Adamantanes are emerging building blocks for active pharmaceutical ingredients. In this work, we sought to understand how systematic modification of the hydrophobic cage in adamantanes could result in changes to crystal packing in single and multicomponent organic solids. Read more »
Superhard Materials at the Nanoscale: Smaller is Better
In the superhard material, rhenium diboride, smaller grain size leads to greater yield strength (i.e., the amount of stress tolerated before permanent deformation). Because such transition-metal borides are extremely hard, metallic, and can be synthesized at ambient pressure, they have exciting potential for use in next-generation cutting tools. Read more »![]()
![]()
Two-dimensional perovskite templates for durable, efficient formamidinium perovskite solar cells
When the lattice-matched 2D perovskite BA2FAPb2I7 (red) is incorporated into a yellow-phase FAPbI3 matrix (yellow), the 2D crystallites present a perovskite-like surface, which serves as a template for the FAPbI3 to convert to its photoactive phase (black). The resulting phase-stabilized FAPbI3 shows substantially improved optoelectronic properties and exceptional stability under 85°C and sunlight. Read more »
A Novel Staircase Pattern in Spin-Stripe Periodicity
Striped patterns of spins in a magnetic thin film were found to evolve under an applied magnetic field in steps reminiscent of a structure known as the “Devil’s Staircase.” Such studies are valuable for understanding competing interactions at the atomic level for applications such as magnetic sensors and spintronic devices. Read more »![]()
![]()
A Cleaner Way to Produce Ammonia
A cavity made from linked rare-earth metals, such as zirconium and titanium, can convert abundant molecular nitrogen (N2) into useful nitrogen compounds, including ammonia or tris(silyl)amines, at room temperature. Read more »
Direct Observation of Room-Temperature Magnetic Skyrmion Motion Driven by Ultra-Low Current Density in Van Der Waals Ferromagnets
Researchers demonstrate current-driven magnetic skyrmion motion in van der Waals ferromagnets at room temperature. The skyrmion motion presents ultra-low critical current density to activate their dynamics, thanks to minimized defects in the van der Waals gap. The findings will provide a new platform for spintronics application in the future. Read more »
How Bulky Molecules Improve Next-Generation Solar Cells
Adding “bulky” organic molecules earlier in solar-film synthesis slows crystal growth, leading to the formation of a protective surface layer that improves durability and efficiency. These next-gen materials could revolutionize solar-cell technology, offering increased efficiency, lower cost, lighter weight, and flexible solar modules. Read more »![]()
![]()
Surprise Mineral Precursor Found in Coral Skeletons and Mollusk Shells
Researchers studied samples from corals, mollusks, and sea urchins, at edges where mineral precursors start to form the new shell or skeleton. There, they found a surprise: corals and mollusks produced a mineral precursor that had never been observed before in living organisms or rocks, and had only recently been created synthetically. Read more »
ALS in the News (May 2024)
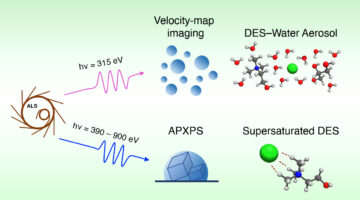
Probing the Liquid/Vapor Interface of a Tunable Solvent
Despite the ready tunability and industrial promise of deep eutectic solvents (DESs), there have been few x-ray spectroscopy studies at their liquid/vapor interfaces—which is relevant for their use in applications such as greenhouse-gas capture. Here, researchers probed the liquid/vapor interface of a benchmark DES using complementary spectroscopies. Read more »
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- …
- 83
- Next Page »