Scanning transmission x-ray microscopy at the ALS’s COSMIC beamline contributed to a battery study that used an innovative approach to machine learning to speed up the learning curve about a process that shortens the life of fast-charging lithium batteries. It represents the first time this brand of “scientific machine learning” was applied to battery cycling. Read more »
ALS Work Using STXM
Scanning transmission x-ray microscopy (STXM) generates microscopic images of a thin section of specimen by raster-scanning it in a focused x-ray beam. The flux of transmitted x-rays is measured to obtain the image intensity. By holding the beam at a microscopic region of interest on the sample while the photon energy is scanned, chemically sensitive x-ray absorption spectra can be measured at that specific location (spectromicroscopy).
Reversible Room-Temperature Fluoride-Ion Insertion in a Tunnel-Structured Transition Metal Oxide Host
Fluoride ions show promise as charge carriers in batteries but have limited cyclability. Here we show the reversible and homogeneous topochemical insertion/deinsertion and bulk diffusion of F ions within the one-dimensional tunnels of submicrometer-sized FeSb2O4 particles at room temperature. Read more »
A Closer Look at Water-Splitting’s Solar Fuel Potential
Although bismuth vanadate (BiVO4) is a theoretically attractive material for electrodes in photoelectric chemical cells (PECs) used for artificial photosynthesis, it hasn’t lived up to its potential. Researchers used a multimodal approach to gain new insight into what might be happening at the nanoscale to hold BiVO4 back. Read more »
COSMIC Probes Evolution of Single-Atom Platinum Catalyst
Researchers synthesized a single-atom platinum catalyst that outperformed, by a factor of 15, conventional platinum-based catalysts, which are used for fuel cells and automotive emissions control. Operando x-ray spectromicroscopy at the ALS’s COSMIC beamline revealed how electronic interactions affect the material’s morphology. Read more »
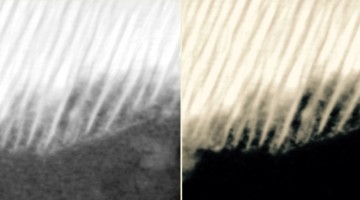
The Inside‐Outs of Metal Hydride Dehydrogenation: Imaging the Phase Evolution of the Li‐N‐H Hydrogen Storage System
Hydrogen absorption and release in lithium amide involves chemical and structural change. Scanning transmission x‐ray microscopy visualizes this phase evolution inside particles, showing a core‐shell architecture, with the more hydrogenated species as the shell for hydrogenation and, more surprisingly, for dehydrogenation as well. Read more »
Machine Learning Helps Stabilize Synchrotron Light
Researchers showed that machine learning can predict noisy fluctuations in the size of beams generated by synchrotron light sources and correct them before they occur. The work solves a decades-old problem and will allow researchers to fully exploit the smaller beams made possible by recent advances in light source technology. Read more »![]()
![]()
Renewed Prospects for Rechargeable Mg Batteries
Contrary to previous reports, it’s possible to create a rechargeable battery using magnesium ions if the electrode material is first conditioned at high temperature. With twice the charge of lithium ions, magnesium ions hold great promise as the basis for high-energy-density batteries suitable for use in electric vehicles. Read more »![]()
![]()
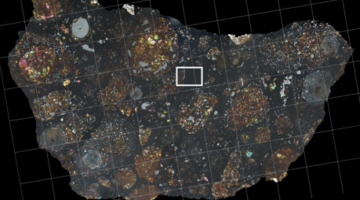
Clues to the Early Solar System Preserved in a Meteorite
Scientists analyzing a tiny carbon-rich pocket inside a meteorite found unexpected chemical signatures. Their findings are the first direct evidence that material from the outer solar system may have traveled inward long before planets formed, providing insight into the early solar system. Read more »
Salt in the Amazon Air Comes from Local Fungi
The abundant salt in the atmosphere above the Amazon basin has long been attributed to the Atlantic Ocean. But now, using the Advanced Light Source, scientists have found that much of it originates much more locally: fungal spores in the rainforest. Pinpointing the origin will improve climate models and understanding of rainforest ecosystems. Read more »
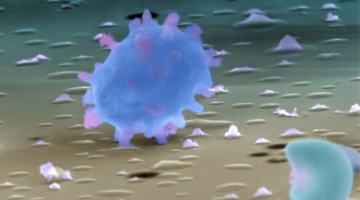
Meteorites Suggest Galvanic Origins for Martian Organic Carbon
Nanoscale analyses of Martian meteorites suggest that organic carbon on Mars may have been formed by electrochemical reactions between briny liquids and volcanic minerals, as might occur in a galvanic cell. The study has major implications for astrobiology and could also shed light on the reactions that led to life on the early Earth. Read more »