The reticular design and synthesis of metal–organic frameworks enable the structures to be engineered at an atomic level, allowing their properties to be harmoniously harnessed. AI-assisted design of building units can reduce human labor in the enumeration and search for possible structures, thereby accelerating the discovery of MOFs. Read more »
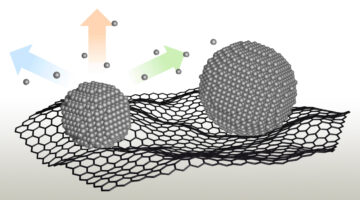
Tracking Platinum Movement on Fuel-Cell Electrodes
Researchers tracked the movement of the platinum nanoparticles that catalyze reactions in polymer electrolyte fuel cells (PEFCs) and correlated this movement with nanoparticle degradation. The results yielded solutions that can immediately reduce platinum waste in emission-free heavy-duty fuel-cell vehicles. Read more »![]()
![]()
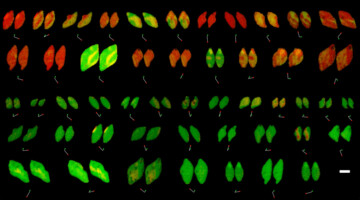
Computer-Aided Protein Design for New Biomaterials
Using a computer-based approach, researchers designed porous protein crystals that were revealed to be stable, tunable, and atomically accurate using x-ray scattering and diffraction at the ALS. The work provides a powerful new platform for biological materials engineering and opens up wide applications in biotechnology and medicine. Read more »![]()
![]()
“Computer Vision” Review of X-Ray Movies Leads to New Insights
Using a type of machine learning called “computer vision” to mine data from x-ray movies, researchers made new discoveries about the reactivity of a material in rechargeable batteries. The results suggest that optimizing the carbon layer thickness on the electrode surface could help researchers to design more efficient batteries. Read more »
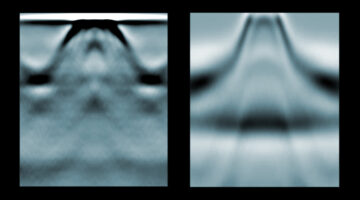
Building a Two-Dimensional Magnet One Atom at a Time
Researchers synthesized a new two-dimensional ferromagnet and measured how its electronic and magnetic properties evolve with increasing thickness and temperature. Such atomically thin magnetic materials with tunable magnetic properties would be very useful in next-generation microelectronic and spintronic applications. Read more »
ALS in the News (November 2023)
-
-
-
-
- Berkeley Lab’s CAMERA enhances DOE’s scientific facilities with new math and software innovations
- Visit of Ambassador Zappia to Berkeley Lab and SkyDeck and meetings with the Italian and Italian-American associations of San Francisco
- Discoveries go full circle in the hunt for an elusive protein’s function
- Peeking inside lithium-ion batteries offers new ways to put a stop to deadly fires
- Capturing wellhead gases for profit and a cleaner environment
- Why do batteries sometimes catch fire and explode?
- Unveiling the importance of calcite dissolution for stabilizing soil organic matter
-
-
-
Influences of Metal Electrodes on Stability of Non-Fullerene Acceptor-Based Organic Photovoltaics
Researchers investigate interfaces in an organic photovoltaic device, revealing that the aluminum (Al) top electrode undergoes thermally activated diffusion into inner layers forming ionic and organo-metallic-like species, compromising long-term device performance. Chemical degradation process is characterized by 27Al solid-state NMR and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Read more »
Optical Properties of Individual Tar Balls in the Free Troposphere
Tar balls are found in biomass-burning smoke, and their sunlight-absorption properties are highly uncertain. This study investigates the optical properties of individual tar balls in the free troposphere to better understand their influence on climate. Read more »
Why Do Batteries Sometimes Catch Fire and Explode?
In order to better understand how a resting battery might undergo thermal runaway after fast charging, scientists are using a technique called “operando x-ray microtomography” to measure changes in the state of charge at the particle level inside a lithium-ion battery after it’s been charged. Read more »
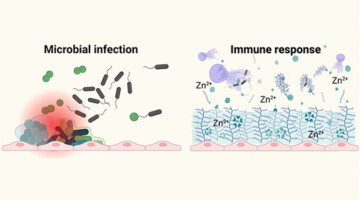
Immune Response Spurs Growth of “Soft” Kidney Stones
Matrix stones are an unusual type of soft kidney stone closely associated with the presence of bacteria from unchecked urinary tract infections. Researchers conducted a comprehensive study of surgically extracted matrix stones, work that highlights how host defense mechanisms against microbes can simultaneously encourage harmful stone formation. Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- …
- 83
- Next Page »