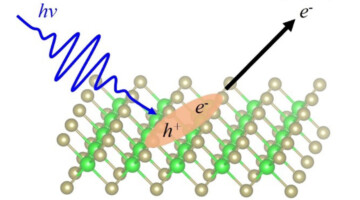
We report on the electrical and optoelectronic characterization of field-effect transistor (FET) devices based on few-layered HfS3 nanoribbons. The results support the contention that in the presence of light, the photocarriers include both electrons and holes, enhancing the photocurrent of devices. Read more »
ALS Work Using Spectroscopy
These techniques are used to study the energies of particles that are emitted or absorbed by samples that are exposed to the light-source beam and are commonly used to determine the characteristics of chemical bonding and electron motion.
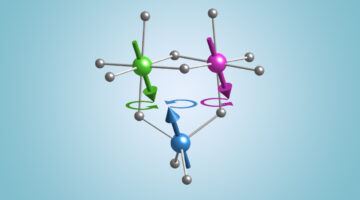
Capturing the Spin Dynamics of a Complex Magnetic Material
Magnetic iron oxides (ferrites) are complex materials with broad electronic applications that are often driven by microwaves. Here, researchers have precisely measured the spin behavior of several distinct cations in a ferrite material under an applied microwave field, validating a longstanding assumption about magnetic oxide dynamics. Read more »
Excitons Dance the Two-Step in a 2D Material
Excitonic insulators are a rare form of macroscopic quantum state that can be realized at a high temperature, which can be useful for quantum information science. At the ALS, researchers found that in a 2D material, a novel two-step “folding” behavior in the ARPES data signals the existence of an intermediate exciton gas state. Read more »
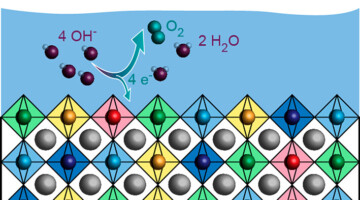
Surface Engineering Boosts Water-Splitting Efficiency
Researchers modified the surface of an electrocatalyst to maximize its efficiency at splitting water. The optimized material is approximately 40 times more efficient than similar commercial electrocatalysts and could help make the production of clean hydrogen fuel more sustainable and economical. Read more »![]()
![]()
Chiral Twists and Turns Lead Way to New Materials
Researchers found that, in crystals with structural chirality (left- or right-handedness), tuning the electronic behavior reveals hidden chiral phases and singularities. The results provide a new way to predict, test, and manipulate novel materials that exhibit desirable properties for next-generation electronic and spintronic devices. Read more »![]()
![]()
New Pathway for SO2 Breakup Sheds Light on Earth’s Oxygenation
While calibrating a new scientific apparatus at the ALS, researchers discovered that ultraviolet light can break up sulfur dioxide (SO2) in a new way, with molecular oxygen (O2) as an unexpected product. The discovery sheds light on Earth’s Great Oxygenation Event 2.4 billion years ago, when atmospheric oxygen levels first began to rise. Read more »
Vestiges of the Early Solar System in Ryugu Asteroid
Samples returned to Earth from the asteroid Ryugu revealed that the building blocks of life formed 4.6 billion years ago in the extreme cold of space, followed by reaction with water. The dark, coal-like organic matter in the carbonaceous asteroid could have contributed to the formation of habitable planetary environments. Read more »![]()
![]()
Synergistic Effect Could Boost Production of Green Hydrogen
Researchers developed a composite material of earth-abundant elements that catalyzes the production of green hydrogen much more effectively than similar homogeneous compounds. The composite could potentially be used for efficient hydrogen generation without the need for rare and precious metals like platinum. Read more »
Increasing the Energy Density of Hybrid Supercapacitor Electrodes
Hybrid supercapacitors (HSCs) integrate the merits of batteries with those of supercapacitors. However, the fraction of active material in HSC electrodes has remained too low for commercial requirements. Now, researchers have found a clever way to increase the active-mass ratio to achieve dramatic improvements in key measures. Read more »
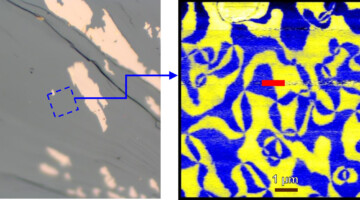
Probing Walls between Electrically Polarized Domains
Researchers used infrared light to investigate the properties of the domain walls that separate electrically polarized (ferroelectric) regions in a rare-earth ferrite material. An understanding of domain-wall behavior is relevant to the development of advanced logic and memory applications for ultralow-power digital devices. Read more »![]()
![]()
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- …
- 30
- Next Page »