In situ electron microscopy provides atomic-scale insight into the dynamic structure evolution of LaNiO3 perovskite during vacuum heating. This research established a sequential two-step process in the decomposition of LaNiO3 and gives evidence of the diffusion pathway for the lattice oxygen released during the perovskite decomposition. Read more »
Synthesis of new two-dimensional titanium carbonitride Ti2C0.5N0.5Tx MXene and its performance as an electrode material for sodium-ion battery
Researchers report on the synthesis and characterization of a new 2D carbonitride MXene, Ti2C0.5N0.5. They explore the performance of this new MXene as electrode materials for sodium-ion batteries (SIBs). It outperformed its carbide counterpart (i.e., Ti2C) and all the other reports for multilayer MXenes in SIBs, and it showed a stable electrochemical performance over 500 cycles. Read more »
The three-dimensional construction of leaves is coordinated with water use efficiency in conifers
3D anatomical views of conifer leaves with diverse morphologies, generated using synchrotron microCT imaging (colors show different segmented tissues). Top–bottom: Pinus monticola, P. pungens, and Wollemia nobilis. Image courtesy of Santiago Trueba. Read more »
Direct Observation of Surface-Bound Intermediates During Methanol Oxidation on Platinum Under Alkaline Conditions
A comprehensive mechanism for the methanol oxidation reaction (MOR) in alkaline media is presented, and it is shown that the MOR proceeds via two different pathways (via COad or H3C–Oad intermediates). The latter dominates the overall MOR current, suggesting that the H3C–Oad oxidation could be a viable pathway to accelerate the MOR in alkaline systems. Read more »
Ptychography Reduces Spectral Distortions Intrinsic to Conventional Zone-Plate-Based X-Ray Spectromicroscopy
The point spread function (PSF) of a conventional zone-plate-based microscope limits the achievable spatial resolution and results in spatially resolved spectra that do not accurately reflect the spatial heterogeneity of the samples when the scale of the detail approaches the probe size. X-ray ptychography, a coherent-scattering-based imaging scheme that effectively removes the probe from the image data, returns accurate spectra from regions smaller than the probe size. Read more »
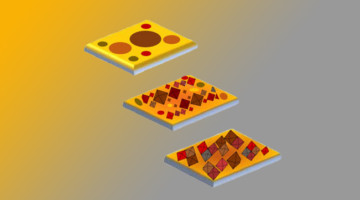
Strategies for Reducing Platinum Waste in Fuel Cells
Industry and university researchers used the ALS to explore why the platinum used as a catalyst in hydrogen fuel cells degrades unevenly. The resulting knowledge has enabled the development of simple, effective strategies to reduce the waste of precious catalyst material, lowering the costs associated with a promising green technology. Read more »![]()
![]()
An Antibody That Broadly Neutralizes SARS-CoV-2
An antibody that appears to neutralize all known SARS-CoV-2 strains and closely related coronaviruses was discovered with the help of the ALS. The work highlights principles underlying antibody potency, breadth, and escapability that can guide the development of therapeutics against the current and potential future pandemics. Read more »![]()
![]()
ALS in the News (October 2021)
-
-
-
- New way to image whole organisms in 3D brings key skin color pigment into focus
- Why skyrmions could have a lot in common with glass and high-temperature superconductors
- Roman noblewoman’s tomb reveals secrets of ancient concrete resilience
- Cell ‘fingerprinting’ could yield long-awaited Alzheimer’s disease diagnostic
- UW’s Scougale one of 65 graduate students nationwide selected to DOE’s SCGSR program
-
-
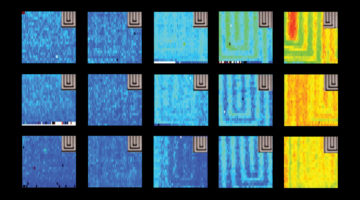
A Split-Screen View of Solar-Cell Crystallization
Researchers simultaneously monitored both the structure and function of a photovoltaic material as it crystallized from solution. The work raises the prospect of rationally tuning materials for optimal performance in photovoltaics and other light-manipulating devices, including light-emitting diodes, detectors, and lasers. Read more »![]()
![]()
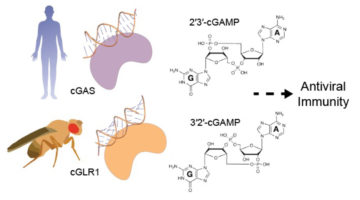
Sounding the Antiviral Alarm: A New Family of Immune-System Sensors
Comparison of enzyme structures from humans and insects revealed a new family of evolutionarily related immune-system sensors, triggered by viral RNA or DNA to produce tailored signals that initiate antiviral action. The results shed new light on the diversity and development of immune defenses in animals. Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- …
- 83
- Next Page »