sensors, and microelectronic heat management. Read more »![]()
![]()
4f-Orbital Mixing Increases the Magnetic Susceptibility of Cp’3Eu
The ability to harness the 4f-orbital anisotropies and magnetic susceptibilities of lanthanide elements is key to their application in molecular magnetism, including as molecular qubits and single-molecule magnets. Here, 4f orbital mixing and its impact on the magnetic susceptibility of a trivalent Eu organometallic complex was analyzed experimentally. Read more »
Tuning the Spin Transition and Carrier Type in Rare-Earth Cobaltates via Compositional Complexity
This work demonstrates that tunable disorder in a crystal can be quite useful: compositional site disorder was used to modify oxide semiconductors by changing the carrier type, improving crystallinity and tuning a spin transition. Applications include electrothermal thresholding devices such as radio frequency limiters. Read more »
Unveiling Direct Electrochemical Oxidation of Methane at the Ceria/Gas Interface
Ceria-based oxides embedded in solid-oxide fuel cells are recognized for their critical role in managing hydrocarbon activation and carbon coking. However, even for the simplest hydrocarbon molecule, CH4, the mechanism of electrochemical oxidation at the ceria/gas interface is not well understood. This study presents a Sm-doped ceria thin-film model cell that selectively monitors CH4 direct-electro-oxidation on the ceria surface. Read more »
Strategic ALS Projects Reach Key Milestones
Thanks to the hard work and dedication of multidisciplinary teams from groups across the ALS, a spate of important milestones occurred over the past month, for projects involving the new QERLIN beamline, the MERLIN beamline upgrade, and a new chamber for computer-chip metrology in Sector 12. Read more »
Stabilizing Pristine α-Sn Thin Films for Topological Investigation
Researchers developed a recipe for the room-temperature stabilization of thin films of α-Sn, a form of elemental tin that exhibits a variety of topologically nontrivial phases, but only at low temperatures. By dramatically reducing contamination from the film’s substrate, the recipe greatly simplifies electronic structure studies. Read more »![]()
- « Previous Page
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- …
- 30
- Next Page »