High-energy Li-ion batteries can provide both high capacity and high voltage, both of which are important in electric vehicles for greater range and faster acceleration. Here, researchers untangled the contributions of nickel and cobalt in high-energy Li-rich battery cathodes, pointing the way to optimizing them via a compositional approach. Read more »
ALS Work Using Spectroscopy
These techniques are used to study the energies of particles that are emitted or absorbed by samples that are exposed to the light-source beam and are commonly used to determine the characteristics of chemical bonding and electron motion.
Flat Bands Signal Electrons Trapped in 3D
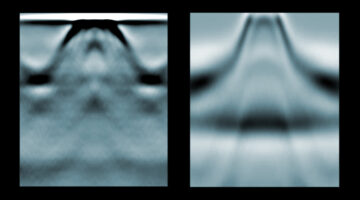
Researchers found flat electronic band structures—known hallmarks of electrons trapped in two dimensions—but in a material that extends this phenomenon to three dimensions. The work opens up a material framework for exploring superconductivity and other exotic states in three dimensions for advanced electronic applications. Read more »![]()
![]()
Tracking Platinum Movement on Fuel-Cell Electrodes
Researchers tracked the movement of the platinum nanoparticles that catalyze reactions in polymer electrolyte fuel cells (PEFCs) and correlated this movement with nanoparticle degradation. The results yielded solutions that can immediately reduce platinum waste in emission-free heavy-duty fuel-cell vehicles. Read more »![]()
![]()
Building a Two-Dimensional Magnet One Atom at a Time
Researchers synthesized a new two-dimensional ferromagnet and measured how its electronic and magnetic properties evolve with increasing thickness and temperature. Such atomically thin magnetic materials with tunable magnetic properties would be very useful in next-generation microelectronic and spintronic applications. Read more »
Optical Properties of Individual Tar Balls in the Free Troposphere
Tar balls are found in biomass-burning smoke, and their sunlight-absorption properties are highly uncertain. This study investigates the optical properties of individual tar balls in the free troposphere to better understand their influence on climate. Read more »
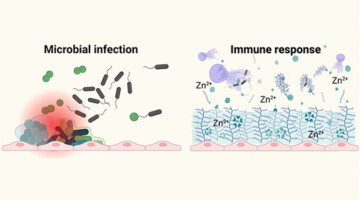
Immune Response Spurs Growth of “Soft” Kidney Stones
Matrix stones are an unusual type of soft kidney stone closely associated with the presence of bacteria from unchecked urinary tract infections. Researchers conducted a comprehensive study of surgically extracted matrix stones, work that highlights how host defense mechanisms against microbes can simultaneously encourage harmful stone formation. Read more »
HyMARC Aims to Hit Targets for Hydrogen Storage Using X-Ray Science
Understanding how materials absorb and release hydrogen is the focus of the Hydrogen Materials Advanced Research Consortium (HyMARC). At the ALS, the HyMARC Approved Program was recently renewed, underscoring the key role that soft x-ray techniques have played in addressing the challenges of hydrogen storage. Read more »
Spectroscopic investigation of a Co(0001) model catalyst during exposure to H2 and CO at near-ambient pressures
We have performed near-ambient-pressure X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy on Co(0001) model catalysts during exposure to gases relevant to Fischer–Tropsch synthesis, i.e., CO and H2, at 0.25 mbar total pressure. At this pressure, CO seems to be more efficient at keeping the Co(0001) surface metallic than H2, which is the opposite behavior as reported in the literature for other pressure ranges. Read more »
Organic Matrix Derived from Host–Microbe Interplay Contributes to Pathological Renal Biomineralization
A composite image of a rare form of kidney stone, illustrating extensive organic filamentous networks abundant with immune response-related proteins such as calprotectin (displayed in red), myeloperoxidase (in yellow), and DNA molecules (in blue). Originating from intricate host-microbe interplay, these organic networks promote the heterogeneous nucleation and precipitation of inorganic particulates. Read more »
Case study evaluation of size-resolved molecular composition and phase state of carbonaceous particles in wildfire influenced smoke from the Pacific Northwest
Wildfires are significant sources of carbonaceous particles in the atmosphere. Given the dependence of atmospheric processes on particle physical and molecular properties, the interplay between particle size, phase state and chemical composition is investigated here for aerosols influenced by a 2021 Pacific Northwest wildfire event. Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- …
- 30
- Next Page »