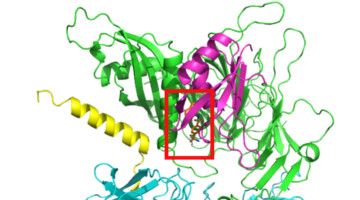
Protein structures obtained by Novartis researchers helped reveal how a cancer drug promotes the degradation of proteins essential to cell proliferation. A detailed understanding of the drug’s mechanism of action is key to determining whether the protein-degradation system can be reprogrammed to degrade different targets. Read more »![]()
The Bottleneck Step of a Complex Catalytic Reaction
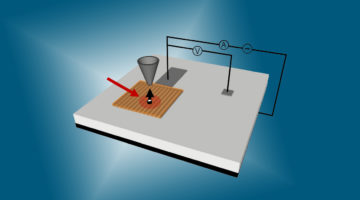
The rate-limiting step in catalysis involving oxygen uptake was identified through analysis of the reaction pathways and observations performed under operating conditions. The work lays the foundation for improving the efficiency of energy conversion and storage devices such as fuel cells, catalytic reactors, and batteries. Read more »![]()
![]()
Controlling antiferromagnetic domains in patterned La0.7Sr0.3FeO3 thin films
Antiferromagnetic spintronics have gained interest because they can be controlled at terahertz frequencies and are insensitive to external magnetic fields. Due to dimensional confinement as well as microstructuring by ion implantation, the spin axis of an antiferromagnetic oxide can be robustly controlled in a deterministic way up to room temperature. Read more »
A Scalable Platform for Two-Dimensional Metals
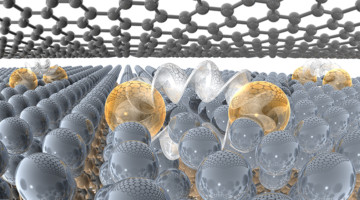
Using a new method for stabilizing a two-dimensional (2D) metal on a large-area platform, researchers probed the origins of the material’s superconductivity. The work represents a notable milestone in advancing 2D materials toward broad applications in topological computing, advanced optics, and molecular sensing. Read more »![]()
![]()
ALS in the News (May 2020)
-
-
- Untangling a key step in photosynthetic oxygen production
- Worth it? Corona-lockdowns shutter research into vital solutions for our many other problems
- Antibody neutralizes SARS and COVID-19 coronaviruses
- In a step forward for orbitronics, scientists break the link between a quantum material’s spin and orbital states
- Ralston and Allaire step into new roles
- Linking properties to defects in 2D materials
- New mechanism links ozone and disease resistance
- World x-ray science facilities are contributing to overcoming COVID-19
- Berkeley Lab researchers and collaborators elected into National Academy of Sciences
- National Labs pivot to pandemic research
- Water is key in catalytic conversion of methane to methanol, scientists find
- Royal Society elects Berkeley Lab physicist Ramamoorthy Ramesh
- 2 Berkeley Lab scientists, visiting scientist elected as new members of honorary society
- Pursuing particle chemistry
- Researchers discover ferroelectricity at the atomic scale
-
X-Ray Experiments Zero in on COVID-19 Antibodies
In the fight against SARS-CoV-2, scientists have been working on identifying neutralizing antibodies that could be used in preventative treatments or as post-exposure therapies. The latest findings, which include data from the ALS, indicate that antibodies from SARS survivors could potently block entry of SARS-CoV-2 into host cells. Read more »![]()
Masks On, Ready to Work: Meet the People Supporting COVID-19 Science
David Richardson’s job is literally to make sure the light stays on. But it’s not just any light—it’s a very special x-ray light that could play a crucial role in an eventual treatment for COVID-19. Richardson is an operator at the ALS, and is one of a handful of workers providing essential services to scientists working on COVID-19-related research. Read more »
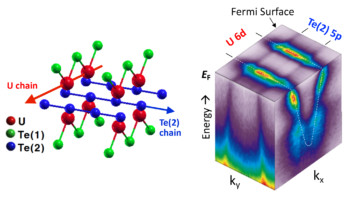
A Forked Path for Superconductivity
Uranium ditelluride (UTe2) exhibits a form of superconductivity that could, in theory, enable fault-tolerant quantum computing. Angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy revealed several aspects of the material’s unusual electronic environment, including one-dimensional conducting channels that are orthogonally oriented. Read more »
Efficient Organic Solar Cell with 16.88% Efficiency Enabled by Refined Acceptor Crystallization and Morphology with Improved Charge Transfer and Transport Properties
Feng Liu and co‐workers report a detailed structure‐performance relationship to help understand the success of Y6 non‐fullerene acceptors. Through the analysis of the single crystal structure of Y6, it is found that Y6 forms a polymer‐like conjugated backbone through its banana‐shaped structure and π‐π interactions between molecules, and forms a 2D electron transport network under the ordered arrangement of the lattice. Read more »
Divergent Adsorption-Dependent Luminescence of Amino-Functionalized Lanthanide Metal–Organic Frameworks for Highly Sensitive NO2 Sensors
A novel gas-sensing mechanism exploiting lanthanide luminescence modulation upon NO2 adsorption is demonstrated. Two isostructural lanthanide MOFs are used, including an amino group as the recognition center for NO2. Energy transfer from the ligands to Ln is strongly dependent on the presence of NO2, resulting in an unprecedented photoluminescent sensing scheme. Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- …
- 83
- Next Page »